ERP Implementation Credibility Damage: The Lamb Weston Case
In April 2024, Lamb Weston Holdings disclosed that a failed SAP S/4HANA implementation had cost the company $135 million in lost sales in a single quarter. The stock price collapsed 19.4%. Securities class action lawsuits followed. The CIO was replaced. The implementation strategy was completely revised from simultaneous multi-site rollout to sequential plant-by-plant deployment.
That was 10 months ago. The question organisations considering ERP implementations should be asking now is not just what went wrong at Lamb Weston in Q3 FY2024. It is what the long-term reputational and capital market consequences look like? Especially when an ERP failure transitions from an operational disruption into a sustained credibility crisis.
According to analyst commentary syndicated on Yahoo Finance in February 2026, Lamb Weston continues to face challenges. Specifically, in rebuilding credibility with investors. This is not because the ERP system remains broken. But because the ERP implementation credibility damage has fundamentally altered how the market evaluates. Particularly, the company’s ability to execute on capital allocation, operational strategy, and future growth commitments. Public filings indicate that Liberty One Investment Management disclosed a material reduction in its Lamb Weston stake in Q4 2025. Valued at approximately $32 million, is one visible indicator. As of early 2026, Lamb Weston’s share price remained materially below pre-ERP failure levels. Unfortunately, it continued to underperform the S&P 500.
This blog examines what happens when ERP implementation credibility damage extends beyond. When the operational failure leads to sustained investor scepticism, management turnover, strategic constraint, and competitive disadvantage. Also, what does that mean for organisations currently in the early stages of ERP planning or procurement?
The Timeline: From Go-Live Failure to Ongoing Credibility Crisis
To understand the long-term consequences, the timeline from November 2023 through February 2026 is essential:
- November 2023: SAP S/4HANA goes live across Lamb Weston’s North American operations. Thus, replacing a decades-old legacy system with complex warehouse management integrations.
- January 2024: CFO Bernadette Madarieta characterises operational issues as “usual bumps”. Also, states no expected material impact on full-year results—a statement later central to securities litigation.
- April 2024: Q3 FY2024 results reveal the full damage.
- $135 million in lost sales
- $72 million reduced net income
- $95 million decreased EBITDA
- 16% volume decline (8 points ERP-related)
- $25 million inventory write-offs
- $330 million revenue guidance cut
- Stock fell nearly 20% in one session
- June 2024: Securities class action lawsuits filed alleging material misrepresentations about ERP readiness.
- October 2024: New CIO Benjamin Heselton appointed. Company revises strategy from simultaneous multi-site deployment to sequential plant-by-plant implementation—nearly a year post go-live.
- Q4 2025: Liberty One Investment Management reduces Lamb Weston stake by 544,473 shares ($32 million). Thus, cutting portfolio weight from 3.1% to 2.23%.
- February 2026: Analyst commentary highlights ongoing credibility concerns.
- Stock at $49.82 (down 12.4% year-over-year)
- ROIC declined from 15.9% to 11.1%
- $3.8 billion net debt against $6.9 billion market cap constrains growth options
This timeline reveals that ERP implementation credibility damage persists long after operational restoration. The failure fundamentally altered how institutional investors, equity analysts, and credit agencies evaluate the company’s execution risk, a consequence that continues to compound nearly two years later.
The Four Dimensions of Long-Term ERP Implementation Credibility Damage
The immediate financial consequences of ERP failure i.e. lost revenue, reduced EBITDA, write-offs, are severe. But they are also one-time events that eventually cycle out of year-over-year comparisons. The long-term credibility consequences are more insidious because they compound over time rather than resolving.
Institutional Investor Confidence Erosion Creates a Sustained Valuation Discount
Liberty One’s Q4 2025 stake reduction is not an isolated event, it is representative of a broader pattern. When a company misses earnings guidance by $135 million in a single quarter due to an internal execution failure, institutional investors do not simply price in the loss and move on. They fundamentally reassess their confidence in management’s ability to execute on future strategic initiatives.
The mechanism works like this:
- Before the ERP failure: Lamb Weston announces capital allocation plans, capacity expansion, margin improvement initiatives, market share growth targets. Institutional investors evaluate those plans based on the company’s historical execution track record.
- After the ERP failure: The same capital allocation announcements are now evaluated through the lens of “this is the management team that lost $135 million implementing an ERP system that was supposed to improve operational efficiency.”
The result is a sustained valuation discount. Lamb Weston’s current EV-to-EBITDA ratio of 9 and P/E ratio of 11 are reasonable by sector standards, but the company’s stock continues to underperform the broader market by 25 percentage points year-over-year. Institutional investors are not pricing in just current performance. They are pricing in reduced confidence in future execution. This is the ERP implementation credibility damage that most organisations fail to factor into their risk assessments. A $135 million revenue loss in one quarter creates perhaps $500 million in destroyed market capitalisation, but the sustained underperformance relative to sector peers over 18+ months creates billions more in foregone equity value.

Management Turnover Eliminates Institutional Knowledge and Continuity
CIO Benjamin Heselton was appointed in October 2024, approximately 11 months after the ERP system went live and six months after the financial damage became public. This is the standard pattern following major ERP failures: the executive accountable for technology strategy exits, and a replacement is brought in to “stabilize” operations and rebuild credibility. The challenge is that management turnover, particularly at the CIO level, eliminates precisely the institutional knowledge the organisation needs most during post-failure remediation:
- Understanding of what went wrong and why — the original CIO and programme leadership team carry the detailed knowledge of which decisions created which consequences
- Vendor and SI relationship continuity — negotiating remediation commitments from SAP and the implementation partner requires leverage that comes from a working relationship built over the project lifecycle
- Internal stakeholder credibility — the business units most affected by the ERP failure trust the new CIO less than they trusted the predecessor, slowing adoption of corrective measures
The result is that organisations often lose 6–12 months of remediation momentum during CIO transition periods. The new executive needs time to assess the situation independently, establish relationships with key stakeholders, and build credibility with the board before making major strategic decisions. During that transition, the ERP system continues to operate sub-optimally, and the organisation’s operational performance continues to suffer in ways that compound the ERP implementation credibility damage.

Strategic Constraint: Capital Allocation Decisions Are Now Evaluated Under Higher Scrutiny
Lamb Weston committed nearly $2 billion in capital expenditures between 2020 and 2024 for capacity expansion. Under normal circumstances, that level of capital investment would position the company for margin expansion and market share growth as demand recovered. But the ERP failure occurred precisely when demand was normalizing, meaning the company now faces excess capacity, fragile pricing discipline, and compressed profit margins in an environment where institutional investors are sceptical of management’s ability to allocate capital effectively.
Analyst estimates suggest Lamb Weston’s return on invested capital declined materially between fiscal 2023 and fiscal 2025. That decline reflects not just the ERP failure itself, but the compounding effect of ERP implementation credibility damage on all subsequent capital allocation decisions:
- New capacity expansion projects face higher internal approval thresholds because the board and executive team are risk-averse following the ERP failure
- M&A opportunities are constrained because equity analysts and institutional investors question whether the company can successfully integrate acquisitions when it struggled to implement an internal ERP system
- Innovation investments are delayed because management is focused on operational stabilisation rather than strategic growth initiatives
This is the strategic constraint dimension of ERP implementation credibility damage that extends far beyond the ERP system itself. The organisation’s ability to pursue growth, deploy capital, and respond to competitive threats is impaired, not because it lacks resources, but because it lacks credibility with the stakeholders whose confidence it needs to execute on those strategies.
Competitive Disadvantage: Operational Weakness in a Consolidating Industry
Lamb Weston is North America’s largest frozen potato products producer, supplying approximately 15% of McDonald’s annual sales. In a consolidating industry with large-scale customers who demand operational reliability, supply chain visibility, and consistent delivery performance, an ERP failure creates competitive exposure that lasts well beyond the period when normal operations are restored.
The mechanism is straightforward:
- Customer confidence erosion: Major QSR chains evaluating supplier reliability over multi-year contract periods now have documented evidence that Lamb Weston experienced extended periods when it could not ship products, generate invoices, or produce accurate sales reporting
- Competitor positioning: Rival suppliers can reference Lamb Weston’s operational disruption as a differentiator in competitive bids – “we have stable systems and proven execution”
- Pricing pressure: Customers who experienced supply disruptions during the ERP failure have leverage to negotiate more favourable contract terms, knowing that Lamb Weston cannot afford further relationship damage
The competitive disadvantage created by ERP implementation credibility damage is particularly acute in industries where switching costs for customers are low and operational reliability is a primary ERP selection criterion. Lamb Weston’s capacity expansion investments were designed to support market share growth. The ERP failure has forced the company into a defensive posture where retaining existing customer relationships is the priority and even that requires contract concessions that compress margins.
What This Means for Organisations Currently Considering ERP Implementations
The Lamb Weston case is instructive not because it represents a unique failure, but because it demonstrates with unusual transparency what the long-term consequences look like when ERP implementation credibility damage transitions from an operational event into a sustained reputational and strategic constraint.
Three specific lessons apply to any organisation currently in ERP planning, procurement, or early implementation:
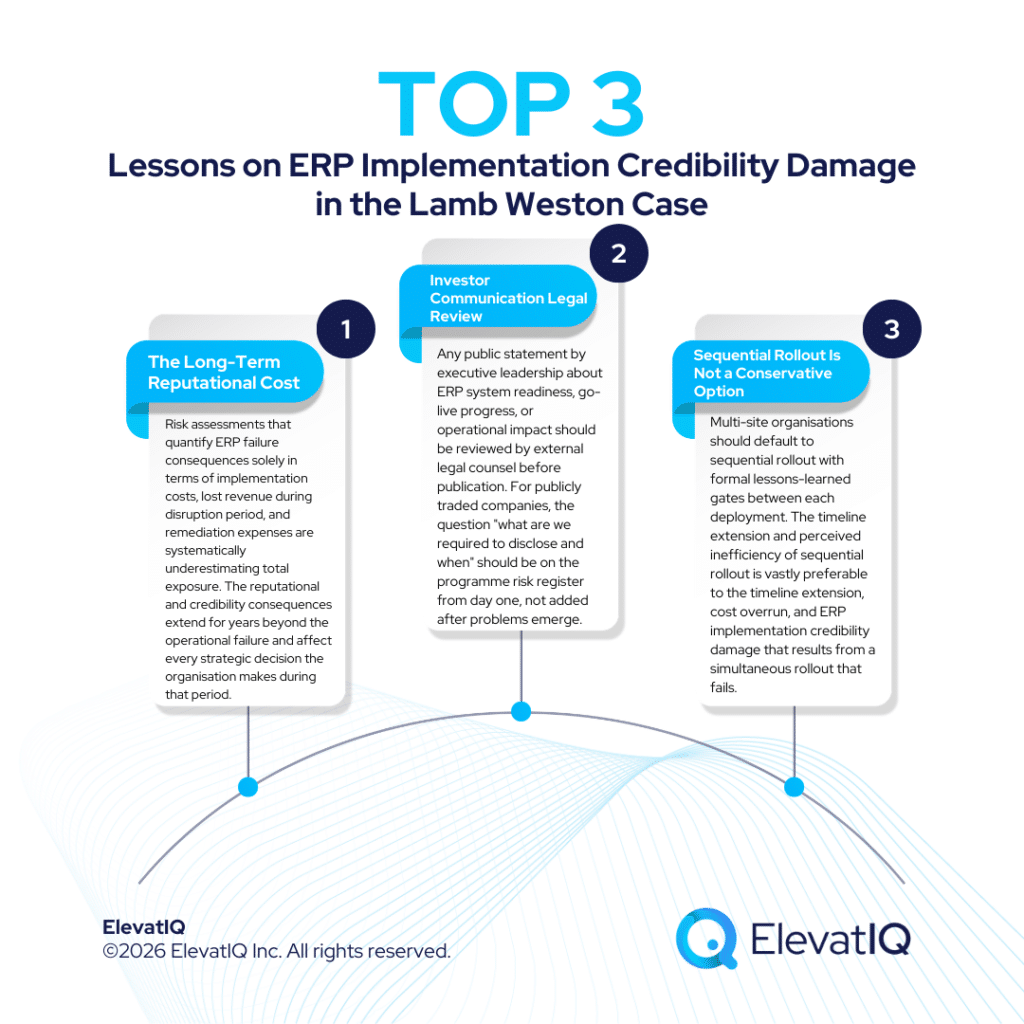
The Long-Term Reputational Cost of ERP Failure Exceeds the Immediate Financial Cost by Orders of Magnitude
Lamb Weston’s Q3 FY2024 operational losses totalled approximately $300 million (lost sales, reduced EBITDA, write-offs, legal costs). That is a substantial financial impact. But the sustained market underperformance, 12.4% stock decline year-over-year, 25 percentage points below S&P 500 performance, represents billions in foregone equity value. Add to that the strategic constraint on future capital allocation, the competitive disadvantage in customer negotiations, and the management turnover that eliminates institutional knowledge, and the true long-term cost is multiples of the immediate operational loss.
Implication for current ERP programmes: Risk assessments that quantify ERP failure consequences solely in terms of implementation costs, lost revenue during disruption period, and remediation expenses are systematically underestimating total exposure. The reputational and credibility consequences extend for years beyond the operational failure and affect every strategic decision the organisation makes during that period.
Investor Communication About ERP Readiness Requires Legal Review, Not Just Programme Team Sign-Off
Lamb Weston’s CFO stated during the January 2024 earnings call characterising early ERP issues as “usual bumps” with no expected material impact became central to securities litigation when the Q3 results revealed $135 million in losses. This is the ERP implementation credibility damage mechanism that transforms an operational failure into a legal and governance crisis.
Implication for current ERP programmes: Any public statement by executive leadership about ERP system readiness, go-live progress, or operational impact should be reviewed by external legal counsel before publication. For publicly traded companies, the question “what are we required to disclose and when” should be on the programme risk register from day one, not added after problems emerge.
Sequential Rollout Is Not a Conservative Option: It Is the Correct Risk Architecture
Lamb Weston’s post-failure strategic revision replaced simultaneous multi-site deployment with sequential plant-by-plant implementation. This is the rollout architecture that should have been applied from programme inception. The attempt to go live across multiple distribution centres simultaneously amplified both the operational risk (more failure points) and the financial risk (larger revenue base exposed to disruption).
Implication for current ERP programmes: Multi-site organisations should default to sequential rollout with formal lessons-learned gates between each deployment. The timeline extension and perceived inefficiency of sequential rollout is vastly preferable to the timeline extension, cost overrun, and ERP implementation credibility damage that results from a simultaneous rollout that fails.
The Conclusion
Lamb Weston’s ongoing struggle to rebuild investor confidence 18+ months after its ERP failure demonstrates what most risk assessments underestimate. The long-term reputational and strategic consequences of ERP failure extend far beyond the immediate operational disruption and financial loss. When institutional investors reduce stakes, when ROIC declines from 15.9% to 11.1%, when strategic capital allocation decisions are constrained by board and investor scepticism, and when competitive positioning is weakened by documented operational unreliability, those are not temporary setbacks that resolve when the system is stabilised. They are sustained ERP implementation credibility damage that affects every aspect of the organisation’s strategic execution for years.
For organisations seeking to avoid the multi-year credibility consequences that Lamb Weston continues to navigate, the team at ElevatIQ provides independent ERP advisory support across readiness assessment, governance framework design, and risk mitigation strategy, at exactly the stages where these decisions determine whether an ERP implementation becomes a transformation success or a credibility crisis.
(All commentary and analysis represents independent editorial perspective based on publicly reported information and cited primary sources.)

FAQs
ERP Implementation Credibility Damage: The Lamb Weston Case Read More »