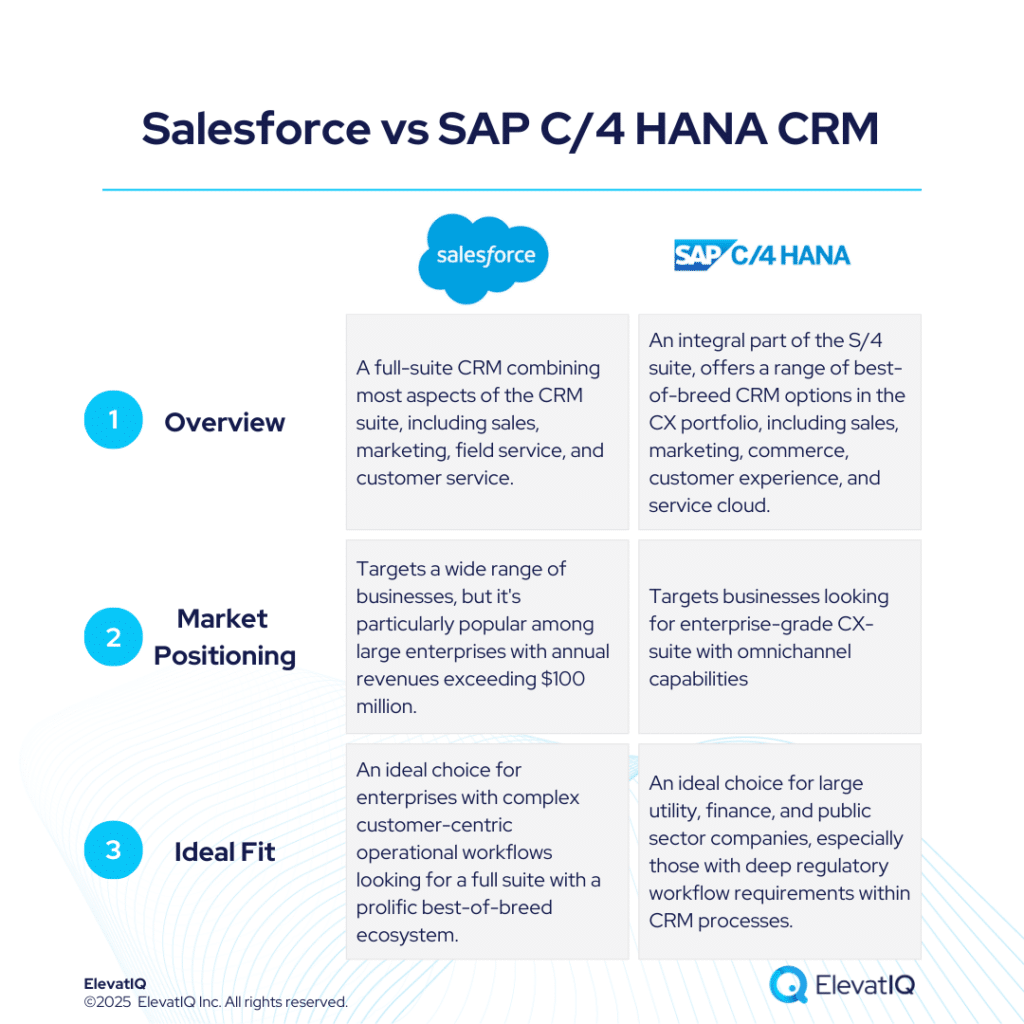
SAP S/4 HANA is SAP’s flagship product and one of the few viable options for large enterprises, especially those with the transactional demands of Fortune 500. Compared to its counterpart, ECC, SAP S/4 HANA features a modern architecture that merges best-of-breed capabilities with enterprise-grade SaaS offerings, while maintaining tightly integrated ERP processes at its core. This suite includes leading solutions like SAP SuccessFactors for HCM, SAP Hybris for commerce, SAP EWM for WMS, Ariba for P2P, and also Concur for T&E management. Unlike other market solutions that treat these processes as ERP modules, SAP S/4 HANA ensures seamless adoption and delivers a superior omnichannel experience, particularly important for HR processes across various devices.
SAP S/4 HANA is also favored by enterprise-grade companies for its ability to handle large transaction volumes and meet stringent governance and traceability requirements. It is particularly well-suited for product-centric enterprises needing mature capabilities such as MRP and allocation. Additionally, for enterprises needing advanced eCommerce platforms with components like CDP or CPQ systems, SAP S/4 HANA offers essential functionalities. It is also highly effective for multinational companies needing unified databases for easier reconciliation.
However, SAP S/4 HANA may not be ideal for companies transitioning from smaller ERP systems or QuickBooks, as it requires a certain level of IT maturity for successful implementation. Although it has deep ERP capabilities, the suite experience might fall short compared to prescriptive platforms like Infor LN or QAD. Moreover, reliance on third-party add-ons for integrations can lead to vendor conflicts, increased budgets, and higher implementation risks. Despite its cloud advancements, SAP still trails behind some competitors. Nonetheless, the following sections will delve into the key features, advantages, and drawbacks of SAP S/4 HANA.
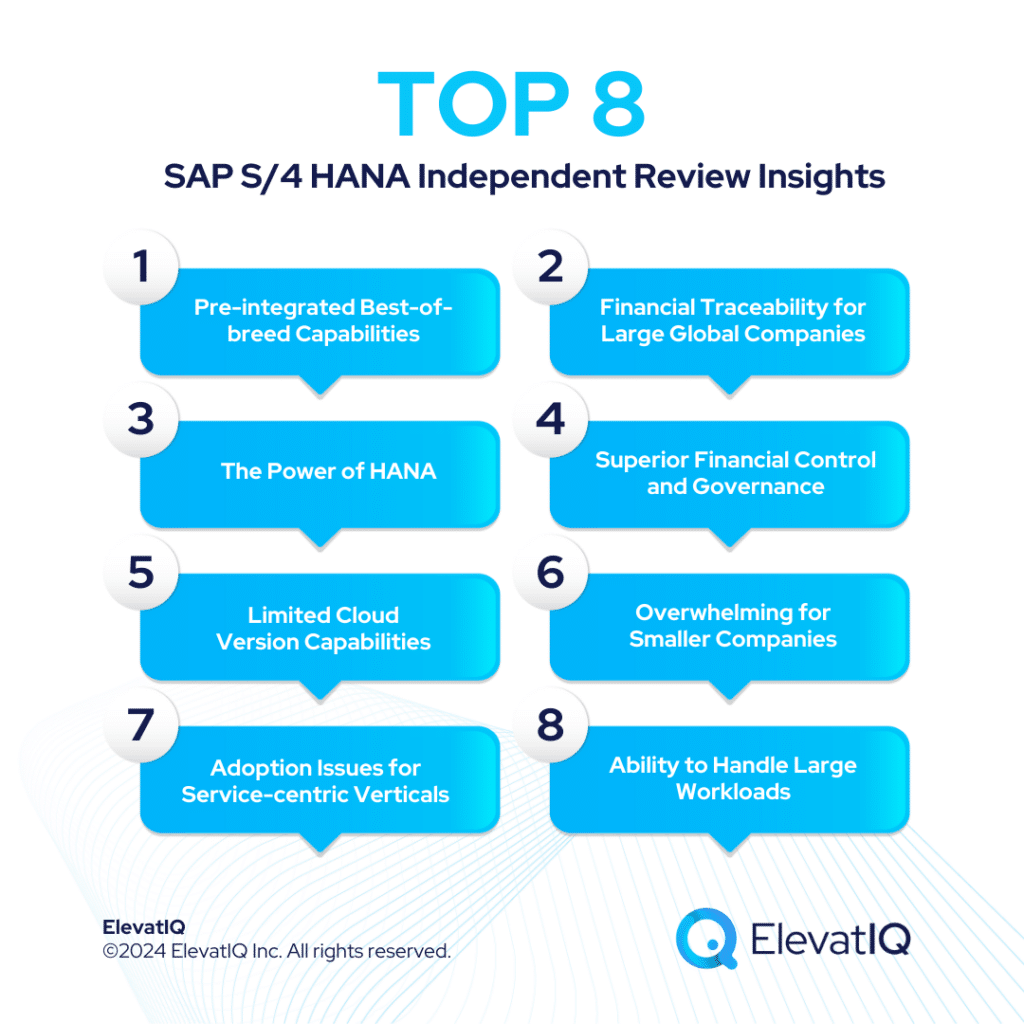

Key Review Insights of SAP S/4 HANA
1. Pre-integrated Best-of-breed Capabilities
The best-of-breed software, such as SAP Commerce Cloud, Hybris, Concur, SuccessFactors, and EWM, is pre-integrated with SAP S/4 HANA, potentially saving millions of dollars with integration. The best-of-breed architecture can also support the business model of large distributors, irrespective of whether they are a traditional distributor or a combination of 3PL, which typically has a different warehouse and TMS architecture than traditional distributors.
2. Financial Traceability for Large Global Companies
It is one of the most intuitive ERP products for particularly such complex operations with its transactional maps capabilities built with the products, making debugging complex financial enterprises easier. SAP S/4 HANA is also capable of building end-to-end traceability of SOX compliance workflows with every document and transaction, which is often required by large complex financial organizations.
3. The Power of HANA
Because of the power of HANA, SAP S/4 HANA can process very complex MRP runs with product models containing millions of serial numbers and SKUs and the ability to process millions of costing and scheduling entries much faster than most ERP systems.
4. Superior Financial Control and Governance
Some of the capabilities include several financial hierarchies particularly to support complex, global organizations without requiring ad-hoc arrangements for global traceability or consolidations. Fortune 500 organizations with shared service models spread in multiple countries would appreciate the financial traceability that is built at the document level.
5. Limited Cloud Version Capabilities
The cloud version is behind with development particularly in comparison to the on-prem variant. Equally limited are the marketplace options compared to other competing solutions. Despite advanced financial traceability and technical capabilities, the functional capabilities are not as rich as with its on-prem version.
6. Overwhelming for Smaller Companies
The complex workflows built to support the processes of large, complex organizations may particularly overwhelm organizations seeking simpler solutions without unnecessary processes and approval flows.
7. Adoption Issues for Service-centric Verticals
Unlike product-centric organizations, service-centric verticals don’t have as financially embedded transactions, causing efficiency issues with teams if their workflows were to be managed inside complex ERP systems such as SAP S/4 HANA.
8. Ability to Handle Large Workloads
Our simple test of HANA’s capabilities with 100K serialized goods receipt found it to be faster than most systems out there. SAP S/4 HANA could process it in under 22 seconds, while Oracle cloud ERP took more than 18 mins for the same test. This is especially friendly for businesses with complex products aiming to run their consolidated global MRP runs in one system.
Key Features of SAP S/4 HANA
Financial Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the financial management module of SAP S/4 HANA, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Financial Management | Features | |
| Overhead Cost Accounting | Records journal entries, tracks costs by cost center, and also defines each center’s output through activity types. | |
| Product Cost Management | Analyzes costs at each stage of the value chain using an integrated system, and also aligns quantity flow from logistics with financial values. | |
| Profitability and Cost Analysis | Helps assess the profitability of the market segments and cost objects and also provides real-time contribution margins. | |
| Predictive Accounting | Utilizes data from sales orders to forecast future outcomes before actual journal entries are made. | |
| Investment Management | Facilitates planning, budgeting, commitment tracking, and also monitoring actual costs. | |
| General Ledger | Performs the necessary tasks of financial accounting. | |
| Asset Accounting | Manages and monitors tangible fixed assets. | |
| Revenue and Cost Accounting | Identifies revenues and also calculates contract liabilities and contract assets. | |
| Inventory Accounting | Helps assess and oversee the material and work-in-process inventory according to legal regulations. | |
| Accounts Payable | Submits the invoices created in purchasing. | |
| Accounts Receivable | Records and manages accounts receivable data of all customers. | |
| Settlement Management | Encompasses several settlement processes, particularly including those integrated into the order-to-cash cycle or procure-to-pay scenarios. |
Human Resources
In this section, we explore and analyze the human resources module of SAP S/4 HANA, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Human Resources | Features | |
| Organizational Structure Management | Helps create, maintain, and also restructure organizational structures. | |
| Time Sheet Management | Helps record and manage time data of all employees. | |
| Integration with External HR System | Supports integration with SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central to duplicate employee and organizational data. |
Manufacturing Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the manufacturing management module of SAP S/4 HANA, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Manufacturing Management | Features | |
| Just-in-Time Supply to Production | Enables material replenishment for manufacturing and assembly from either an internal location or an external supplier. | |
| Just-in-Time Supply to Customer | Covers JIT processes from the perspective of the supplier. | |
| Production BOM Management | Manages bills of material, assigns them to the plants, monitors multilevel BOM assignments, and can also find BOM for a component. | |
| Master Recipe/Routing Management | Enables modeling of the capabilities of the manufacturing equipment and also monitors their performance. | |
| Material Requirements Planning | Helps ensure the availability of materials and perform basic production planning. | |
| Production Scheduling | Helps change the production plan particularly according to the capacity shortage, and demands in time and quantity. | |
| Demand-driven Replenishment | Helps plan and also manage supply chain based on customer demand. | |
| Production Control and Execution | Helps dispatch production operations and also make all necessary preparations for production execution. | |
| Repetitive Manufacturing | Helps plan and organize production particularly in repetitive manufacturing and flow manufacturing environments. | |
| Kanban | Helps manage production and also material flow based on physical material stock in production. | |
| Quality Planning, Inspection, and Improvement | Helps ensure the quality of the products and processes, also prepares and executes quality inspections, and provides tools to improve them. | |
| Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul | Supports processes for particularly maintenance and repair during the product lifecycle. | |
| Pegging and Distribution for Project Manufacturing | Helps enhance project manufacturing efficiency in an engineer-to-order setting particularly by utilizing shared common materials across various projects. |
Sourcing and Procurement
In this section, we explore and analyze the sourcing and procurement module of SAP S/4 HANA, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Sourcing and Procurement | Features | |
| Real-time Reporting and Monitoring | Provides a set of actionable cards: both operational and also analytical which can be navigated to find detailed information and resolve. | |
| Spend Visibility | Visualizes the daily work in different charts and by criteria. | |
| Purchase Contract Management | Helps manage the long-term purchase contracts with suppliers particularly regarding the supply of materials or performance of services. | |
| Self-service Requisitioning | Helps create, manage, and also track the orders. | |
| Requirement Processing | Assists in acquiring a specific quantity of a material or service particularly to ensure availability at a designated time. | |
| Purchase Order Processing | Assists in instructing an external supplier to deliver a specific quantity of a material or service particularly to ensure availability at a designated time. | |
| Service Purchasing and Recording | Manage and record the purchase orders of external service providers. | |
| Invoice Management | Helps with processing purchase orders and goods receipt, along with integration with business networks to collaborate with suppliers. | |
| Supplier Management | Helps with supplier classification, segmentation, and evaluation. |
Supply Chain Management
In this section, we explore and analyze the supply chain management module of SAP S/4 HANA, shedding light particularly on their features and capabilities.
| Supply Chain Management | Features | |
| Goods Movement | Helps in managing goods issues, goods receipt, and reservations. | |
| Inventory Analytics and Control | Helps in evaluating and displaying stock information along with checking analytics reports. | |
| Physical Inventory | Helps in recording the actual stock levels of materials. | |
| Returnable Packaging Logistics | Helps with the exchange of reusable packaging materials with business partners. | |
| Empties Management | Helps in mapping the administration and deposit requirements of returnable packages. | |
| Delivery Management | Helps in managing the inbound and outbound deliveries. | |
| Transportation Management | Helps in supporting the entire transportation chain. | |
| Warehouse Management | Helps maintain optimized warehouse operations by supporting and managing real-time transparency into material movements. | |
| Stock Room Management | Provides capabilities for warehouses with low complexity. | |
| Available to Promise | Helps in configuring, executing, and monitoring the availability checks. | |
| Business Process Scheduling | Helps plan dates for different logistics activities involved in various business processes. |
Pros and Cons of SAP S/4 HANA
| Pros | Cons |
| Large complex financial organizations require end-to-end traceability of SOX compliance workflows, also built with each document and transaction with SAP S/4 HANA. | The data model is designed for large, complex organizations, and also overwhelming for smaller organizations outgrowing QuickBooks or smaller ERP systems. |
| The best-of-breed software, such as SAP Commerce Cloud, Hybris, Concur, SuccessFactors, and EWM, is pre-integrated with the SAP S/4 HANA, potentially saving millions of dollars with integration. | The pre-baked last-mile capabilities specific to micro-industries might be limited, requiring either development or add-ons on top of the core solution. |
| Enterprise Product Designed for Product-centric Companies. The item master, product model, and warehouse architecture can accommodate the needs of most manufacturing business models. | Despite advanced technical capabilities such as AI, the last mile industry capabilities and operational functionality are limited in their cloud ERP version. |
| SAP S/4 HANA could process more than 100K serialized goods receipts within 22 secs, while Oracle Cloud ERP took more than 18 mins for the same test. | The third-party integration options, such as integration with eCommerce platforms, POS systems, channel connectivity, etc, may require substantial development efforts. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, SAP remains a dominant force in the ERP market, particularly favored by enterprise-grade companies due to its robust SAP S/4 HANA offering. This solution integrates leading products like SAP SuccessFactors, SAP Hybris, SAP EWM, Ariba, and Concur, particularly catering to diverse enterprise needs. With strengths in handling large transaction volumes, governance, and traceability requirements, SAP S/4 HANA excels in product-centric enterprises, offering mature capabilities such as MRP and allocation.
However, it may pose challenges for smaller organizations lacking sufficient IT maturity, and SAP’s SMB presence faces uncertainties. Despite notable progress in cloud offerings, SAP trails competitors in this arena. Nevertheless, the key review insights highlight the pre-integrated best-of-breed capabilities, financial traceability, and scalability for large workloads offered by SAP S/4 HANA. While SAP S/4 HANA presents compelling advantages for enterprise-grade companies with complex operational needs, smaller organizations and those prioritizing cloud solutions may find it less suitable. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for businesses considering SAP S/4 HANA as their ERP solution. Also, companies may benefit from consulting an independent ERP consultant who can provide valuable insights and assessments to determine if SAP S/4 HANA aligns seamlessly with their organizational requirements.