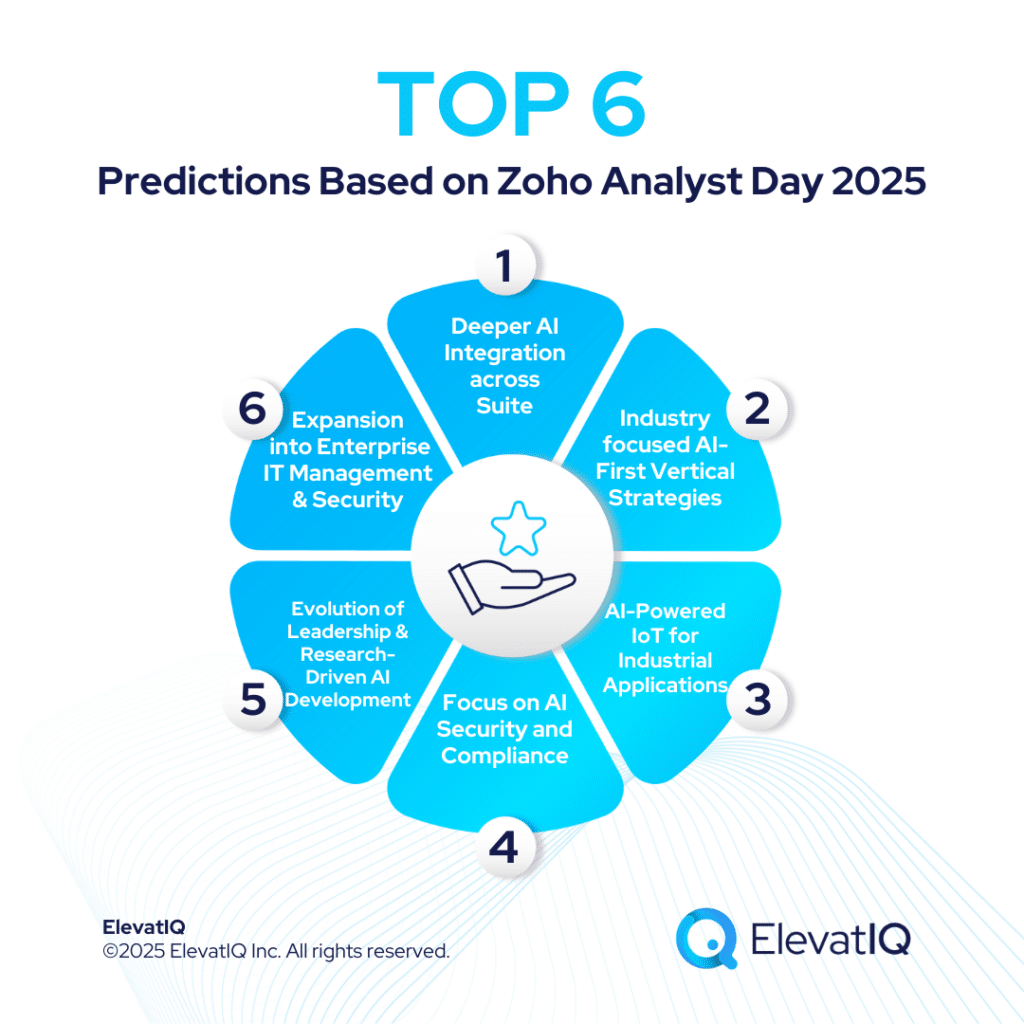
Last Updated on April 13, 2025 by Sam Gupta
Large companies, like other market segments, have specific needs that call for specialized capabilities. As they move beyond the mid-market segment, these organizations must unify their global workloads within a single system to enable cohesive governance and effective global planning. Their workflows and security needs often involve multiple approval stages and layered access controls, which may seem excessive for mid-market businesses. With global teams, diverse business models, and complex compensation structures, their RevOps processes require a heightened level of customization.
CRMs in this category are designed with robust infrastructure to support the complex workflows of larger teams. They include tools for environment migration with carefully managed access privileges and offer an intuitive customization layer to enable enterprise-scale development and implementation. Additionally, these CRMs often integrate enterprise-grade data warehouses, consolidating data from numerous systems and departments. They also feature data structures capable of accommodating any datasets required by sales and marketing teams, utilizing reverse ETL processes for seamless integration.
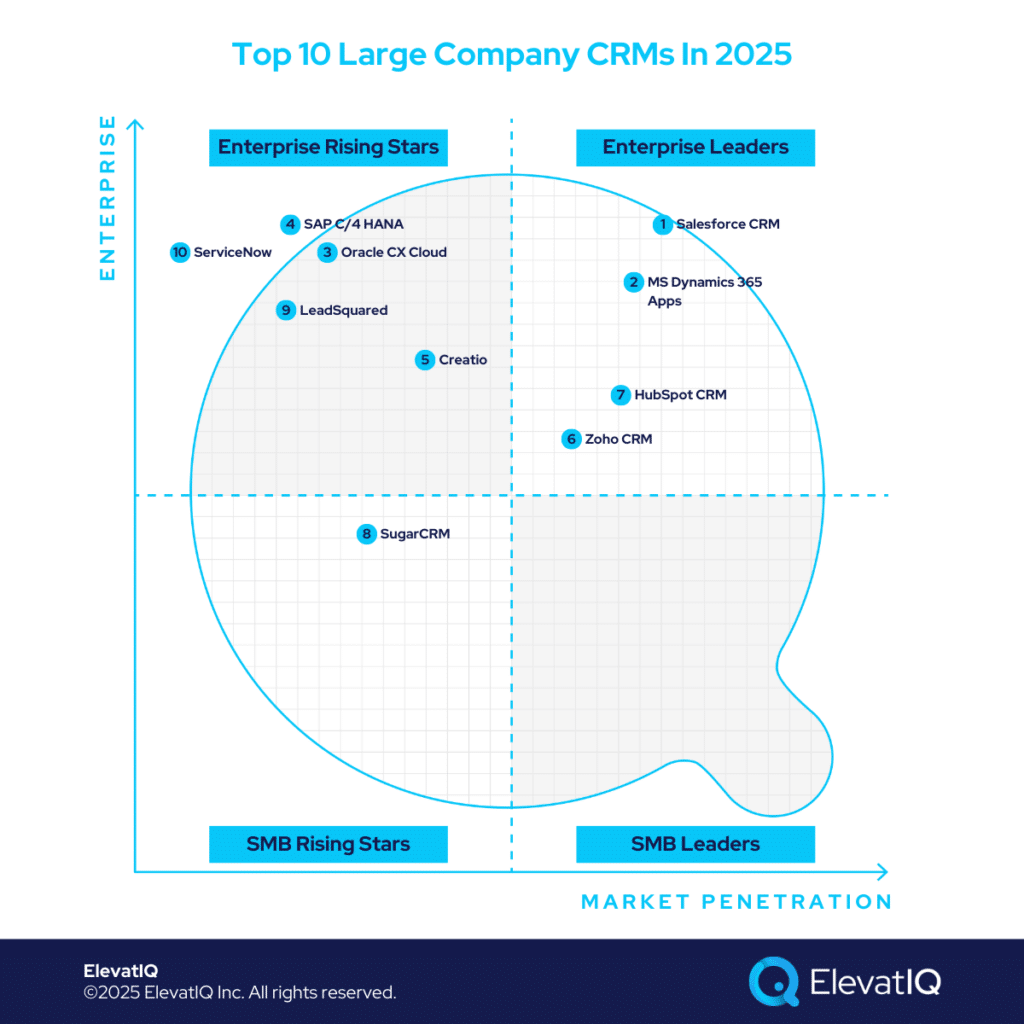
In the mid-market segment, processes like market development funds (MDF) or channel traceability may not be as critical due to lower spending levels. However, in the larger enterprise segment, these processes must be seamlessly integrated on a global scale to evaluate the impact of marketing investments and inform strategic planning. These requirements often vary by industry. For instance, consumer-focused enterprises such as financial services or telecom frequently implement extensive customizations on their core CRMs to analyze consumer behavior and craft marketing strategies accordingly. This can lead to the development of additional custom applications for data collection. Considering these specialized needs, which are the top 10 large CRMs in 2025?

Criteria
- Definition of large organizations. More than $1B in revenue or more than 1000 employees. Might be publicly traded and operating in more than ten countries. Global regulations for privacy and data sharing.
- Overall market share/# of customers. Higher market share among large companies ranks higher on our list.
- Ownership/funding. Funding through well-capitalized firms as well as public equity, drives a higher ranking on this list.
- Quality of development. Cloud-native capabilities and modern development drive higher rankings on our list.
- Community/Ecosystem. Communities with a heavier presence of large logos drive higher rankings on this list.
- Depth of native functionality for specific industries. Native industry-specific capabilities without requiring add-ons command higher rankings on this list.
- Quality of publicly available product documentation. Publicly available documentation with a productized release cycle for documentation drives higher rankings on this list.
- Larger company market share. The higher the focus on large companies, the higher the ERP system ranks on our list.
- Ability to natively support diversified business models. The ability to support diverse business models in the same product scores a higher ranking on this list.
- Acquisition strategy aligned with large companies. The more aligned the acquisitions are with the large companies, the higher it ranks on our list.
- User Reviews. User reviews concentrated with large companies command higher rankings on our list.
- Must be a CRM product. It can’t be a module of an ERP system. It must be a best-of-breed CRM system, preferably recognized in the CRM category by leading analyst firms.
10. ServiceNow
ServiceNow is not traditionally seen as a major CRM player and holds a limited market share in the CRM space. Its primary focus has been on IT-centric workflows and device or asset management processes. This makes it particularly strong in industries like telecom, where large IT departments and extensive asset management are key. ServiceNow’s strength lies in enabling sophisticated workflow automation, which is crucial in CRM operations, making it a standout choice for businesses requiring such capabilities. Hence, ServiceNow has secured the #10 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Data center and IT-centric operational processes. For data centers or IT-centric verticals, CRMs must cater to industry-specific needs, particularly in CPQ processes. These CPQ functionalities must integrate seamlessly with operational systems.
- Workflow automation. Even though most CRM systems claim similar capabilities, ServiceNow excels in managing workflows more effectively, particularly for enterprise enablement.
- Enterprise security and customizability. This includes handling comprehensive GRC processes and integrating hybrid technologies.
Weaknesses
- Not as well adopted as a CRM solution. They are not as well adapted as the CRM solution compared to other CRM systems on this list.
- Requires substantial consulting expertise to be successful. It is a highly technical system, often requiring significant consulting support for successful implementation. Unlike many other CRM systems, it may lack pre-built workflows, necessitating deep enterprise architecture and IT expertise to tailor the system effectively to an organization’s needs.
- Upstream marketing. It is going to be fairly limited as well. They are not going to be natively built as part of the platform.
9. LeadSquared
LeadSquared is a unique system with a strong industry focus. It is commonly found in sectors like public sector, education, and BSFI. While it has proven capability of handling enterprise workloads in larger market segments, its approach is highly prescriptive. For organizations operating in specific industries, such as public sector education or BFSI, where business models are stable and unlikely to evolve significantly, LeadSquared offers valuable industry-specific capabilities. These features can help streamline operations but may require a significant consulting budget to customize beyond standard CRM functionalities. Therefore, LeadSquared has secured the #9 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Customizable. While customizable, LeadSquared doesn’t offer the same level of flexibility as ServiceNow. In contrast, LeadSquared provides a more business-focused model, catering to different needs but offering less customization.
- Well adopted among large public sector and education companies. This has been proven by a large number of logos in the public sector and education companies.
- Student accounts management. LeadSquared also supports student account management workflows, which are essential for educational institutions. These workflows, including student account management, student cloud, or student information systems, need seamless integration with CRM processes.
Weaknesses
- Limited security layers. Its security model may not support as many enterprises as with larger systems designed to support the complex organizational structure of Fortune 500 companies.
- Portal stability. Users have reported issues with portal stability, so buyers are encouraged to vet these capabilities thoroughly if they are likely to be your critical needs.
- Not as well adopted as a mainstream CRM. While it’s proven in the niche industries, it’s not as diverse as other mainstream CRM systems on this list.
8. Sugar CRM
SugarCRM is heavier on downstream operational customer-facing processes. Unlike other CRMs on this list primarily designed with an upstream focus, the detailed transactional layers are especially suitable for large companies running on manufacturing ERPs. It also has unique subscription-centric capabilities, making it appealing to IT and financial services industries. While some lower enterprises may be using Sugar CRM at the divisional level, it’s not as proven in the large segment as some of the other larger options on this list, securing its spot at #8 on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- BPM for complex ad-hoc use cases. They offer a comprehensive BPM solution, positioning it as a low-code, no-code workflow system designed for handling complex, ad hoc use cases.
- Alignment with ERPs and subscription-based functionality. Its financial layers are crucial for customer-centric workflows in ERP-centric industries. Its subscription-based functionality is especially relevant for IT and financial services.
- Integrated project management module. This capability is likely more suitable for organizations where project management processes are closely integrated with sales processes rather than with accounting.
Weaknesses
- Not as diverse. SugarCRM targets very specific industries, so it might not be the best fit for large companies active with M&A cycles due to their ever-evolving business model.
- Integration and ecosystem. The integration and ecosystem are not as advanced as those offered by some other CRM systems.
- Marketing automation. While SugarCRM has marketing automation capabilities and might be friendlier for companies that might not appreciate the expensive and ever-increasing price tag of platforms such as HubSpot, making it friendlier for large companies with limited budgets.
7. HubSpot CRM
HubSpot CRM is an excellent choice for large companies using it alongside another CRM designed for operational downstream use cases. Its scope in this market segment is limited due to its inability to handle complex transactional workflows, such as sales compensation or territory planning. These workflows require robust data layers that are not part of HubSpot’s model. Hence, HubSpot CRM has secured the #7 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Marketing automation. HubSpot CRM excels in marketing automation, offering robust capabilities. If your primary goal is connectivity and traceability with the website, this system could be an excellent choice.
- Ecosystem and integration. It also offers a strong ecosystem and integration options supported by an extensive community. If certain capabilities are not available natively, the ecosystem often provides alternative solutions.
- Omnichannel tracking across channels. The biggest plus with HubSpot is its omnichannel traceability, especially across upstream marketing channels
Weaknesses
- Limited customizability. HubSpot’s customizability is somewhat limited, which can be a key drawback for this market segment. As a result, businesses may outgrow HubSpot relatively quickly.
- Limited operational capabilities. The operational capabilities are not as detailed as some of the other CRM systems.
- Not suitable for large companies unless used for marketing automation in conjunction with another CRM. HubSpot CRM may not be the best fit for this market segment unless it is being used specifically for marketing automation purposes.
6. Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM offers more operational capabilities than systems like HubSpot CRM. However, its data model lacks the tight integration found in some other CRM systems. The apps within Zoho are relatively disconnected, making it less suitable for the global consolidation of customer experience workflows across multiple geographic regions. For instance, if a company operates in several countries and aims to centralize customer-centric processes, Zoho may face limitations. Its data centers may not effectively communicate, restricting the ability to consolidate customer-centric workflows. Therefore, it has secured the #6 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Data model similar to Salesforce for building complex workflows. The data model closely resembles Salesforce, offering robust technical capabilities for creating complex workflows.
- Great capabilities with sales comp and territory planning. From a sales compensation and territory planning standpoint, Zoho offers significant capabilities. However, its less integrated data model may pose challenges in fully enabling these features.
- Integration with other Zoho apps. Zoho CRM excels in integrating with other Zoho applications. While this may be less critical in certain market segments, it becomes highly relevant if you require integration with project management tools, as Zoho offers comprehensive capabilities in this are
Weaknesses
- Not as integrated in the upstream ecosystem. The upstream ecosystem and integration are not as developed as other leading options such as HubSpot or Salesforce.
- Not as open ecosystem as HubSpot or Salesforce. Zoho is less open, making HubSpot or Salesforce a more popular recommendation among vendors due to their stronger integration with them.
- Not as well adopted among large companies. Not as well adopted among large companies, Zoho CRM is more suitable for smaller to mid-sized businesses.

5. Creatio
Creatio is a highly technical system, comparable to platforms like ServiceNow or Pega. It is well-suited for organizations with unique or unconventional sales processes requiring extensive customization. This system is ideal for large companies seeking to implement highly tailored CRM workflows. Creatio’s low-code/no-code capabilities make it a strong choice for enabling complex workflows without extensive programming, providing flexibility for businesses with specialized needs. Therefore, it has secured the #5 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Customizability. The biggest benefit of Creatio is its customizability because of its fluid technical model, which will have much higher scalability for ad-hoc processes than any business-centric business objects and platforms exposed by most systems on this list.
- Integration and ecosystem. You have greater flexibility in terms of integration options and exploring various features within their ecosystem.
- Deployment flexibility. For instance, if you’re working with a tight budget and are concerned about licensing costs, they may assist you in deploying the system on another cloud platform.
Weaknesses
- Clunky UI. Because of which, you’ll need to build all the necessary boilerplate components that are typically included in systems like HubSpot or Salesforce.
- Marketing automation not as intuitive. While they might mimic some marketing automation capabilities, it might not be as intuitive as platforms designed for marketing automation, such as HubSpot.
- Not as well adopted among large companies. Not as well adopted among large companies, Creatio is often seen as more suitable for smaller to mid-sized businesses, so it will fit large companies in the lower enterprise segment.
4. SAP C/4 HANA
SAP C/4HANA is ideal for companies operating in industries with high transaction volumes and strict regulatory requirements. For instance, in sectors like medical devices or pharmaceuticals, CPQ workflows often need to adhere to regulatory constraints. Similarly, in financial services, customer workflows involve stringent restrictions that demand robust enablement within CX processes. Smaller systems may lack the necessary layers or hierarchies to handle such complexities effectively. With SAP C/4HANA, businesses benefit from both extensive customization capabilities and advanced security layers to support and control these workflows seamlessly. Hence, it has secured the #4 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Operational workflows. The operational workflows will generally be much more comprehensive, offering deeper and more advanced capabilities for implementing sales funnel scenarios or territory planning scenarios.
- CPQ. The CPQ processes are especially friendlier for industrial companies implementing configurator-driven 3D experience, which might be challenging with other systems using an external CPQ and configurator because these processes require tightly embedded data sets among these systems.
- Complex sales comp processes and regulated product releases. The system allows the implementation of all those complex regulatory workflows, including sales compensation and territory planning workflows, effectively.
Weaknesses
- Marketing automation. The marketing automation capabilities are generally limited, so an external tool may be necessary, which is acceptable, but it won’t provide as much integration.
- Need substantial consulting support for integration. From a traceability standpoint, maintaining the required data layers and enabling those workflows will require significant consulting support for customization.
- Ecosystem and integration with marketing-centric vendors. Other systems tend to offer more seamless integration between marketing automation, CMS, and operational workflows.
3. Oracle CX Cloud
Oracle CX Cloud offers robust CRM capabilities, particularly excelling in areas like traceability for ad spend and CPQ processes. Its strengths often surpass those of SAP C/4HANA, depending on the industry. For instance, in retail-focused sectors with consumer-driven workflows, Oracle CX Cloud stands out with its superior marketing automation and customer experience features. Similarly, in telecom verticals, which often have consumerized workflows, Oracle enjoys a strong market presence. Additionally, for public sector and nonprofit organizations, Oracle provides highly integrated products that align seamlessly with CRM workflows, making it a standout choice for these industries. Hence, Oracle secures the #3 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Enterprise-grade marketing automation product. It offers an enterprise-grade marketing automation product, similar to Pardot, which is tightly integrated with its CRM workflows, providing robust marketing and automation capabilities.
- CPQ. The CPQ processes are especially friendlier for telecom and media companies because of their data model, which might be challenging with other systems using an external CPQ and configurator because these processes require tightly embedded data sets among these systems.
- Field service workflows embedded with the core CRM processes. Salesforce also offers a field service portfolio, making it suitable for industries like oil and gas or public sector verticals that require omni-channel traceability and the ability to integrate these capabilities effectively.
Weaknesses
- Upstream marketing integrations and ecosystem. The upstream marketing integration and ecosystem are comparable to those found in solutions like SAP C/4HANA.
- Requires consulting help. Maintaining the required data layers and enabling those workflows will require significant consulting support for customization.
- Change management. Since the platform is relatively large and technical, substantial change management is required to be successful.

2. MS Dynamics 365 Apps
Microsoft Dynamics 365 CE is ideal for companies seeking a highly customizable CRM system with enterprise-grade capabilities. While the platform is designed with a business-centric approach, it offers extensive flexibility for customization, allowing users to tailor the system to their specific needs. However, implementing such customizations often requires hiring skilled developers, unlike more user-friendly systems like HubSpot, where marketers can handle certain tasks independently. For organizations with complex enterprise scenarios that demand advanced customization, Microsoft Dynamics 365 CE proves to be a strong and relevant choice.
Strengths
- Power platform. This allows for building custom apps on top of the CRM and facilitating data collection for workflow automation. This capability is particularly advantageous for service-centric industries, which often require managing ad hoc workflows.
- Data model designed for complex operational use cases. Unlike other smaller systems with substantial constraints to their custom objects exposed for ease of use, MS offers a developer-friendly customization layer, allowing the overriding of most capabilities.
- Ecosystem and integrations. The ecosystem and integrations offer a wide array of add-ons and tools specifically tailored to various industries.
Weaknesses
- Upstream marketing capabilities. While stronger with CDP capabilities, the execution capabilities combining various business models are not as robust, requiring dedicated marketing automation tools for each business model.
- Upstream marketing integrations. Upstream marketing integration would be limited compared to other ecosystems for specific business models such as B2B or B2C, which are likely to be stronger with dedicated tools for those industries, such as HubSpot for B2B and Klaviyo for B2C.
- Steep learning curve. Due to its data and process model designed for enterprise workflows, the learning curve would be steep.
1. Salesforce CRM
Salesforce offers capabilities comparable to Microsoft Dynamics 365 CE, supporting complex transactional and operational models to develop advanced customer-centric workflows. It is particularly suited for large enterprises looking for a robust, enterprise-grade CRM suite to meet their intricate business requirements. Hence, Salesforce CRM has secured the #1 spot on our list of top large CRMs.
Strengths
- Pre-populated industry templates. Certain industry templates, such as those for financial services, education, and non-profits, come pre-populated within the service packs. However, challenges may arise if processes vary substantially from the service packs, as their model is generally highly constrained.
- Highly customizable. The core platform offers substantial customization capabilities, exposing the entire UI, service, or data layers for developers to override the capabilities, which is generally limited with other platforms.
- Enterprise territory planning and sales comp. Territory planning and sales comp capabilities are enterprise-grade or large, complex organizations.
Weaknesses
- Marketing automation products not as embedded with the core CRM objects. Salesforce’s marketing automation product is not as tightly integrated with its core CRM objects, which can be a significant drawback. This may be a challenge for businesses requiring a deeply connected experience with marketing automation workflows.
- Expensive. Generally, Salesforce is one of the most expensive CRMs out of all platforms due to its enterprise-grade capabilities so it might not be the best fit for large companies limited on budget.
- Data models might not be as customizable for complex relational use cases. The data model may lack the level of customizability needed for certain relational use cases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the right CRM for large enterprises is a critical decision that hinges on understanding the unique needs of the organization. Each platform on this list offers distinct strengths tailored to various industries and business models, from advanced marketing automation to intricate operational workflows. The top CRMs distinguish themselves by balancing customization, scalability, and native functionalities while addressing the complexities of global operations.
However, no CRM is without its limitations. Factors such as integration capabilities, ease of customization, and cost considerations play a significant role in determining the best fit. While this list offers valuable insights, seeking advice from an independent CRM consultant can greatly enhance the implementation success.