What is Infor? Infor has a complete product suite to meet the needs of an enterprise similar to particularly Epicor, SAP, Oracle, or Microsoft. Infor is also perhaps the only vendor after the larger ones that has the capabilities to build best-of-breed architecture akin to SAP, Oracle, and Microsoft. In fact, Infor might have deeper capabilities than Microsoft in some areas with pre-integrated best-of-breed solutions such as Infor WFM and Nexus. Infor is also the only vendor that can provide depth in several industries while not struggling with the transactional processing requirements of large accounts.
Infor LN is ideal for discrete manufacturing companies. It is successful in the upper mid-market, particularly targeting the $250M – $750M revenue range. Positioned for companies surpassing entry-level ERP systems like Acumatica, Infor CSI, or NetSuite, this solution also delivers mature capabilities for intricate manufacturing intertwined with distribution operations. Infor LN also provides a superior suite experience akin to SAP and Oracle, featuring enterprise-grade best-of-breed functionalities, including PLM, WMS, WFM, BI, and a supply chain collaboration platform.
Limitations with process-centric operations. While Infor LN excels in discrete manufacturing and offers a robust suite experience, it faces certain challenges in specific scenarios, such as process-centric operations for companies. They might also include business operations such as plastic or chemicals as part of their automotive operations. Despite limitations in broader capabilities compared to other vanilla solutions, it’s a great fit in verticals such as Automotive, Aerospace, and industrial manufacturing, seeking operational and supply chain synergies among their global entities and looking for the entire suite purpose-built for these micro-verticals.

Key Review Insights of Infor CloudSuite LN
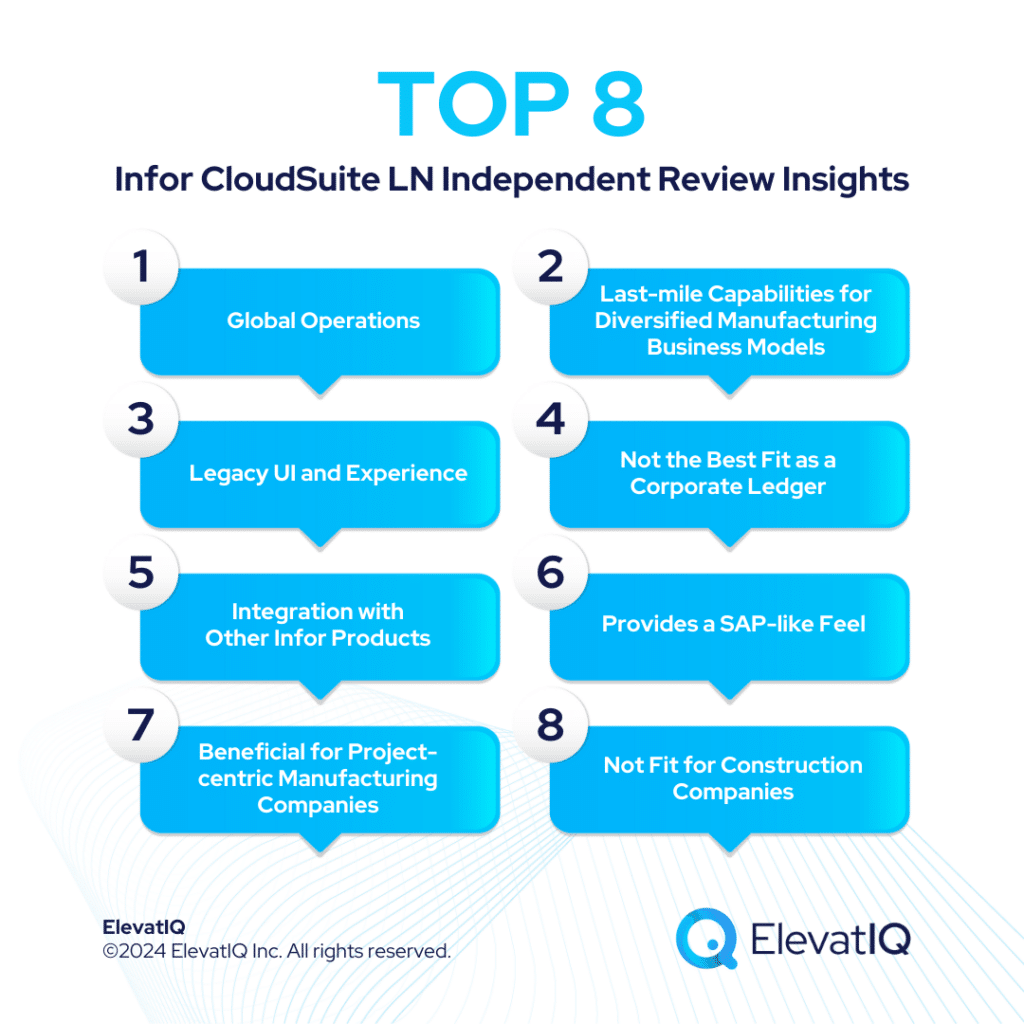
1. Global Operations
Among the solutions available in the market, Infor LN is one of the few solutions with robust financial hierarchies and also comprehensive global trade compliance functionalities embedded within its product. This can adequately support manufacturers particularly seeking to enhance their global financial and operational synergies. It is specifically designed to address the complexities of international trade and finance, providing the necessary tools to navigate diverse regulatory environments, streamline cross-border operations, and optimize global supply chain management.
2. Last-mile Capabilities for Diversified Manufacturing Business Models
Verticals such as apparel manufacturing demand deeper integration of PLM, vendor portals, and merchandising solutions to effectively manage their unique processes. These industries benefit from a seamless connection between design, production, and distribution stages, ensuring efficiency and also compliance across the entire lifecycle. Such complex manufacturing sectors require sophisticated handling of units, multiple layers of allocation management, and also stringent international trade compliance. Thus, the capabilities in Infor LN help manage the intricate logistics, inventory control, and regulatory adherence inherent in complex manufacturing environments.
3. Legacy UI and Experience
Infor LN is considered a legacy solution primarily due to its outdated user interface and overall user experience. Unlike modern ERP systems, it lacks several key cloud-native capabilities. For instance, it does not offer a comprehensive universal search function, which limits users’ ability to find information across the system quickly. Additionally, its support for mobile experiences is limited, meaning that users may find it challenging to access and interact with the ERP system effectively on mobile devices. These shortcomings can hinder the efficiency and flexibility expected from contemporary ERP solutions.
4. Not the Best Fit as a Corporate Ledger
Infor LN might not be the ERP system for private equity firms and holding companies that need robust global solutions particularly paired with tier-2 solutions at the subsidiary level. Also, its strengths do not align well with the requirements of these entities, which often need highly integrated and scalable systems to manage complex financial structures and global operations. As a result, Infor LN may fall short in meeting the comprehensive needs of these organizations, making it less suitable as a corporate ledger in such contexts.
5. Integration with Other Infor Products
Infor Cloud Suite comprises various products, including Infor SCM, WFM, PLM, and also Burst. These offerings cater to larger multinational companies with complex supply chain networks, providing more robust capabilities than those found in smaller mid-market solutions. For example, Infor WFM excels in managing unionized labor and handling specific reporting and payment requirements. The PLM and SCM systems, as add-ons to the LN product, deliver deep industry-specific capabilities, particularly suited for the automotive and aerospace sectors. Additionally, Infor’s acquisition of Nexus has significantly enhanced the capabilities of its SCM product in global supply chain planning. Previously, Infor’s major gap was in the MES solution, which they have successfully addressed through the acquisition of Lighthouse, resulting in a much stronger MES offering overall.
6. Provides a SAP-like Feel
The integration of Infor LN with MES enhances its capabilities, particularly in complex manufacturing processes. The Gantt view from the project perspective, similar to SAP’s Gantt chart, highlights Infor LN’s robust SAP-like feel, with features such as code configuration, costing, and production management. Infor LN is particularly designed for intricate manufacturing processes that can take months or even years to complete, necessitating meticulous tracking of changes and payments.
7. Beneficial for Project-centric Manufacturing Companies
Infor LN offers significant benefits for project-centric manufacturing companies. The system provides integrated project management, covering everything from engineering to production, estimation and bidding, accounting, procurement, and service. Its robust project scheduling feature encompasses every aspect of a project and is particularly advantageous for industries like aerospace and automotive. Infor LN distinguishes itself from other ERPs with its resource management capabilities, enabling skill-based scheduling for production or services. Additionally, the system helps eliminate silos by providing a common platform for different teams to collaborate and identify bottlenecks.
8. Not Fit for Construction Companies
Infor LN may not be the ideal choice for construction businesses because it has limitations in managing operational aspects like the relationships between general contractors and subcontractors, RFP collaboration, the submittal process, and compliance procedures.
Key Features of Infor CloudSuite LN
Financial Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the financial management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Financial Management | Features | |
| General Ledger | The core component of Infor LN Financials, recording all transactions within the application that affect accounting. | |
| Accounts Payable | Manages and tracks sales invoices, credit notes, credit checking, credit management, customer balances, and generates interest invoices. | |
| Accounts Receivable | Handles purchase invoices and credit notes, encompassing registration, invoice matching, and supplier balance management. | |
| Cash Management | Oversees cash transactions, including payments and receipts with business partners, and supports manual postings and electronic banking for automatic payments, direct debits, and electronic bank statements. | |
| Financial Budget System | Tracks and manages budget amounts and quantities for planning, enabling overhead cost planning for cost centers and other dimensions. | |
| Cost Accounting | Delivers detailed and summarized cost analysis and allocation, tracking actual amounts and performance quantities to control costs by dimension, and calculating actual rates and surcharges. | |
| Budget Control | Tracks and manages budget-related transactions, monitoring financial health in real-time to prevent deficits, and integrates accounting and budgeting functions into business processes. |
Manufacturing Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the manufacturing management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Manufacturing Management | Features | |
| BOM | Lists component items of a manufactured product, detailing each item’s position, required quantity, and expiry date. | |
| Routing | Organizes manufacturing operations by linking them to work centers or machines, offering flexibility with standard, item-specific, network, and order quantity-dependent options. | |
| Assembly Planning | Facilitates planning and generating assembly orders for product variants in high-volume, complex, mixed-model flow production environments. | |
| Assembly Control | Supports companies producing complex product variants in flow assembly lines, adaptable for low-volume environments with order-specific transaction handling. | |
| Repetitive Manufacturing | Manages production in repetitive manufacturing environments with high-volume production across multiple models. | |
| Job Shop Control | Oversees production order creation, planning, and execution procedures. | |
| Project Control | Handles customer-order-driven production, supporting various project and item types with capabilities for estimating, planning, and manufacturing customized and make-to-order items. | |
| Product Configurator | Defines product models and generates BOMs/routings based on selected features and options, ensuring buildable products through constraint enforcement at sales time. | |
| Product Classification | Establishes a coding system for item data and facilitates efficient data retrieval and classification of new and existing items based on defined criteria. | |
| Manufacturing Control | Includes dashboards and stores as-built structures of production and assembly orders for monitoring and analysis. |
Sales Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the sales management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Sales Management | Features | |
| Sales Orders | Facilitates the sale and delivery of items or services to a sold-to business partner under specified terms. Orders originate from various sources such as contracts, quotations, EDI, and planning, allowing for creation and modification within the Sales module. | |
| Sales Quotations | Provides detailed information to help a business partner make purchasing decisions. They can be created in response to RFQs or used as sales tools to initiate engagements with potential partners. | |
| Sales Contracts | Formalizes agreements for delivering specific goods to a business partner. These agreements include detailed terms and conditions, delivery schedules, pricing, and discounts, and can be categorized into normal and special contracts. | |
| Sales Schedules | Supports long-term sales projects with frequent deliveries, offering detailed specifications for delivery dates and times. | |
| Margin Control | Manages margins for standard item sales orders and quotations. It ensures that if the net price exceeds defined margins, appropriate actions are taken to maintain profitability. | |
| Consumption Handling | Involves the issue of consigned items from the warehouse to customers for their use in sales and production activities. | |
| Retrobilling | Allows for the re-invoicing of previously shipped items when price changes occur after the renegotiation date. | |
| Commissions and Rebates | Incentivize sales performance by rewarding sales-related achievements. |
Procurement Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the procurement management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Procurement Management | Features | |
| Purchase Requisitions | Allows non-purchasing users to request materials or services without needing full knowledge of purchasing processes, even for new items or suppliers. | |
| Requests for Quotations | Sends RFQs to bidders for goods procurement, specifying items, quantities, and receipt dates, with responses compared, negotiated, and also converted to purchase orders or contracts. | |
| Purchase Orders | Creates and modifies orders for goods and services, forming a legal obligation upon confirmation, and also distributing order information across various company departments. | |
| Purchase Contracts | Registers agreements with suppliers particularly for the delivery of specific goods. | |
| Purchase Schedules | Provides a detailed timetable for material supply, supporting long-term purchasing with frequent deliveries, and also offering full visibility and time-phased material requirements. | |
| Purchase Vendor Rating | Measures vendor performance using objective and subjective criteria to particularly determine the best supplier for raw materials and supplies. |
Warehouse Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the warehouse management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Warehouse Management | Features | |
| Inventory Planning and Analysis | Reviews planned inventory transactions and also manages inventory commitments efficiently. | |
| Warehouse Orders | Manages item receipt, issuance, transfers, inspections, inventory adjustments, cycle counts, and also kit assembly. | |
| Inventory Change Orders | Facilitates item ownership changes, inventory allocation, and also cost peg transfers. | |
| Cross-docking | Streamlines goods flow from receiving to shipping docks directly particularly for efficient logistics management. | |
| Direct Material Supply | Goods move from suppliers or manufacturing directly to consumption points via automatic, interactive, or manual processes. | |
| Handling Units | Helps utilize handling units linked particularly to warehouse movements such as orders, receipts, inspections, and shipments. | |
| Receipts and Inspections | Warehouse receipts record physical goods acceptance, detailing quantities, dates, packing slips, and also inspection results. | |
| Shipments | Documents goods transport specifics particularly including items, destinations, dates, times, and routes. | |
| Quarantine Inventory | Manages rejected goods in quarantine to decide particularly on disposition options like scrap, rework, or return. | |
| Cycle Counting and Adjustment Orders | Conducts manual inventory counts and adjusts LN records at specific stockpoints. | |
| Inventory Reporting | Generates comprehensive reports and inquiries on inventory, transactions, as well as item issues by period and warehouse. | |
| Inventory Costing | Analyzes inventory with methods like ABC analysis, slow-moving item assessments, as well as valuation techniques. |
Freight Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the freight management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Freight Management | Features | |
| Freight Order Control | Manages and tracks freight orders throughout their lifecycle, particularly from planning to execution and subcontracting. | |
| Freight Planning | Plans inbound and outbound transportation to ensure cost-effective and timely goods movement, also with overviews of transport capacity. |
Project Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the project management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Project Management | Features | |
| Contract Management | Manages and retrieves contract-related tasks and data, particularly including contract type, invoice type, amount, and budgeting method. | |
| Estimate | Creates and simulates project estimates to secure contracts, also with the option to generate bids from accepted estimates. | |
| Project Budget | Manages and retrieves budget-related tasks and data, particularly including various budget types and cost analysis. | |
| Requirements Planning | Generates planned orders for materials, equipment, and also subcontracting based on data from Budgeting and Planning modules. | |
| Project Progress | Measures, records, and also monitors project progress. | |
| Project Accounting | Creates and maintains transactions particularly for costs, commitments, revenues, and financial results. |
Service Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the service management module of Infor CloudSuite LN, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Service Management | Features | |
| Configuration Management | Manages multi-level asset configurations, defining warranties, and also generating service configurations from various sources, with a graphical overview. | |
| Contract Management | Manages service contracts, creating quotes, defining terms, and also invoicing by installments for steady revenue streams. | |
| Service Quotations | Creates and manages service order quotations, planning, monitoring, processing, and also invoicing, including on-site repairs and upgrades. | |
| Preventive Maintenance | Uses preventive maintenance for particularly customer or internal assets, with activities covered by service contracts and controlled automatically. | |
| Territory Planning | Optimizes travel by simulating and assigning engineers to territories, balancing required and also available capacities. | |
| Group Planning | Assigns service engineers or departments to work orders or planned activities, preparing groups for resource assignment. | |
| Field Service | Manages service orders for on-site repairs, replacements, or upgrades, particularly including various order types and work scheduling. | |
| Depot Repair | Handles depot-related logistics and financial transactions, particularly including Return Material Authorization (RMA). | |
| Service Inspection | Registers inspections, creates maintenance notifications, and also transfers them for follow-up actions. | |
| Subcontract Management | Defines and manages subcontract agreements, aligning them with main service contracts, particularly including call dispatching and reminders. | |
| Activity Management | Defines and maintains predefined maintenance activities based on documents and reports to also support planning and execution. |
Pros and Cons of Infor CloudSuite LN
| Pros | Cons |
| Ideal for upper mid-market companies or as subsidiary solutions in a two-tier setting for private equity-owned or holding companies. | The limited focus on certain business models poses the risk of requiring other ERP systems to support complex and diverse business operations such as process manufacturing or metal-centric A&D companies. |
| It can support the most complex manufacturing business models, WBS-centric manufacturing, or support for attributes with MRP planning. | Private equity and holding companies requiring global solutions particularly with a tier-2 solution at the subsidiary level might not be the best use of Infor LN’s strengths. |
| Most tools that make-to manufacturer would require, such as HCM, PLM, data lake, ERP, WMS, TMS, and advanced supply chain planning, are all pre-integrated with LN. | Infor LN is a legacy solution with limited cloud-native capabilities such as universal search, mobile experience, etc |
| While most smaller solutions might require ad-hoc arrangements for global financial operations, both have them natively built. | The consulting base and marketplaces are virtually non-existent for Infor LN. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Infor LN stands out as a robust solution for discrete manufacturing companies, particularly those in the upper mid-market. Its comprehensive suite of functionalities, including advanced PLM, WMS, WFM, and also BI, offers a SAP-like experience tailored to the needs of complex manufacturing and distribution operations. With strong global trade compliance and financial management capabilities, Infor LN is well-suited to support manufacturers particularly seeking to optimize their international operations and navigate diverse regulatory environments. The system’s project-centric features are particularly beneficial for industries like aerospace and automotive, providing integrated project management and resource scheduling that enhance efficiency and collaboration.
However, Infor LN does face certain limitations, especially in areas requiring process-centric operations or modern ERP functionalities. Its legacy user interface and limited cloud-native capabilities, such as universal search and mobile access, can hinder the overall user experience. Additionally, Infor LN may not be the best fit for private equity firms or holding companies needing highly integrated and scalable systems for managing complex financial structures and global operations. Despite these drawbacks, Infor LN’s depth in manufacturing and industry-specific functionalities makes it a valuable asset for companies with intricate and project-based business models, providing a solid foundation for efficient and streamlined operations. Also, companies may benefit from consulting an independent ERP consultant who can provide valuable insights and assessments to determine if Infor CloudSuite LN aligns seamlessly with their organizational requirements.