In the past, sales and marketing operations could suffice with ad-hoc tools like spreadsheets or siloed software. However, the complexity of today’s sales and marketing departments demands more. CRM workflows differ significantly across industries and business models. For a natural and seamless experience, your CRM needs to support the specific data model required for your industry. The power of CRM lies in its ability to gather high-quality data from various systems and make it easily accessible to salespeople. However, obtaining this data can be challenging, especially if the CRM’s data model significantly deviates from your customer hierarchies and transactions.
Furthermore, the boundaries between CRM, CMS, call center systems, e-commerce, and ERP are becoming increasingly blurred. Modern CRMs now incorporate functionalities that traditionally belonged to ERP or e-commerce systems. The CRMs also overlap substantially with CMS systems, which have traditionally been home-grown due to the custom development required to build unique customer-centric workflows, especially the industries that want to track and manage their digital interactions.
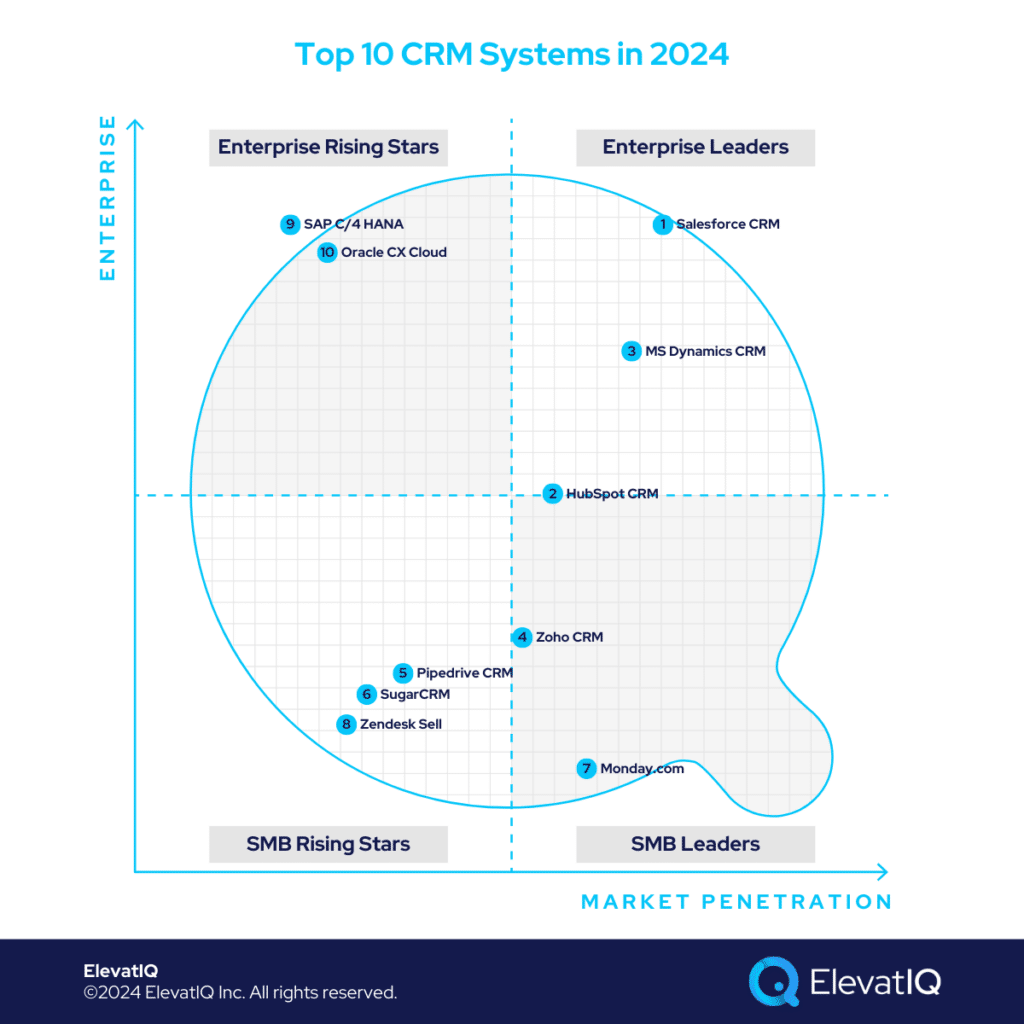
This intersection necessitates a clear definition of the roles and responsibilities of various systems involved in managing customer-centric workflows. Without a well-structured architecture, challenges in adoption and data integrity may arise. Although some CRM systems may showcase adaptability across industries, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the leading CRM systems, despite their market dominance, may not universally cater to every industry or business model. Consequently, selecting a CRM demands a thorough examination of your architecture and a comprehensive understanding of available solutions. To kickstart this process, consider exploring a list of the top CRM systems in 2024.

Criteria
- Overall market share/# of customers. The higher the market share in the CRM market, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Ownership/funding. The more commitment to the CRM offerings, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Quality of development (legacy vs. legacy dressed as modern vs. modern UX/cloud-native). The more cloud-native capabilities, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Community/Ecosystem. The larger the community with a heavy presence from CRM users, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Depth of native functionality for specific industries. The deeper the publisher-owned out-of-the-box functionality, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Quality of publicly available product documentation. The poorer the product documentation, the lower it ranks on our list.
- Ability to natively support diversified business models. The more diverse the product, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Acquisition strategy aligned with CRM offerings. The more aligned the acquisitions are with CRM offerings, the higher they rank on our list.
- User Reviews. The deeper the reviews for CRM offerings, the higher the score for a specific product.
- Must be a CRM product. It can’t be a CRM integrated with an ERP (that enterprise software vendors can’t sell standalone). Must contain deep sales and marketing operations capabilities. For example, marketing automation, territory planning, and sales and marketing workflow management.
10. Oracle CX Cloud
Oracle CX Cloud incorporates various best-of-breed CRM components, including sales, marketing, service, content management, and advertising cloud. It is tailored for large B2C enterprises, specifically those in industries like communications, media, and financial services. With Oracle Commerce being discontinued, the scope of Oracle CX Cloud may be confined to fewer industries.
The recent acquisition of Cerner, which serves as a customer-facing channel for the healthcare market, raises questions about Oracle’s continued investment in the CRM portfolio. Furthermore, Oracle has consistently pursued industries with substantial data and analytical workloads. Given the current economic landscape, healthcare emerges as a more lucrative market compared to commerce and customer experience. Consequently, Oracle CX may not receive equivalent attention within the company’s portfolio. Despite this, it maintains the #10 ranking on our list as an enterprise-grade solution for businesses seeking an integrated CRM experience.
Strengths:
- Marketing Automation and Ad Spend Tracking: Providing in-depth insights into customer behavior across various advertising platforms.
- Content and Centralized Asset Management: These features are particularly crucial for content-intensive industries such as media and telecom.
- Integration with Enterprise-grade CPQ and Sales Performance Management Tool: Offering a configurator for subscription-based offerings. This integration is especially beneficial for verticals like media and telecom.
Weaknesses:
- Clunky UI: Oracle has incorporated various systems into its CX portfolio to enhance its capabilities, making a seamless experience challenging.
- Not as Strong B2B and Post-sales Capabilities: Oracle’s CRM falls short in post-sales CRM processes, particularly in B2B industries where pre-sales processes, such as manufacturing or distribution, are less extensive.
- Not as Strong for Regulated and Audit-centric Industries: Additionally, Oracle CRM may face challenges in industries and regions with significant audit requirements, such as GDPR compliance and version control.

9. SAP C/4 HANA
SAP C/4 HANA, an integral part of the S/4 suite, offers a range of best-of-breed CRM options in the CX portfolio, including sales, marketing, commerce, customer experience, and service cloud. It caters primarily to large utility, finance, and public sector companies, especially those with deep regulatory workflow requirements within CRM processes.
The recent spin-off of Qualtrics may suggest that SAP is not as committed to the CX portfolio. Moreover, SAP faces substantial challenges with newer entrants in the headless space to disrupt its commerce portfolio. Still a viable option for companies requiring tight integration with CPQ and configurator available through the Hybris portfolio, SAP C/4 HANA still maintains the same ranking as last year.
Strengths:
- Integration with Gigya and Customer Data Cloud. Noteworthy strengths include consent and preferences with audit-ready capabilities for compliance workflows such as GDPR, CCPA, and LGPD. It also offers cross-channel personalization and identity management.
- Integration with Other SAP S/4 HANA Products. Embedded experience because of the tight integration among SAP products is one of the biggest highlights of SAP C/4 HANA.
- Integration with Enterprise-grade CPQ and Sales Performance Management Tool. Companies with enterprise-grade quoting, sales territory, and compensation management needs will find C/4 HANA appealing.
Weaknesses:
- Marketing Automation. C/4 HANA lacks sophistication in pre-sales processes, including marketing automation.
- Tight Integration with SAP Products. The data model may feel restrictive for sales and marketing teams seeking fluidity to focus on sales rather than operational details.
- Inflexibility and Complexity of the Solution. Enterprise workflows like approval management, regulatory checks, and budgetary approvals may seem unnatural and complex for small to mid-size organizations seeking more straightforward CRM solutions.
8. Zendesk Sell
Zendesk Sell, an entry-level CRM among top CRM systems designed for companies utilizing ZenDesk for customer service and ticketing workflows, acquired these capabilities through the Base CRM acquisition. It targets smaller companies with under 10-15 employees, lacking mature CRM capabilities such as sales ops planning, marketing automation, and territory management. However, larger companies may find its capabilities limiting.
Also, most enterprises exploring CRMs require custom development capabilities because of the unique customer experience and service workflows. So Zendesk would not be a fit for them seeking customizability as offered by other platforms such as Salesforce or HubSpot on this list. Zendesk maintains its ranking from the previous year, with no significant developments observed.
Strengths:
- Simple Interface for Startups. Zendesk’s interface is appealing to users with straightforward CRM needs, especially for lead and opportunity tracking, resembling the look and feel of HubSpot and Close.io.
- Easier Transition for Zendesk Users. Users of Zendesk will find it attractive due to the similar interface and the ability to create integration workflows between the two apps.
- Easier Calling and Emailing Natively within the App. Zendesk’s design is user-friendly for sales development reps involved in multi-touch campaign execution and tracking directly within the app.
Weaknesses:
- Zendesk Sell and Support are not tightly integrated. Despite being part of the Zendesk suite, Sell and Support apps lack tight integration, resulting in a disjointed experience and minimal data exchange between them.
- Marketing Automation. Marketing automation capabilities in Zendesk CRM are not as robust, necessitating the use of third-party marketing automation software and an additional license.
- Advanced CRM Capabilities. Zendesk CRM offers limited advanced features such as reporting, CSV import/export, and revenue operations planning.

7. Monday.Com
Monday.com is geared towards small companies already using it for project management and those with custom CRM workflow needs, such as real estate and non-profits. However, it may not be an ideal choice for companies that can easily find other options through a pre-built platform.
Implementing Monday.com internally would require a tighter governance process, especially if it is being used for cross-functional workflows. The fluidity of the platform might lead to business users’ overengineering process, leading to the creation of technical backlog and maintenance nightmares in the long term. Also, confidently predicting and estimating the final costs requires solution architecture expertise. The ranking for Monday.com remains unchanged from the previous year, with no significant developments observed.
Strengths:
- Better Customizability. Monday.com serves as a highly customizable technical platform, excelling in ad-hoc workflows and offering superior customization capabilities.
- Easily Build Automated Actions and Integration with Other Apps. Business users find it easy to construct automated actions for notifications and approval flows.
- Best for Industries Such as Real Estate and Non-profits. Industries like real estate and non-profits requiring flexibility for customized processes may find Monday.com suitable for their unique needs.
Weaknesses:
- Risk of Over-Engineering Processes. While its customizability is beneficial for specific industries, there’s a risk of over-engineering processes, potentially impacting downstream workflows.
- Primarily a Project Management Tool. Monday.com is fundamentally a project management tool, necessitating the construction of advanced CRM functionality and reports.
- Data Integrity. Due to its technical nature, Monday.com may lack referential integrity between business objects, potentially leading to data integrity issues.
6. SugarCRM
SugarCRM caters to smaller companies seeking free or open-source software and those with specific CRM workflows. However, it may not be the best fit for larger companies in search of a robust CRM solution. SugarCRM maintains its ranking among top CRM systems, with no significant developments observed.
Strengths:
- On-prem Option with the Community Edition. SugarCRM provides a community edition that can be hosted on-premises, making it favorable for companies with existing server infrastructure.
- Ability to Build Ads Right from the Platform. SugarCRM stands out with features like the ability to build ads directly from the platform, streamlining the interface for companies managing ads without juggling multiple tools.
- Great for Cost-sensitive Organizations. Cost-sensitive organizations with in-house developers benefit from SugarCRM, eliminating concerns about recurring licensing fees.
Weaknesses:
- Clunky Interface. The interface lacks modernity, potentially hindering user adoption, particularly within sales teams.
- Limited Reporting Capabilities. SugarCRM’s reporting capabilities are restricted, requiring significant investment in development and internal costs to generate reports.
- Potential Higher Costs with the Community Edition. While the community edition doesn’t have a licensing fee, organizations are responsible for support, upgrades, patches, hosting, and security. Despite its cost-saving intent, it may end up being as expensive as SaaS options.
5. Pipedrive CRM
Pipedrive CRM is designed for smaller companies and solo founders with limited budgets seeking an entry-level CRM solution for customer interaction management. However, it may not be the best fit for larger companies with mature CRM processes requiring features like territory planning, quoting, and sales compensation management. Pipedrive CRM maintains its previous ranking among top CRM systems, with no significant developments noted.
Strengths:
- Workflow Automation: Pipedrive CRM offers workflow automation capabilities that are beneficial for companies looking to minimize data entry and automate lead capture and nurturing processes.
- Similar Look-and-feel as HubSpot: With a data model and user interface similar to HubSpot, Pipedrive CRM provides a familiar experience that aids sales teams, especially those less technically inclined.
- Easy Customization of Reports and Goal Setting: Teams with limited technical proficiency will find Pipedrive’s reports easy to customize compared to more complex tools.
Weaknesses:
- Weak Data Structure for Complex B2B Organizations: B2B organizations with intricate customer hierarchies may struggle to integrate with Pipedrive due to its weak data structure. Limitations in data model sharing for leads and contacts can pose challenges for larger companies.
- Limited Data Import and Export Functionality: Companies seeking robust data import and export capabilities, especially for leads and opportunities from external systems, may find Pipedrive limiting.
- Not Suitable for Larger Organizations: Pipedrive CRM may not meet the needs of larger organizations with deeper requirements for territory management, sales compensation, and approval workflows.
4. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM is tailored for smaller professional services companies like marketing agencies, tech startups, and software development firms. It proves especially effective for those already utilizing Zoho for HCM or accounting purposes. However, it may not meet the advanced CRM needs of product-centric organizations. Zoho CRM maintains its previous ranking with no significant developments noted.
Strengths:
- Data Model Similar to Salesforce: Zoho’s data model mirrors Salesforce’s, facilitating implementation and integration with systems like ERP that have complex customer masters.
- Workflow for Data Quality: Zoho CRM includes a pre-packaged workflow builder, allowing teams with development expertise to construct intricate workflows. This aids in maintaining data hygiene and enhancing CRM adoption.
- Zoho Creator: The inclusion of Zoho Creator, an app development platform in the suite, enables developers to swiftly integrate other software and create custom apps without relying on additional third-party tools.
Weaknesses:
- Advanced CRM Features: Zoho CRM may not be suitable for large companies with regulatory, compliance, or planning needs due to its weaker out-of-the-box support for these capabilities.
- Territory Management and Sales Team Planning: Zoho CRM lacks robust support for territory management and sales team planning compared to some of the other leading CRM solutions.
- Limited Integration Options Outside of Zoho: While excelling within the Zoho ecosystem, integration options outside Zoho are limited. Connecting with other systems would require custom integration and development efforts.
3. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot CRM is a leading choice for smaller companies aiming for seamless integration of customer-centric workflows, covering essential CRM processes such as sales, service, CMS, and marketing automation. In contrast to Salesforce, HubSpot excels in user-friendliness and customization, even though it may not match the depth of customer and field service workflows or provide as many built-in custom objects for specific industries.
However, this adaptability might pose challenges for companies unfamiliar with robust data and process governance. HubSpot CRM proves advantageous, especially for content-heavy B2B companies aiming for centralized management of digital marketing and sales channels. The recent acquisition of Clearbit further enhances HubSpot’s capabilities by integrating data and intelligence with core CRM processes, solidifying its position as the third-best CRM solution on our list.
Strengths:
- Price: HubSpot CRM stands out for companies seeking a more affordable CRM option than Salesforce.
- Marketing Automation and Omnichannel Tracking: One of the strongest marketing automation tools integrating all channels, including emails, social media, and the web.
- Ecosystem: HubSpot boasts a strong ecosystem and seamless integration with other CRM systems, CMS platforms, and eCommerce tools for users focusing on marketing automation.
Weaknesses:
- Weaker Data Model for B2B Businesses: The companies requiring ERP-like operational capabilities, including CPQ inside HubSpot, might struggle with the leaner object model of HubSpot.
- Advanced CRM Features: HubSpot may not suit companies with deeper compliance, regulatory, and quoting needs, necessitating substantial development on top of the platform.
- Territory Management and Sales Team Planning: The weaker data model makes it less suitable for industries requiring robust out-of-the-box capabilities for territory management and sales team planning, where referential data integrity is crucial for accurate CRM data.
2. Microsoft Dynamics CRM
Microsoft Dynamics 365 CRM is designed for mid-to-large-sized companies, especially those leveraging other Microsoft products such as Dynamics 365 ERP. However, for smaller companies seeking data model fluidity, it may not be the ideal choice.
Microsoft secures the second-largest market share in the CRM space, following Salesforce. It particularly appeals to companies prioritizing robust operational capabilities within the CRM, including features like territory planning, global and centralized compliance, complex CPQ processes, and tight integration with project management workflows.
While Microsoft excels in supporting operational processes, its integration support may be limited to commerce and content management platforms, modern search technologies, headless platforms, data and intelligence providers, and centralized social media management platforms. Despite these considerations, Microsoft Dynamics CRM remains a formidable player in the CRM market, securing its position at #2 in our list of top CRM options.
Strengths:
- Complex Business Object Support: Facilitates the creation of necessary permissions and approval flows crucial for larger, regulated enterprises.
- Integrated Microsoft Ecosystem: With database-level replication and a shared common data model, integration with other Microsoft products is seamless.
- Advanced Territory Management: The CRM comes pre-packaged with strong capabilities for advanced territory management and global sales compensation planning.
Weaknesses:
- Less Fluid Data Model: Dynamics 365 CRM has tighter dependencies between objects, particularly regarding pricing, products, and their correlations with accounts, posing usability challenges compared to more flexible CRM systems.
- CSV Import and Export Challenges: The platform lacks intuitive support for CSV import and export, making it less user-friendly for sales teams looking to import opportunities and leads from external systems.
- Limited Marketing Automation: The marketing automation component in Dynamics 365 lacks strong ecosystem support with external CMS providers.
1. Salesforce CRM
Salesforce serves companies of all sizes, featuring a startup-friendly version and excelling in managing complex CRM workflows. While not always the ideal choice for entities with unique CRM processes, such as those in real estate or uniquely structured non-profit organizations, Salesforce comprehensively covers enterprise sales and marketing workflows throughout all phases—pre-sales, sales, and post-sales. The platform stands out for its depth in industry-specific sales and marketing processes, offering pre-populated layers of business objects without the need for custom development on vanilla platforms.
The Salesforce ecosystem holds authority in headless and commerce spaces, positioning it as an ideal enterprise Cx platform for various industries. These strengths contribute to Salesforce CRM maintaining its #1 position on our list.
Strengths:
- Robust Data Model for Varied CRM Needs: Salesforce boasts the most extensive data model, catering to the complex requirements of diverse industries and business models.
- Specialized Capabilities in Telecom and Media: Salesforce stands out with advanced product and CPQ capabilities, particularly beneficial for industries like medical devices and telecom.
- Comprehensive Product Portfolio and Ecosystem: Offering best-of-breed solutions across all CRM areas, including marketing automation, field services, and eCommerce.
Weaknesses:
- Cost: Salesforce may have a higher price tag compared to other CRMs, making the per-seat cost more expensive.
- Complex Customization Process: Customization in Salesforce may not be as intuitive as in other CRM systems, with a potentially complex and dated object model due to the mix of lightning and legacy interfaces.
- Industry-Specific Limitations: While Salesforce excels in certain industries, it may not be the best fit for every sector, requiring deep collaboration with ERP systems.
Conclusion
As customer experience takes center stage in securing business deals, sales and marketing departments increasingly require advanced CRM capabilities. A comprehensive CRM is essential for maintaining a centralized view of customers throughout their journey, whether in the pre-sales or post-sales phase. Without a CRM offering a centralized workflow and interaction management platform, competing in today’s market conditions can pose significant challenges.
The choice of CRM directly influences your enterprise architecture. Therefore, selecting a CRM that aligns with your business model and enterprise architecture is paramount for the success of digital transformation initiatives. If you’re currently evaluating CRM systems, consider the points highlighted above in addition to the expertise of independent CRM consultants. This list aims to assist you in narrowing down suitable options for your needs.