The SAP Solution Manager end-of-life announcement has created urgency across enterprise IT departments worldwide. With support ending in 2027, organizations face critical decisions about their application lifecycle management (ALM) strategy. This transition affects thousands of companies currently relying on SAP Solution Manager for change management, monitoring, and IT service management functions. The discontinuation impacts more than just software support. It also represents a fundamental shift in how organizations manage their SAP ecosystems. Companies must evaluate multiple pathways forward while considering operational continuity, compliance requirements, and long-term strategic alignment.
Understanding the SAP Solution Manager End-of-Life Impact
SAP Solution Manager has served as the central ALM platform for many enterprises, providing integrated capabilities for:
- Transport management across landscapes
- Change Request Management (ChaRM)
- IT Service Management (ITSM)
- System monitoring and alerting
- Test management and coordination

The 2027 end-of-support date means no security patches, bug fixes, or feature updates beyond that point. Organizations can potentially extend support until 2030 through SAP’s Extended Maintenance program, though this comes with significantly higher costs and limited functionality improvements. This timeline creates planning pressure for IT teams who must balance operational stability with strategic modernization goals. The complexity increases for organizations with heavily customized Solution Manager implementations or those with strict regulatory compliance requirements.
Evaluating SAP Solution Manager Alternatives
Organizations have several pathways to consider when planning their post-Solution Manager strategy.
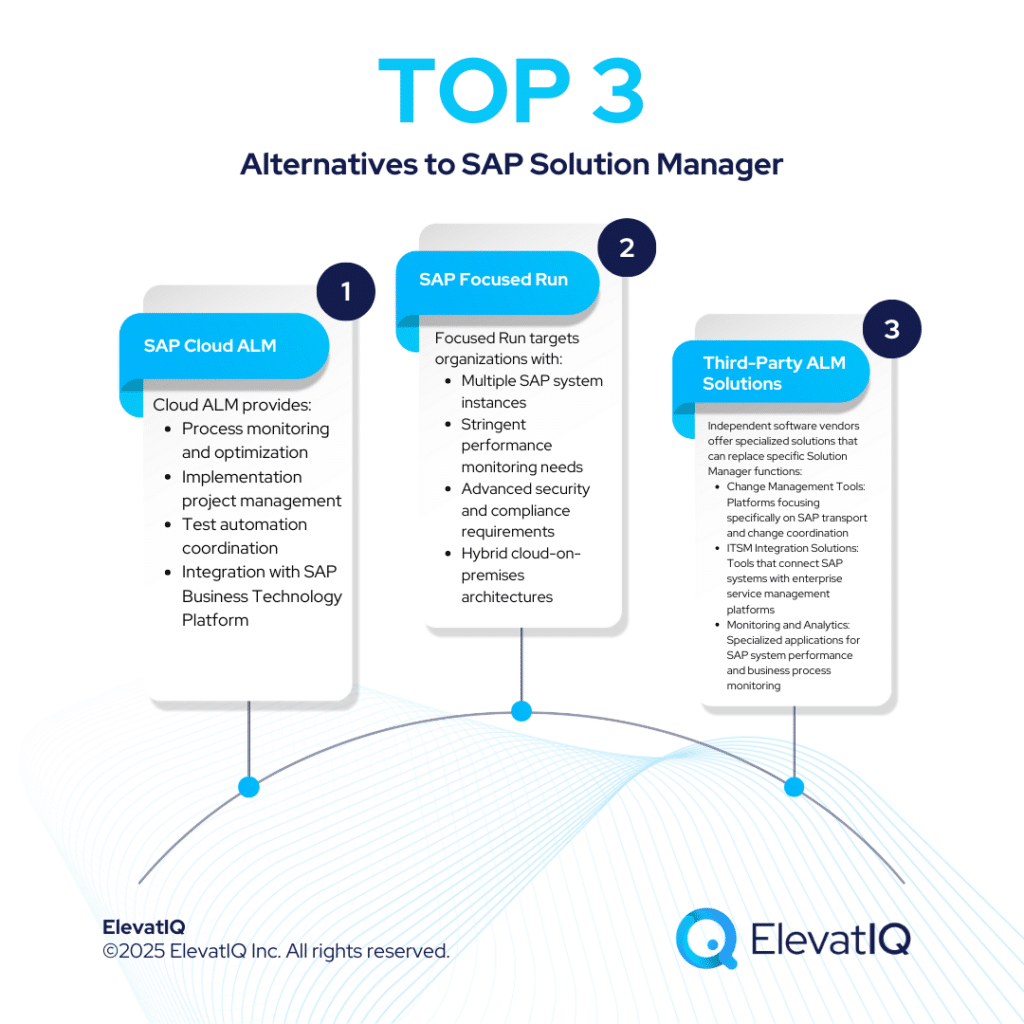
SAP Cloud ALM
SAP’s official successor offers cloud-native ALM capabilities designed for modern SAP environments. Cloud ALM provides:
- Process monitoring and optimization
- Implementation project management
- Test automation coordination
- Integration with SAP Business Technology Platform
However, Cloud ALM doesn’t replicate all Solution Manager functionality. Notable gaps include comprehensive change management capabilities and certain on-premises integration features that many organizations currently depend on.

SAP Focused Run
Designed for complex SAP landscapes requiring advanced monitoring and security capabilities, Focused Run targets organizations with:
- Multiple SAP system instances
- Stringent performance monitoring needs
- Advanced security and compliance requirements
- Hybrid cloud-on-premises architectures
Focused Run requires significant technical expertise and may not suit every organization’s operational model or resource constraints.
Third-Party ALM Solutions
Independent software vendors offer specialized solutions that can replace specific Solution Manager functions:
- Change Management Tools: Platforms focusing specifically on SAP transport and change coordination
- ITSM Integration Solutions: Tools that connect SAP systems with enterprise service management platforms
- Monitoring and Analytics: Specialized applications for SAP system performance and business process monitoring
These solutions often provide faster implementation timelines and more flexible integration capabilities compared to SAP’s native offerings.

Strategic Considerations for Migration Planning
Beyond evaluating available alternatives, organizations must assess their specific operational context and strategic requirements to determine the most suitable migration approach. This assessment spans multiple dimensions that directly impact both the complexity and success of the transition.
Operational Continuity Assessment
Organizations must evaluate their current Solution Manager usage patterns to understand migration complexity:
- Heavy ChaRM Users: Companies with extensive change management processes face the most significant transition challenges, as no direct Cloud ALM equivalent exists
- Monitoring-Focused Implementations: Organizations primarily using Solution Manager for system monitoring may find easier migration paths
- Integrated ITSM Environment: Companies with deep Solution Manager-ITSM integrations require careful planning to maintain service management capabilities
Compliance and Audit Requirements
Regulatory environments influence migration decisions significantly. Organizations in highly regulated industries must ensure any alternative maintains:
- Audit trail capabilities
- Change documentation standards
- Approval workflow integrity
- Historical data accessibility
Independent ERP consultants often help organizations navigate these requirements objectively, ensuring compliance considerations receive appropriate attention without vendor bias.
Enterprise Architecture Alignment
Migration decisions should align with broader digital transformation strategies. Key considerations include:
- Cloud-First vs. Hybrid Strategies: Organizations committed to cloud transformation may prioritize different solutions than those maintaining on-premises systems
- Integration Architecture: Current and planned system integrations influence which alternatives provide optimal connectivity
- Scalability Requirements: Future growth plans should inform platform selection criteria
Implementation Timeline and Resource Planning
With the 2027 deadline creating a defined timeframe, organizations need a structured approach to migration planning that balances thorough preparation with timely execution. A phased timeline allows teams to progress systematically while maintaining operational stability throughout the transition.
Near-Term Actions
- Current State Assessment: Document existing Solution Manager functionality and dependencies
- Alternative Evaluation: Research and test potential replacement solutions
- Stakeholder Alignment: Ensure business and IT leadership agree on migration priorities
Mid-Term Planning
- Pilot Implementation: Test chosen alternatives in non-production environments
- Change Management: Prepare teams for new processes and tools
- Integration Development: Build connections between new tools and existing systems
Migration Execution
- Phased Rollout: Implement alternatives in stages to minimize operational disruption
- Data Migration: Transfer historical information where feasible and necessary
- Knowledge Transfer: Ensure teams understand new platforms and processes
The Role of Independent ERP Selection Consultants
Enterprise software selection requires objective evaluation of multiple factors beyond vendor marketing claims. Independent consultants provide value through:
- Vendor-Agnostic Analysis: Evaluation based on organizational needs rather than vendor relationships
- Industry Experience: Understanding of how similar organizations have addressed comparable transitions
- Technical Assessment: Deep evaluation of integration capabilities and implementation complexity
This independence becomes particularly valuable when evaluating SAP Solution Manager alternatives, as organizations benefit from unbiased assessment of both SAP and third-party options.
Financial Considerations and Total Cost of Ownership
Migration costs extend beyond software licensing. It also includes:
Direct Implementation Costs
The initial investment encompasses all expenses required to establish the new ALM environment:
- Software licensing for new platforms
- Professional services for implementation
- System integration development
- Data migration activities
Operational Transition Costs
During the migration period, organizations incur additional expenses while maintaining business continuity:
- Team training and certification
- Temporary dual-system operation
- Process redesign and documentation
- Change management activities
Long-Term Operational Costs
Post-implementation expenses continue throughout the solution’s lifecycle and should factor into ROI calculations:
- Ongoing licensing and support
- Administrative overhead
- Integration maintenance
- Future upgrade investments
Organizations should model total cost of ownership across multiple years when comparing SAP Solution Manager alternatives, considering both immediate transition expenses and long-term operational costs.
Making the Strategic Decision
The SAP Solution Manager end of life creates an opportunity for organizations to modernize their ALM approach while addressing current limitations. Success requires:
- Comprehensive Assessment: Understanding current functionality usage and future requirements
- Objective Evaluation: Comparing alternatives based on organizational needs rather than vendor preferences
- Strategic Alignment: Ensuring migration decisions support broader digital transformation goals
- Stakeholder Engagement: Building consensus among business and technical teams
Organizations approaching this transition thoughtfully can emerge with more capable, efficient ALM platforms that better serve their long-term objectives.
The 2027 deadline approaches quickly, but organizations that begin planning now have sufficient time to evaluate alternatives thoroughly and execute migrations successfully. Whether choosing SAP’s cloud solutions, specialized third-party tools, or hybrid approaches, the key lies in making informed decisions based on specific organizational requirements rather than default assumptions.
Enterprise software selection expertise becomes invaluable during these transitions, helping organizations navigate complex technical and strategic considerations to identify optimal solutions for their unique environments and objectives.