Last Updated on March 17, 2025 by Sam Gupta
Exceeding the $100 million revenue mark is more challenging than commonly perceived. Relying on ad-hoc planning and siloed processes can result in financial performance issues. To advance to the next stage, robust process integration and global financial and operational synergies are essential—and because of these reasons, companies require mid-sized business ERP designed for this stage.
Moreover, even within mid-market businesses, diverse needs emerge. The larger peer group, denoted as upper mid-market companies (approaching $1B in revenue), frequently opt for extensive ERP systems like SAP S/4 HANA or Oracle Cloud ERP. However, prematurely implementing such enterprise-grade ERP systems can hinder momentum and growth, particularly when facing challenges in predicting size and business model evolution during active M&A cycles. Conversely, others seek global synergies, employing shared services to uncover financial and supply chain benefits in specific regions. These contrasting approaches call for distinct system strategies.
Conversely, the smaller peer group, positioned at the lower end of the mid-market (approximating $100M in revenue), can advance to $250 million without necessitating the same level of process stringency. Nevertheless, they often require planning for more advanced capabilities such as ATP, allocation, or consolidated planning. For seamless cross-functional adoption of planning solutions, teams must streamline their data and processes. However, at this stage, limitations in implementation budgets and skillsets prevent them from adopting the same approach as their upper mid-market peers. Some companies aiming for accelerated growth may emulate the upper mid-market strategy, while others may opt for a conservative approach, selecting systems designed for the lower mid-market segment. So, what constitutes the ideal systems for these mid-market businesses?

Criteria:
- Definition of mid-size organizations. $50M-$1B in revenue or less than 1000 employees. It might be present in 4-10 countries. Getting the proper planning and scheduling is critical for growth. The integration of processes and systems is essential to plan and scale.
- Overall market share/# of customers. The higher the market share among the mid-market companies, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Ownership/funding. The more committed the product roadmap for the mid-market, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Quality of development. The more cloud-native capabilities, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Community/Ecosystem. The larger the presence from the mid-market companies, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Depth of native functionality for specific industries. The deeper the publisher-owned out-of-the-box functionality, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Quality of publicly available product documentation. The poorer the product documentation, the lower it ranks on our list.
- Mid-market market share. The higher the focus on mid-market companies, the higher the ERP system ranks on our list.
- Ability to natively support diversified business models. The more diverse the product, the higher it ranks on our list.
- Acquisition strategy aligned with mid-market. The more aligned the acquisitions are with the mid-market, the higher it ranks on our list.
- User Reviews. The deeper the reviews from the mid-market companies, the higher the score.
- Must be an ERP product. It can’t be an edge product such as QuickBooks, Freshbooks, Xero, Zendesk, HubSpot, or Salesforce. It also can’t be an add-on owned by ISVs or VARs that sits on top of other accounting platforms.

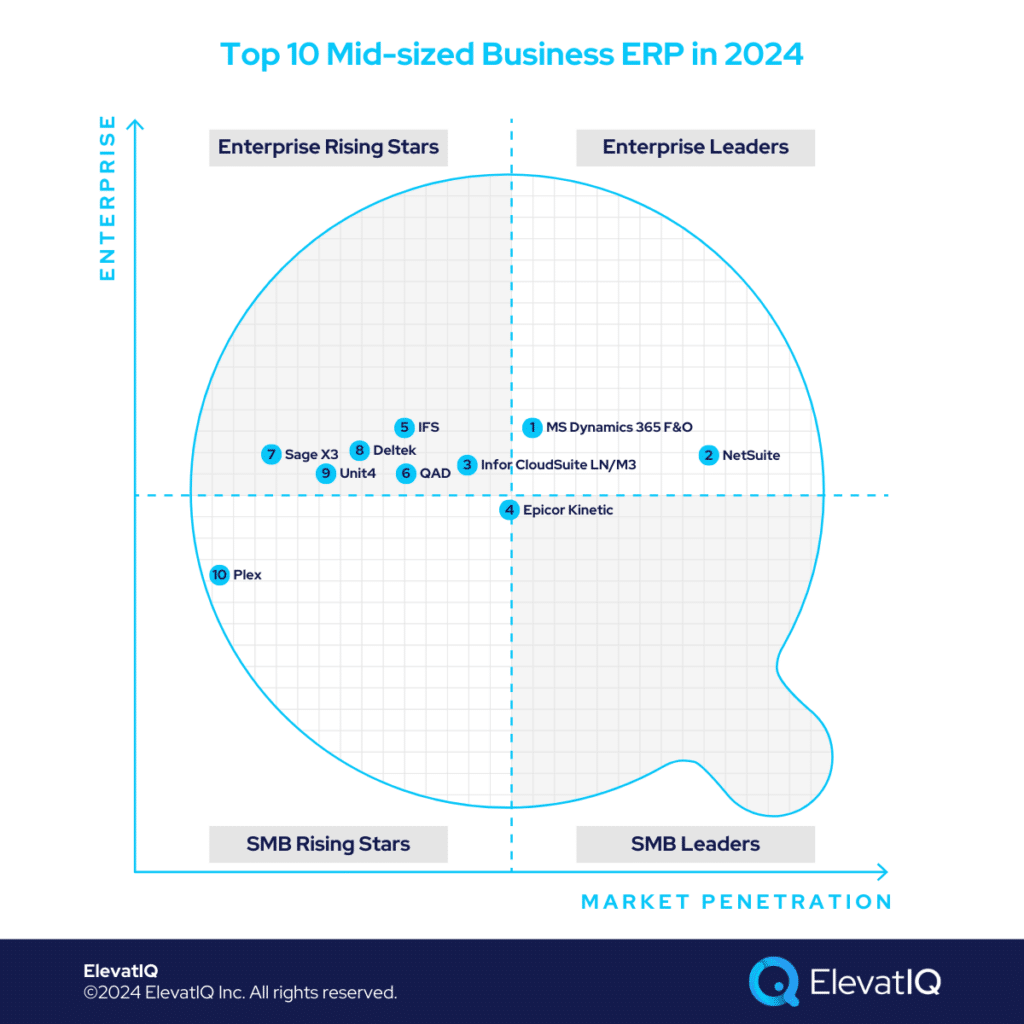
10. Plex
Plex targets mid-market automotive companies, specializing in manufacturers and distributors within the Toyota and Ford ecosystems. Taking an MES-first approach, it provides robust last-mile capabilities tailored to this niche. Plex is particularly suitable for upper mid-market companies adopting a best-of-breed strategy, with Plex as the operational solution and a stronger financial solution handling corporate ledger functions.
It may also be a good fit for lower mid-market businesses aligned with Plex’s core capabilities and stable business models. However, Plex’s lack of significant portfolio developments for mid-market customers has led to a slight downgrade, maintaining its position at #10 among mid-sized business ERP systems.
Strengths
- Last mile capabilities for mid-market companies with limited budgets. Companies limited in their budget would find the last mile capabilities appealing as building them might be technically and financially risky for mid-market companies.
- MES-first approach. Plex is perhaps the only solution in the mid-market space that takes a MES-first approach, making it especially friendly for companies interested in capitalizing on Industry 4.0 strategies.
- Cloud-native. Plex was born in the cloud just like other cloud-native solutions, providing richer cloud capabilities such as enterprise search and being mobile-friendly.
Weaknesses
- Limited focus. The limited focus of the solution might be a challenge for mid-market companies active with M&A cycles. Even for pure-play manufacturers, the capabilities might be on the learner side because of the limited support for mixed-mode manufacturing.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. The consulting base is super limited, with companies primarily relying on Plex to provide professional services.
- It is not an ideal solution as the enterprise core. The ERP layers are substantially limited a challenge for mid-market companies planning to go public or requiring deeper ERP capabilities.

9. Unit4
Unit4 serves service-centric mid-market organizations, standing out with its integrated human resources component. Distinct from counterparts like FinancialForce, Sage Intacct, and Workday, Unit4 excels in supporting the operational processes of schools and public sector entities. Competing with major players such as PeopleSoft, Oracle Cloud ERP, SAP S/4 HANA, Microsoft Dynamics F&O, and Workday, Unit4 proves to be an ideal fit for various mid-market segments. Recent acquisitions have broadened its capabilities, offering integrated suites for P2P, HCM, and ERP in service-centric industries. Despite the lack of momentum in 2024, it still maintains its position at #8 on our list of the top 10 mid-sized business ERP systems.
Strengths
- Enterprise-grade capabilities for universities and non-profits. Unit4 is perhaps the only solution in this space that has such depth in the public sector space. The same capabilities would require substantial consulting efforts atop vanilla solutions.
- Cloud capabilities. While the solution is legacy, they have made substantial progress with their cloud capabilities.
- Pre-integrated HCM and procurement processes tailored for service-centric industries. Solutions such as Workday that offer best-of-breed HCM and indirect procurement capabilities for similar verticals might be technically and financially risky.
Weaknesses
- Limited focus. The limited focus of the solution might be a challenge for mid-market companies active with M&A cycles, especially for business models outside of Unit4’s expertise.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. As of today, their North American presence and consulting base is significantly limited.
- Limited best-of-breed capabilities. Mid-market companies opting to build best-of-breed architecture might not find as many pre-baked integration options, requiring substantial consulting efforts.
8. Deltek
Deltek targets mid-market businesses in construction, government contracting, architecture, and engineering. Setting itself apart from similar solutions like QAD, Plex, Epicor Kinetic, and Infor CSI, Deltek boasts logos as prominent as AWS and Booz Allen Hamilton. However, these logos often leverage their best-of-breed capabilities, which are relevant for mid-market companies considering Deltek as an operational solution. While its multi-entity capabilities position it as a corporate solution in the lower mid-market, additional complementary solutions like CRM may be needed for features found in fully integrated alternatives. In contrast to Sage Intacct or Oracle ERP Cloud, Deltek excels in last-mile functionality for government contractors, particularly in DCAA compliance. Given a substantial downgrade due to a lack of portfolio momentum, Deltek secures its position at #8 among mid-sized business ERP systems.
Strengths
- Last-mile capabilities for GovCon and construction-centric verticals. Deltek has last-mile capabilities in the construction and GovCon space, requiring substantial development atop vanilla solutions.
- Access to the databases and networks relevant to these industries. Deltek has several products in its portfolio with industry databases and networks that provide it a unique advantage over other vendors.
- Multi-entity capabilities. Their multi-entity capabilities are rich, making them suitable for upper mid-market companies seeking one solution to host all of their entities in one database.
Weaknesses
- Limited focus. The limited focus of the solution might be a challenge for mid-market companies active with M&A cycles, especially for business models outside of Deltek’s expertise.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. As of today, their ecosystem and consulting base is significantly limited.
- Limited best-of-breed capabilities. Mid-market companies opting to build best-of-breed architecture might not find as many pre-baked integration options, requiring substantial consulting efforts.
7. Sage X3
Sage X3 holds a distinctive market position, primarily targeting process, agriculture, and food & beverage companies. Unlike many counterparts focused on discrete manufacturing, Sage X3 stands out with profound functionality tailored for process-centric industries. It excels in features like native support for formulation, potency management, use-by-date, sub-lots, and food traceability. They are the right fit for upper mid-market companies seeking operationally rich solutions at the subsidiary level for process-centric industries. Or the lower mid-market companies are seeking one solution for all of their global entities in one database. Sage has had a questionable commitment to their X3 product lately, and because of this, we have downgraded their ranking substantially, now ranking at #7 on this list.
Strengths
- Great for upper mid-market pharma companies. Designed for process and food and beverage manufacturing and distribution. As a result, it provides far deeper functionality for large pharma companies out of the box.
- Deep ERP layers for audit-ready and public companies. Sage X3 is especially strong with its accounting and finance capabilities for mid-market companies aiming to go public or the ones that require audit-ready capabilities.
- Great ecosystem of consultants for pharma validation. The ecosystem includes consulting companies with deep expertise in the Sage X3 product and validation procedures.
Weaknesses
- Limited focus. The limited focus of the solution might be a challenge for mid-market companies active with M&A cycles, especially for business models outside of Sage X3’s expertise.
- Limited ecosystem. While it has great ecosystems of consultants and partners, the number of integrations supported might be limited for business models outside of its core expertise.
- Limited best-of-breed capabilities. Mid-market companies looking for pre-integrated best-of-breed options may struggle to find those options with Sage X3.
6. QAD
QAD focuses on upper-mid-sized companies with intricate supply chain requirements, particularly in the automotive and life sciences verticals. While it may lack the extensive last-mile functionality for Honda or Toyota ecosystems, unlike Plex or Infor LN, QAD excels in international trade and TMS capabilities pre-built with the core solution.
These TMS capabilities closely match those of larger counterparts like Oracle Cloud ERP and Microsoft Dynamics F&O.QAD has made substantial advancements with its technology with its new announcement of rearchitecting its entire platform, securing its rank at #6 on this list.
Strengths
- Pre-integrated best-of-breed suite tailored for specific micro-verticals. QAD shines in specific micro-verticals of Automotive and Life Sciences where the generalized BOMs and recipes of vanilla solutions might struggle.
- ERP + Supply Chain Suite. QAD is perhaps the only suite that combines the capabilities of both suites, such as Supply Chain and ERP. Most solutions would require two different suites, creating data siloes with these suites and struggling with centralized inventory and supply chain planning.
- Multi-entity Support – Unlike other smaller solutions that are likely to have limited global support, QAD has built-in support for companies interested in exploring operational and financial synergies globally.
Weaknesses
- Limited focus. The limited focus might be a challenge for mid-market companies active with M&A cycles, especially with business models outside of QAD’s expertise.
- Limited ecosystem. QAD’s ecosystem is substantially limited, and for the most part, you will be relying on QAD’s professional services for maintenance and support.
- Technology. While QAD plans to rearchitect their entire platform moving away from legacy technologies such as RPG, it might take a few years before they are fully stable on the new platform.
5. IFS
IFS caters to mid-size utility, oil and gas, MRO, airline, and large equipment service companies, positioning itself as a cost-effective alternative to SAP S/4 HANA. Ideal for upper mid-market companies unable to invest millions in consulting and implementation, IFS excels in managing complex field service scheduling, even for massive workforces of up to 500K field workers.
In terms of technology and cloud-native experience, IFS rivals QAD and Plex with its superior user experience. Because of the limited focus of their solution to certain industries and advancements in technology with other vendors, we have downgraded their ranking slightly but still maintain its ranking at #5 on this list.
Strengths
- Enterprise-grade field service and asset management capabilities. While limited in its suite and focus, their last-mile capabilities are the strongest for their target industries.
- The data model is aligned with companies with large programs. Industries such as MRO, Oil, and Gas follow very different project structures and BOMs. And IFS’s data model allows them to manage complex programs without any ad-hoc arrangements.
- Technology. While a legacy solution, IFS technology has been rearchitected and modernized using cloud-native SaaS technologies.
Weaknesses
- Limited focus. The limited focus might be a challenge for mid-market companies active with M&A cycles.
- Limited ecosystem. Its presence and install base are still limited in North America compared to other solutions on this list.
- It is not the right fit for holding and private equity companies as a corporate ledger. While IFS can provide the best-of-breed capabilities in a two-tier architecture or can act as one solution, IFS might not be the best fit to be used just as the corporate ledger for mid-market companies.
4. Epicor Kinetic
Epicor Kinetic specializes in manufacturing, addressing hybrid scenarios in industries like metal, automotive, and aerospace with formal processes and intricate inventory management. Tailored for organizations spanning manufacturing, construction, and distribution, Epicor Kinetic uniquely aligns with their core processes.
In the realm of cloud capabilities, the modernized Epicor Kinetic, distinguished from legacy systems, features mature offerings, including enterprise search. While well-suited for lower mid-market companies, those in the upper mid-market with over three financial hierarchies may find it less ideal, requiring ad-hoc arrangements. With out-of-the-box MES functionality, Epicor Kinetic caters to mid-market companies seeking integrated Industry 4.0 capabilities without extensive consulting costs, securing the 6th position on our list of top 10 ERP systems for small businesses.
Strengths
- Great for formal manufacturing organizations. The manufacturing organizations that follow formal manufacturing processes with revision numbers would relate to the product more.
- Last-mile capabilities for complex manufacturing organizations. 90% of the capabilities required by verticals such as metal, automotive, and aerospace are pre-packaged with the core platform.
- Mature cloud capabilities. Although a legacy product, it includes mature cloud capabilities such as enterprise search and transactional maps for end-to-end transactional traceability.
Weaknesses
- Not a great fit for upper mid-market companies with more than three layers of financial hierarchies. Epicor Kinetic will require ad-hoc arrangements for larger mid-market companies with more than three financial hierarchies.
- Limited focus. The limited focus on certain business models poses the risk of requiring other ERP systems to support complex and diverse business operations.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. The consulting base is highly limited, primarily relying on Epicor’s professional services for consulting and support.
3. Infor CloudSuite LN/M3
Infor CloudSuite LN and M3 stand as flagship solutions tailored for upper-mid market companies, with over $250M in revenue. In particular, Infor M3 excels in unique inventory capabilities, supporting planning based on style, size, and season with native integration for apparel-centric PLM. Conversely, Infor LN has the most comprehensive manufacturing capabilities.
While most smaller manufacturing solutions may have limitations with the type of manufacturing they can support and would require ad-hoc arrangements, Infor LN and M3 can support most manufacturing business models. Given their lack of overlap, LN and M3 collectively secure their position. Although lacking major developments in 2023, their suite-centric approach positions them favorably for mid-market companies, earning them the 3rd spot on our list of top 10 ERP systems in 2024.
Strengths
- Great for upper mid-market pureplay manufacturing business models. Ideal for upper mid-market companies or as subsidiary solutions in a two-tier setting for private equity-owned or holding companies.
- Most comprehensive manufacturing capabilities. Both can support the most complex manufacturing business models, WBS-centric manufacturing, or support for attributes with MRP planning.
- Enterprise-grade capabilities for upper mid-market companies. While most smaller solutions might require ad-hoc arrangements for global financial operations, both have them natively built.
Weaknesses
- Not the best fit as a corporate ledger. Private equity and holding companies requiring global solutions while using a tier-2 solution at the subsidiary level might not find the most value with both.
- Limited focus. The limited focus on certain business models poses the risk of requiring other ERP systems to support complex and diverse business operations.
- Limited ecosystem and consulting base. The consulting base is highly limited, primarily relying on very few Infor resellers for consulting and support.
2. NetSuite
NetSuite stands out as a versatile solution, making it a top choice for private equity and holding companies seeking to streamline their portfolio companies on one solution and skillset. Its broad market coverage caters to diverse segments, offering native capabilities and vibrant ecosystem add-ons for comprehensive global support. While not as tailored for intricate operations like industrial manufacturing or distribution without add-ons, NetSuite excels in supporting various business models, be it product- or service-centric. It proves invaluable for companies requiring robust financial audit support, crucial for publicly traded organizations.
In a pivotal move, NetSuite introduced CPQ and enhanced P2P capabilities in 2023, expanding its offerings, securing its rank at the #2 spot on our list of top 10 mid-sized business ERP systems in 2024.
Strengths
- Diverse capabilities.Supports multiple industries and business models with pre-baked integration flows, reducing consulting and implementation efforts for budget-constrained mid-market companies.
- Ecosystem, with consultants present in most countries and solutions available to augment the core capabilities in most industries.
- Global capabilities. Supported and actively installed in most countries globally, making it a true global ERP for mid-market businesses.
Weaknesses
- Weaker data model. The data model is not as structured as with SAP or Acumatica, making it harder to understand and follow.
- Limited mature last mile capabilities. While NetSuite has a vibrant marketplace to augment its core capabilities, the last-mile capabilities required for manufacturing or industrial distribution are extremely limited.
- Not fit for pure-play manufacturing or industrial distribution holding companies. Companies focused on pure-play manufacturing or industrial distribution might not find the most value in NetSuite.
1. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance & Operations
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations is perhaps the most diverse, with native capabilities to host business models as diverse as discrete and process manufacturing, as well as discrete and service-centric verticals. While it can support most business models natively as part of the same platform, it also offers a vibrant marketplace to augment its core capabilities, making it ideal for private equity and holding companies to streamline all of their global entities on one solution and skillset. Although re-architected for a cloud-native experience, not all modules and workflows have fully transitioned, retaining some legacy components. Given its diversity and applicability for most industries and mid-market companies, it wins the #1 spot on this list.
Strengths
- Diverse capabilities.Supports global operations and business models and pre-baked integration for the best-of-breed CRM and field service solutions, ideal for mid-market organizations growing in complexity.
- Ecosystem, with consultants present in most countries and solutions available to augment the core capabilities of most industries.
- Global capabilities. Supported and actively installed in most countries globally, making it a true global ERP for mid-market businesses.
Weaknesses
- The channel is not as regulated. Microsoft channel is very complex, without any direct support for its resellers and partners, making navigating the Microsoft channel extremely hard.
- Limited best-of-breed capabilities directly through OEM. While Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O has a vibrant marketplace to augment its core capabilities, crucial capabilities such as PLM, etc, might not be owned and pre-integrated by Microsoft.
- Limited last-mile capabilities. The last-mile capabilities required in specific micro-verticals such as dairy, plastic, building supplies, or metal might require add-ons or expensive development on top of the core platform.
Conclusion
Mid-market companies at a critical juncture often contemplate larger solutions like SAP S/4 HANA or Oracle ERP Cloud, risking low adoption due to complexities. Success in the mid-market hinges on exploring dedicated ERP options tailored to their current needs, avoiding unnecessary change management challenges.
Despite a large solution’s capacity, it might not be the most financially prudent decision. This list serves as a starting point, yet expertise is crucial for aligning a solution with unique business requirements. Consulting with an independent ERP expert ensures a successful ERP journey.









