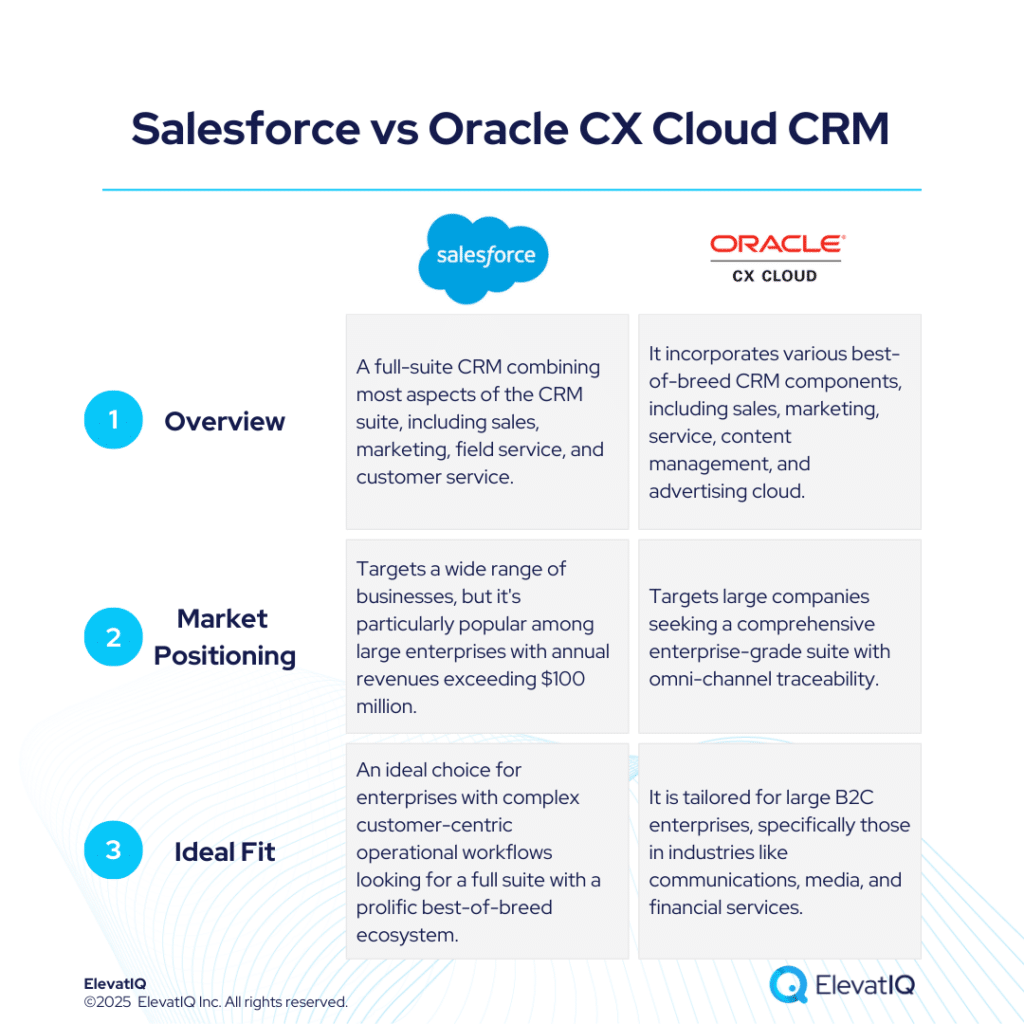
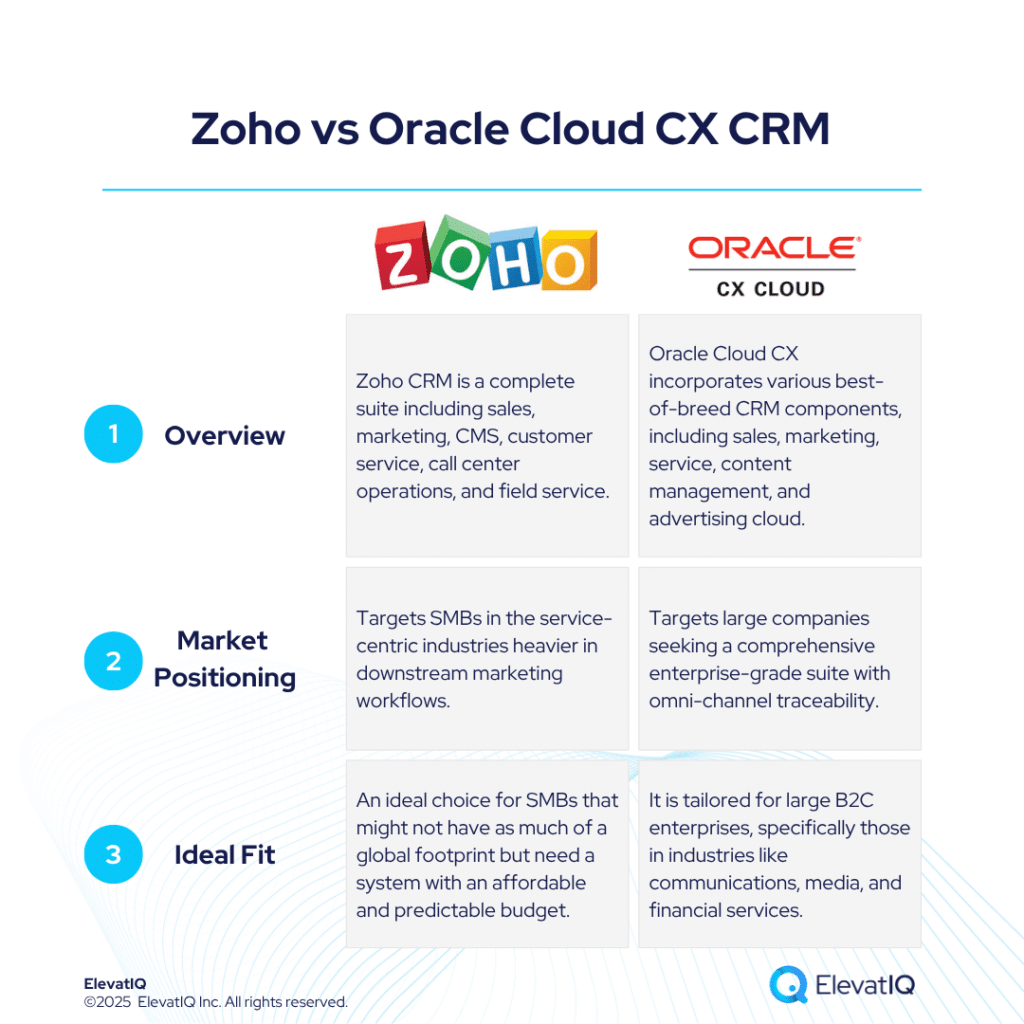
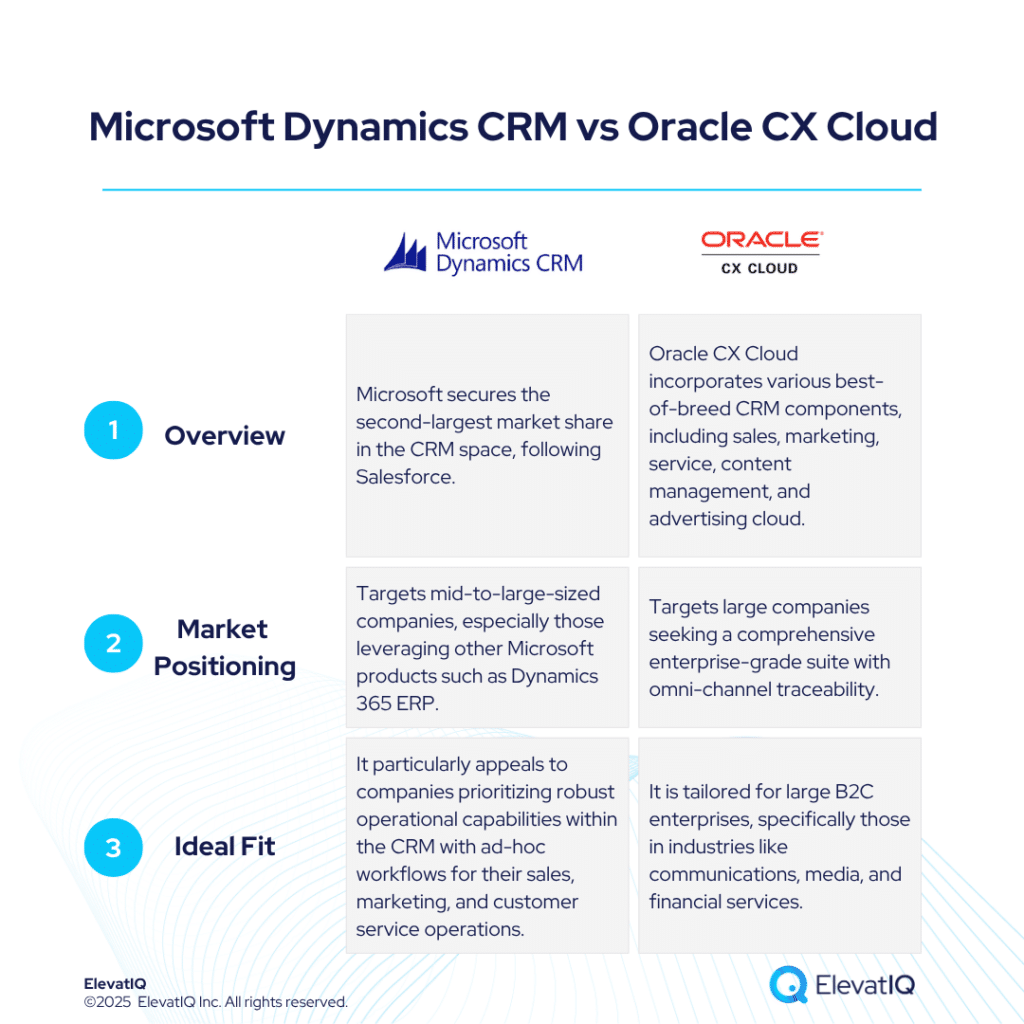
SAP’s announcement of expanding its SAP sovereign cloud services with a new data center in France marks a significant development in the European enterprise software landscape. The initiative addresses longstanding concerns about data sovereignty while enabling access to artificial intelligence capabilities that have remained largely inaccessible to regulated industries across Europe.
According to industry reports, the expansion specifically targets public sector organizations, healthcare providers, and critical infrastructure operators who have faced regulatory barriers to cloud adoption. The SAP sovereign cloud framework ensures customer data remains within national boundaries while providing access to advanced AI functionalities.
Regulatory Landscape Driving Sovereign Cloud Demand
Understanding these regulatory pressures provides essential context for examining how SAP has structured its technical architecture to meet compliance requirements while delivering advanced functionality.
Data Protection Requirements Shape Market
European organizations have navigated complex regulatory requirements since the implementation of GDPR in 2018. The subsequent Schrems II decision further complicated cross-border data transfers, creating what industry analysts describe as a “compliance bottleneck” for cloud adoption. Research indicates that European public sector organizations have delayed AI implementation due to data sovereignty concerns. The SAP sovereign model, addresses these challenges by ensuring data processing occurs exclusively within EU jurisdiction under local personnel oversight.
Industry observers note that this development reflects broader market trends toward localized cloud infrastructure. Major technology vendors have increasingly recognized that regulatory compliance requirements necessitate region-specific solutions rather than global standardization.

Technical Architecture and Compliance Framework
The SAP sovereign cloud operates through partnerships with local providers, ensuring physical and legal data containment within national borders. This approach differs from traditional hyperscaler models that often involve cross-jurisdictional data processing. Technical specifications indicate that the sovereign framework encompasses the complete SAP technology stack, including S/4HANA Cloud, Business Technology Platform (BTP), and AI services. This integrated approach addresses compliance requirements at the infrastructure, platform, and application levels simultaneously.
AI Capabilities Within Sovereign Boundaries
Moving beyond general capabilities, the sovereign cloud framework enables specific industry applications that demonstrate the practical impact of compliant AI implementation across different regulated sectors.
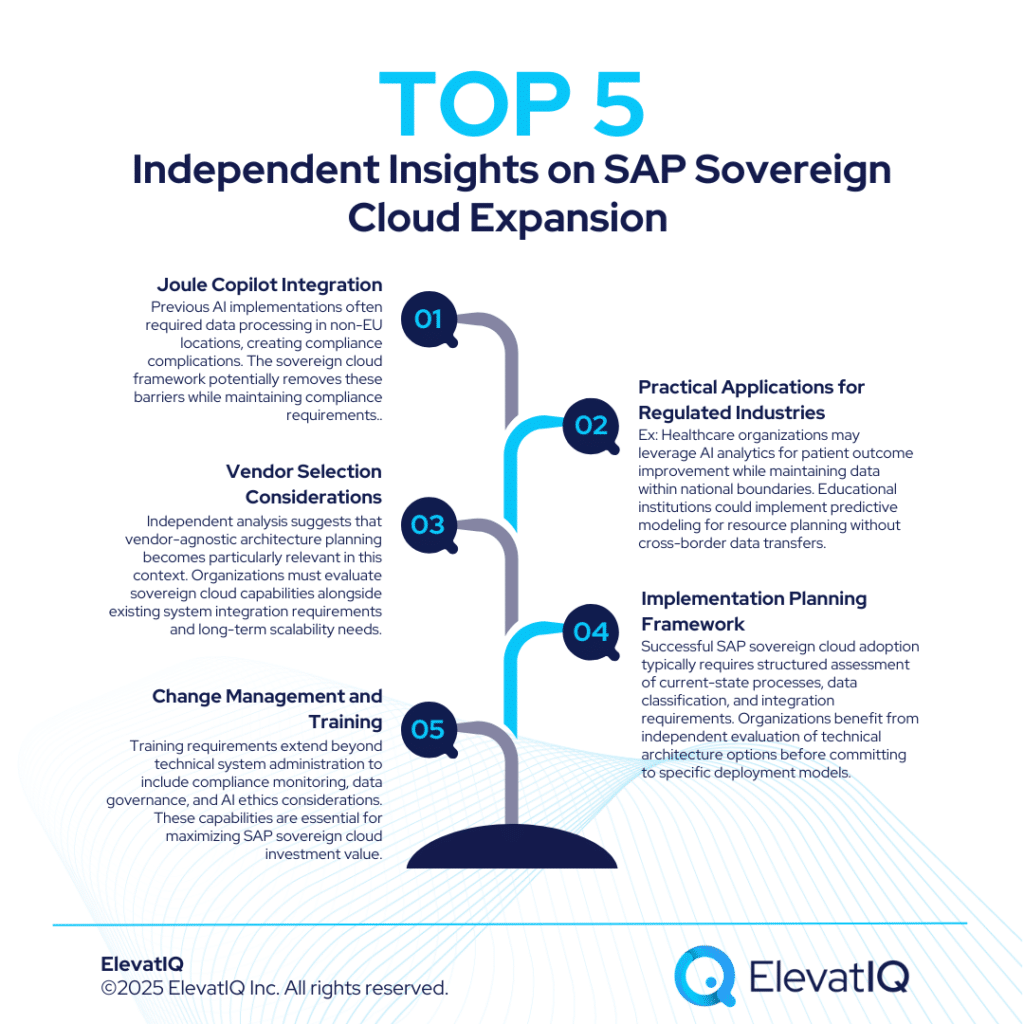
Joule Copilot Integration
The integration of SAP’s Joule Copilot AI assistant within the SAP sovereign cloud environment represents a notable development for European organizations. Previous AI implementations often required data processing in non-EU locations, creating compliance complications. Industry analysis suggests that AI-powered process optimization has remained largely theoretical for many European public sector organizations due to regulatory constraints. The sovereign cloud framework potentially removes these barriers while maintaining compliance requirements.
Reported capabilities include automated workflow optimization, predictive analytics for resource allocation, and intelligent document processing. These functionalities could address common challenges in public administration, healthcare management, and citizen service delivery.
Practical Applications for Regulated Industries
Healthcare organizations may leverage AI analytics for patient outcome improvement while maintaining data within national boundaries. Educational institutions could implement predictive modeling for resource planning without cross-border data transfers. Public administration agencies might utilize AI for citizen service automation, fraud detection in social programs, and infrastructure maintenance planning. These applications previously required careful legal review due to data sovereignty considerations.
Financial services organizations operating under additional regulatory frameworks could explore AI-driven risk assessment and compliance monitoring while adhering to sector-specific data protection requirements.

Strategic Implications for Enterprise Architecture
These AI capabilities translate from theoretical possibilities into concrete implementations across various sectors, each with distinct regulatory requirements and operational challenges
Vendor Selection Considerations
The SAP sovereign cloud offering introduces new variables in enterprise technology selection processes. Organizations previously faced tradeoffs between advanced capabilities and compliance requirements. Independent analysis suggests that vendor-agnostic architecture planning becomes particularly relevant in this context. Organizations must evaluate sovereign cloud capabilities alongside existing system integration requirements and long-term scalability needs.
Industry experts emphasize the importance of building vendor-agnostic architecture that considers data flows between different entities, departments, processes, and systems. This approach enables organizations to maintain flexibility while addressing immediate compliance requirements.
Implementation Planning Framework
Successful SAP sovereign cloud adoption typically requires structured assessment of current-state processes, data classification, and integration requirements. Organizations benefit from independent evaluation of technical architecture options before committing to specific deployment models. Business process documentation becomes critical when migrating to sovereign cloud environments. Organizations must clearly define data flows, processing requirements, and compliance touchpoints to ensure successful implementation.
The complexity of sovereign cloud deployment often necessitates specialized expertise in both technical architecture and regulatory compliance. Organizations typically require support spanning ERP optimization, business process re-engineering, and change management.
Market Response and Competitive Dynamics
While industry-wide trends provide valuable context, the practical implementation of sovereign cloud solutions reveals significant differences across European markets due to varying national regulatory frameworks and business environments.
Industry Analyst Perspectives
Technology industry analysts have characterized SAP’s sovereign cloud expansion as a strategic response to European market demands rather than a purely technical advancement. The move addresses specific regulatory requirements that have limited cloud adoption in regulated sectors. Competitive analysis indicates that hyperscale cloud providers offer sovereign solutions, but SAP’s integrated approach encompasses the complete enterprise application stack. This end-to-end sovereignty model may appeal to organizations seeking simplified vendor management and unified compliance frameworks.
Market research suggests that SAP sovereign cloud adoption may accelerate broader digital transformation initiatives that have been delayed due to compliance concerns. Organizations previously operating legacy systems due to data sovereignty requirements now have clear migration pathways.
Regional Variations in Adoption
Different European markets face varying regulatory requirements and data protection interpretations. French organizations benefit directly from the new data center location, while organizations in other EU countries must evaluate cross-border data transfer implications. German healthcare providers and financial institutions may find particular value in the sovereign framework given national data protection requirements. UK organizations post-Brexit face different considerations regarding data adequacy and transfer mechanisms.

Professional Services and Implementation Considerations
While technical expertise forms the foundation of successful implementation, organizations must also address the human and organizational dimensions of sovereign cloud adoption to ensure long-term success.
Expertise Requirements
SAP sovereign cloud implementation requires specialized knowledge spanning enterprise architecture, regulatory compliance, and SAP technical capabilities. Organizations typically benefit from independent advisory services during evaluation and planning phases. The complexity of sovereign cloud architecture often necessitates support for enterprise technology selection, requirement management, and contract negotiation. These services help organizations navigate technical specifications while addressing specific compliance requirements. Business process optimization becomes particularly important when implementing SAP sovereign cloud solutions. Organizations must align existing workflows with sovereign data processing requirements while maximizing AI capability utilization.
Change Management and Training
Sovereign cloud adoption often requires updated governance frameworks, security protocols, and operational procedures. Organizations benefit from comprehensive change management support to ensure a successful transition. Training requirements extend beyond technical system administration to include compliance monitoring, data governance, and AI ethics considerations. These capabilities are essential for maximizing SAP sovereign cloud investment value.
Future Outlook for Sovereign Cloud Adoption
Technology advancement occurs within a dynamic regulatory environment, where policy changes and legislative developments continue to shape the requirements and opportunities for sovereign cloud solutions.
Technology Evolution Trends
Industry forecasts suggest that sovereign cloud capabilities will expand beyond current SAP offerings as market demand increases. Additional vendors are likely to develop region-specific solutions addressing similar compliance requirements. AI capability evolution within sovereign frameworks may accelerate as regulatory clarity improves and organizations gain confidence in compliant implementation approaches. The SAP sovereign cloud expansion could catalyze broader market adoption of AI technologies in regulated sectors.
Regulatory Development
European regulatory frameworks continue evolving, with proposed legislation addressing AI governance and data protection requirements. Sovereign cloud solutions must adapt to changing compliance landscapes while maintaining operational continuity. The success of SAP sovereign cloud implementation in France may influence similar initiatives in other European markets, potentially creating region-specific sovereign cloud ecosystems.
Conclusion
SAP’s sovereign cloud expansion represents a significant development in European enterprise technology adoption. By addressing data sovereignty concerns while enabling AI capability access, the initiative potentially removes barriers that have limited digital transformation in regulated sectors. Organizations evaluating sovereign cloud options benefit from independent assessment of technical requirements, compliance implications, and long-term strategic alignment. The complexity of these implementations typically requires specialized expertise spanning technology selection, business process optimization, and regulatory compliance.
The SAP sovereign cloud framework demonstrates how technology vendors are adapting to regional regulatory requirements rather than pursuing global standardization. This trend suggests continued evolution toward localized cloud solutions that balance innovation capabilities with compliance requirements. Success in sovereign cloud adoption depends on careful planning, appropriate expertise engagement, and alignment with broader digital transformation objectives. Organizations that approach these initiatives strategically position themselves to leverage advanced AI capabilities while maintaining regulatory compliance standards.
Industry Expertise Note: Independent technology consultants specializing in vendor-agnostic digital transformation planning provide valuable perspective during sovereign cloud evaluation processes. Organizations benefit from objective assessment of technical architecture options, regulatory compliance requirements, and long-term strategic implications when considering major enterprise technology investments such as SAP sovereign cloud implementations.