Last Updated on December 28, 2024 by Sam Gupta
Have you been thinking about implementing an ERP for your business? Your first task would be to research distribution ERP features and craft a plan aligned with the future state of your business. While similarities exist, each distributor’s business model is unique (as well as their transactions and operational capacity considerations). The common dilemma typically is to focus on similarities. Instead, most businesses end up following their industry peers, with the assumption that peers’ working practices might be equally suitable for their unique context. Although a great approach, it generally fires back because of differences in transactions and operational capacity needs. So what do you need to do? You need to identify your unique processes and then select an ERP solution that supports them.
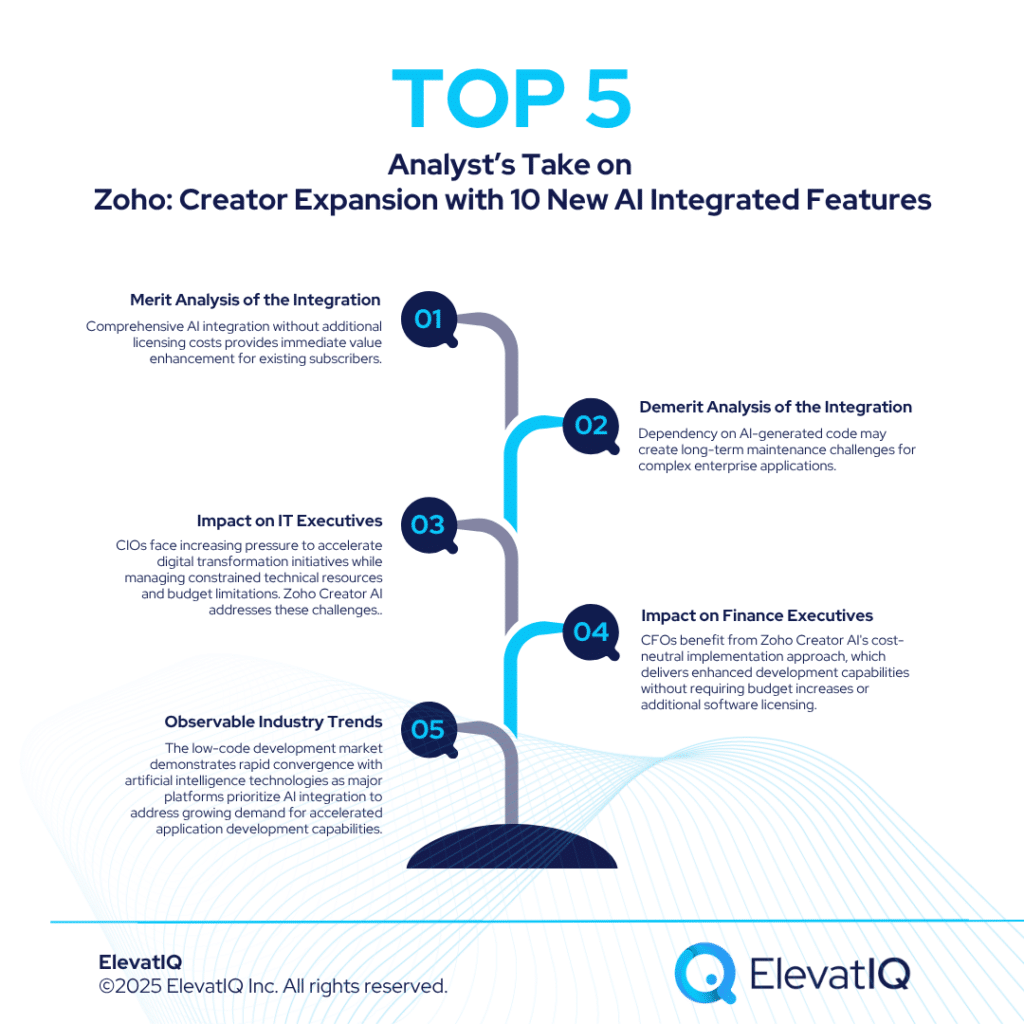
“Understanding of the standard features would help you identify the unique features for your business and prioritize your requirements”

Standard Distribution ERP Features
The main challenge with ERP implementation is that most systems seem very similar due to their standard features. However, these standard features don’t necessarily highlight the distinct characteristics of each system. By setting aside these commonalities, you can concentrate on the unique features, simplifying the comparison process and avoiding overwhelm.
The financial processes would be one example of standard features, which are likely to be the same for distributors. But here is the kicker: some distributors might require features such as consolidated invoicing depending on the type of customers and industries they might target. The account payable process may present challenges, such as accepting pre-payment or partial payments from international vendors. Not to mention Pro-forma invoices. So here are the most common standard finance features for distributors.
Finance
- Accounts Receivable (AR)
- Accounts Payable (AP)
- General Ledger (GL)
- Cash Management
- Currency Management
- Multi-entity Accounting (If you have more than one location or entity)
- Fixed Assets
- Tax Management
- Financial Reporting
- Invoice Consolidation
Inventory
- Inventory Management
- Warehouse Management
- Barcode Reading Capabilities
- Pallets or container management (if you ship or receive as a pallet or container)
- Storage Restrictions
- Cycle and Physical Counting
- Wave and Batch Picking
- Cross-docking and 3PL warehouses
- Carrier, UPS, FedEx, and 3PL integration
- NAFTA documentation (if you ship cross-border)
- Kitting (if you perform re-assembly, disassembly, or light manufacturing of your products)
- Vendor and customer inventory
- Vendor part number, cross-reference
Order Management
- Salas Order Processing
- Purchase Order Processing
- Purchase Approvals
- Customer and Vendor Management
- Pricing and Discount Management
- Sales Quotes
- Vendor Price Matrix
- Customer and Vendor Contracts
Integrations
- E-commerce integration
Critical Success Factors
The critical success factor is what makes or breaks an implementation. They are also your differentiator for your business model. Understanding critical success factors will help you identify the unique features of your business and prioritize your requirements. So you don’t run out of time, missing the features that matter.
Included out-of-the-box with some ERP products, these unique features collectively are also called industry-specific features. Integration and ecosystem for your specific micro-industry are what differentiate ERP products.
“Your least risky option would be to find an industry-specific ERP product that is designed for distributors.”
Unless you have a unique business (a very large IT team and a budget), your least risky option would be to find an industry-specific ERP product. An ERP product designed to support products and planning cycles for distributors. Otherwise, you will not only end up spending more but also increase the implementation failure risk.
The standard features form the foundation of your selection criteria (and priorities). However, once your executive team agrees on core features, unique features will demand the most attention during your evaluation process. We recommend the 80-20 rule. 80% of the time is spent on the industry-specific features, while 20% is spent on the core ERP features.
“We recommend the 80-20 rule. 80% of the time on the industry-specific features while 20% on the core ERP features.”

Conclusion
ERP evaluations are typically overwhelming because of a steep learning curve. This is especially true if you have negligible experience implementing an ERP. Also, since ERP implementations are expensive and risky, they only aggravate the pain further. The best way to soothe would be to master prioritization in the ERP context. Knowing the standard features for distribution is the first step toward your ERP evaluation journey.