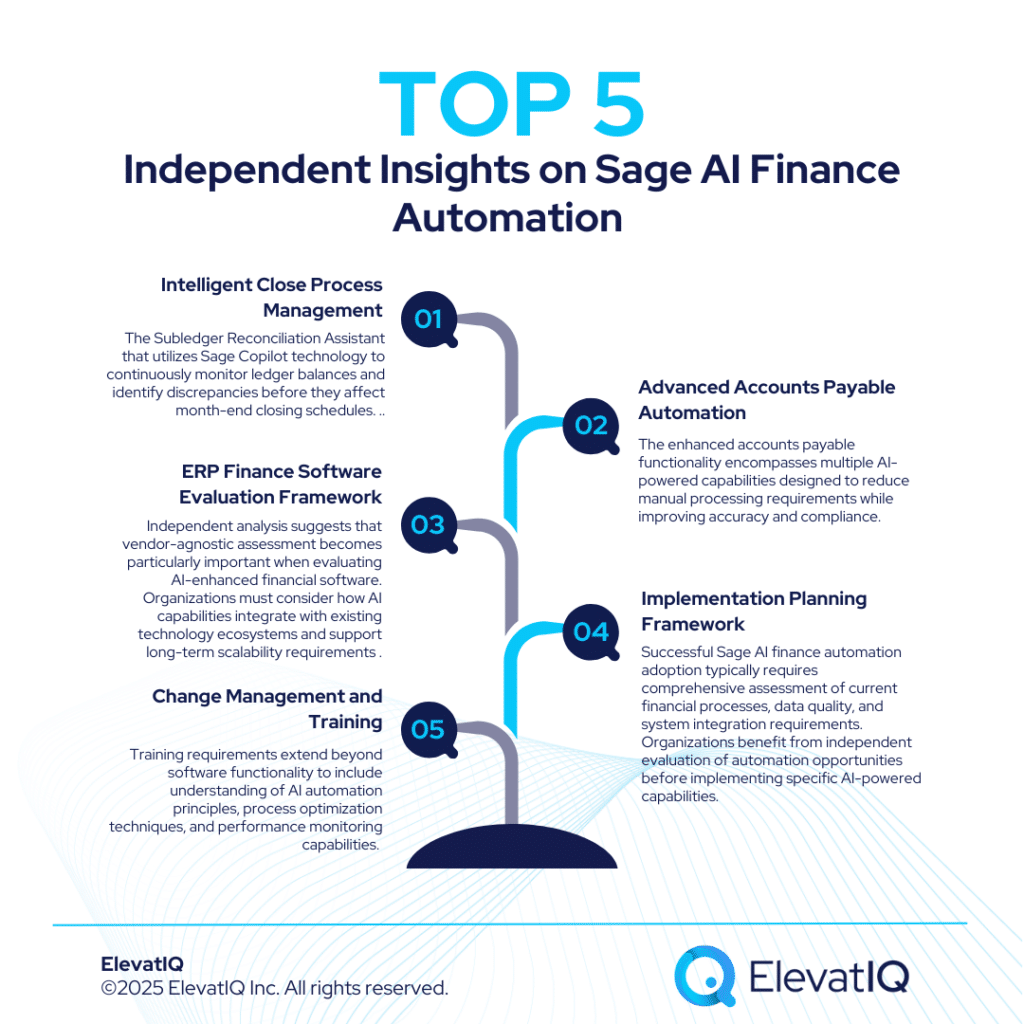
Acumatica R2 2025 Features: An Independent Review
Acumatica R2 2025 features mark the second major update in the company’s biannual release cycle. Designed to improve usability, strengthen automation, and enhance industry-specific workflows, this release reflects Acumatica’s continued focus on putting people at the center of enterprise technology. While many organizations view ERP updates as incremental, the new version emphasizes a “human-first” approach that highlights how technology should adapt to user needs, not the other way around. This article takes a closer look at the Acumatica R2 2025 features, their business impact, potential challenges, and what enterprises should consider when evaluating whether to adopt them.
Overview of Acumatica R2 2025
Acumatica follows a predictable release cycle with two updates each year — R1 in spring and R2 in fall. The Acumatica R2 2025 features continue this cadence, reflecting the company’s strategy of delivering enhancements in smaller, more manageable increments rather than large, disruptive upgrades. The overarching theme of this release is usability. Acumatica’s “human-first leap,” as described in industry commentary, underscores that ERP systems succeed only when employees across finance, operations, sales, and supply chain can use them effectively. This philosophy translates into new user experience upgrades, workflow simplifications, and a stronger emphasis on automation.
According to Acumatica’s Chief Product Officer Ali Jani, the human-first approach emerged directly from customer feedback. When discussing AI capabilities with customers, multiple organizations responded by asking about putting humans first—a perspective that shaped the entire release strategy. The decision to frame this release around human-centered design is significant. Too often, ERP implementations fail not because of technical deficiencies, but because users find systems difficult to navigate or counterintuitive. By addressing these friction points directly, Acumatica acknowledges that the most sophisticated features deliver little value if employees cannot or will not use them consistently.

Key Acumatica R2 2025 Features
The Acumatica R2 2025 features span multiple areas of the platform, from core financials to industry editions. Below are the highlights that stand out for enterprise users.
Redesigned User Interface
One of the most notable Acumatica R2 2025 features is its completely redesigned user interface, which is now the default experience. This represents more than a cosmetic update. The new interface offers deep personalization capabilities that allow users to configure every screen, from individual fields and tabs to entire layouts, without creating IT bottlenecks. The interface empowers users with both flexibility and control. Importantly, users can revert changes easily if needed, ensuring that empowerment doesn’t lead to chaos. This approach addresses a common concern in ERP environments: giving users customization capabilities while maintaining system stability and preventing configuration sprawl.
By focusing on how employees interact with the ERP, Acumatica positions itself as a platform that prioritizes adoption and usability, which are often overlooked during ERP rollouts. The personalization features allow individuals to configure their workspace based on role-specific priorities, reducing the cognitive load on users who previously had to navigate through irrelevant information to reach their core tasks.

AI Studio: Democratizing Automation
Among the Acumatica R2 2025 features, AI Studio represents a significant advancement in making AI accessible to business users. First unveiled at Acumatica’s Summit in January 2025, AI Studio is now generally available as a configurable toolkit that empowers business users and partners to create their own automations by describing desired workflows in plain English.
This no-code approach to automation removes technical barriers that previously prevented business users from implementing process improvements. The AI Studio combines a large language model automation engine with an anomaly detection engine, allowing it to not only execute tasks but also identify insights and feed them into automated processes.
Practical applications include summarizing support ticket histories, generating detailed product descriptions, and automating complex multi-step workflows. For businesses that struggle with resource constraints, AI Studio reduces manual workloads and allows teams to focus on higher-value tasks without requiring programming expertise or IT intervention for every automation need.
Industry-Specific Enhancements
Acumatica’s sector-focused editions are a core part of its product strategy, and the Acumatica R2 2025 features include targeted improvements for industries such as construction, manufacturing, and distribution.
Construction: Project 360 Dashboard and AI-First Document Management
Construction firms gain significant capabilities through the new Project 360 Dashboard, which provides comprehensive, real-time project visibility. This centralized view helps project managers maintain oversight across multiple dimensions of project performance. The release also introduces an AI-first document management system that fundamentally changes how construction firms organize project documentation. Instead of relying on traditional folder structures, the system uses metadata tagging. When users upload files or media, the system can automatically tag documents, use AI to generate detailed descriptions, and make everything fully searchable.
This approach addresses a persistent challenge in construction project management: finding specific documents quickly. The ability to locate any document, PDF, or media file associated with a project through intelligent search saves time, reduces errors, and enables faster decision-making across every project stage. For an industry where margin pressures are constant and project complexity continues to increase, these capabilities address genuine operational challenges.
Distribution: Order Fulfillment Orchestration
Distributors benefit from Advanced Order Management featuring Order Fulfillment Orchestration, which automates warehouse selection to optimize for both speed and cost. This AI-assisted system considers multiple factors simultaneously—including inventory availability, shipping costs, and even customer preferences or sentiment about specific carriers.
This automation transforms a task that previously required hours of manual analysis into a nearly instantaneous process. Recognizing that many businesses aren’t ready to fully trust AI decision-making, Acumatica has built in an optional human review step. This balanced approach allows organizations to gain efficiency benefits while maintaining appropriate oversight. The Order Fulfillment Orchestration helps distributors meet customer expectations for faster delivery while minimizing carrying costs and shipping expenses—a balancing act that defines success in modern distribution operations.

Manufacturing: Advanced Planning and Scheduling Optimization
Manufacturers gain significant performance improvements in Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS), with processing times reduced from hours to minutes through AI optimization. This dramatic improvement in computational speed enables manufacturers to run more frequent planning scenarios and respond more quickly to changing conditions on the shop floor.
The release also introduces enhanced lot and serial traceability with metadata tagging at the lot or individual serial number level. For quality and compliance managers, this granular data provides detailed audit trails to meet regulatory requirements and reduce risk. In the event of a product recall, manufacturers can instantly identify exactly which lots are affected, protecting customers and minimizing financial and reputational damage.
These updates reflect Acumatica’s goal of aligning ERP capabilities with the practical realities of different industries. Rather than forcing businesses to adapt generic software to specialized needs, the industry editions acknowledge that construction project management differs fundamentally from discrete manufacturing or wholesale distribution.
What the Acumatica R2 2025 Features Mean for Businesses
The Acumatica R2 2025 features hold different implications depending on the audience within an organization:
- End-Users Across Functions: A more intuitive interface and the ability to personalize screens make everyday tasks less time-consuming. When software gets out of the way and lets people focus on their work rather than struggling with the tool, job satisfaction improves alongside productivity.
- CFOs and Finance Teams: Greater automation through AI Studio reduces manual reconciliation work and repetitive processes, improving accuracy in financial reporting. The ability to close books faster and with greater confidence supports better financial planning and more responsive business management.
- Operations Leaders: The redesigned user interface means faster onboarding for staff and less reliance on IT support. When employees can navigate the system intuitively and customize their own workflows, operations managers spend less time troubleshooting software issues and more time optimizing processes. This becomes particularly valuable in industries facing labor shortages or high turnover rates.
- IT Managers: Industry-specific updates and AI Studio reduce the need for custom development, lowering the burden on internal teams. Rather than building and maintaining custom modules to address industry-specific requirements or business user automation requests, IT resources can focus on integration with emerging technologies and strategic initiatives that differentiate the business.
- Project Managers (Construction): The Project 360 Dashboard and AI-first document management eliminate time wasted searching for project documents and provide real-time visibility needed for proactive decision-making.
- Supply Chain and Distribution Managers: Order Fulfillment Orchestration automates complex shipping decisions, reducing labor costs while improving delivery speed and customer satisfaction.
- Production and Quality Managers (Manufacturing): APS performance improvements enable more frequent planning cycles, while enhanced traceability provides the granular data needed for compliance and rapid response to quality issues.
Challenges to Consider Before Upgrading
While the Acumatica R2 2025 features bring measurable benefits, businesses must also prepare for potential challenges.
Data Migration Risks
Even incremental upgrades can create issues with data integrity, especially for organizations using multiple third-party integrations. Historical data may need transformation to align with new structures, and integration points require testing to ensure continued functionality. What appears to be a straightforward update can reveal unexpected data quality issues that require resolution before proceeding.
Customization Conflicts
Companies that have heavily customized their ERP environment may need additional testing to ensure compatibility. Custom code, workflows, or reports built for previous versions might behave unexpectedly with new features, requiring remediation before deployment. Organizations with extensive customizations should allocate extra time and resources for compatibility testing.
User Interface Transition
While the redesigned interface offers significant improvements, users accustomed to the previous interface will need time to adjust. The personalization capabilities, while powerful, require users to understand configuration options. Organizations should plan for an adjustment period even though the new interface is designed to be more intuitive.
AI Studio Governance
The democratization of automation through AI Studio creates new governance considerations. Organizations need policies around who can create automations, testing procedures for user-created workflows, and monitoring to ensure automations perform as intended. Without appropriate guardrails, user empowerment could lead to inconsistent processes or unexpected system behavior.
Training Needs
Usability improvements do not eliminate the need for training. Employees must understand new features to take full advantage of them. While the interface may be more intuitive, the expanded capabilities—particularly AI Studio and industry-specific enhancements—still require explanation and practice for users to develop proficiency. Underestimating training requirements is one of the most common mistakes organizations make when adopting new ERP functionality.
Change Management
Resistance to new workflows is common. Without proper communication, even positive changes can create disruptions. Employees comfortable with existing processes may view updates as unwelcome complications rather than improvements, especially if the business case for change is not clearly communicated. Effective change management begins with explaining why updates matter and how they benefit individual users, not just the organization as a whole.
What organizations should do is conduct thorough testing in a sandbox environment, review documentation, and plan structured training before rolling out the Acumatica R2 2025 features across the enterprise. Rushing ERP implementation without adequate preparation increases the risk of business disruption and user frustration.
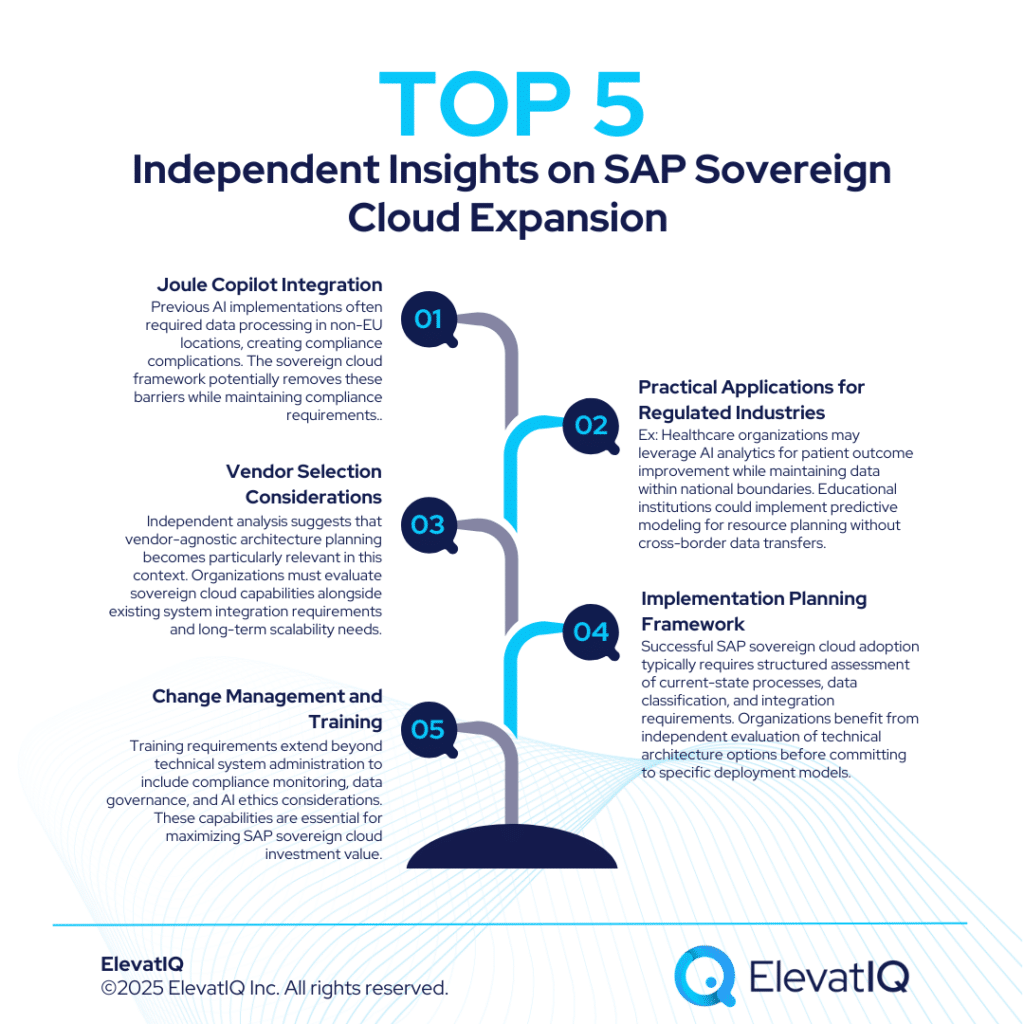
Independent Guidance for ERP Buyers
Adopting new ERP features is not just a technical decision—it’s a strategic one. The value of the Acumatica R2 2025 features depends on how well they align with broader business goals such as digital transformation, automation, and scalability.
This is where independent ERP consulting partners can make a difference. Firms like ElevatIQ specialize in helping organizations evaluate ERP updates in the context of long-term strategy. Unlike vendor-aligned consultants, independent advisors provide unbiased assessments of whether a particular feature set supports an organization’s roadmap.
For example, ElevatIQ assists businesses with:
- ERP selection and implementation roadmaps, ensuring that upgrades support growth objectives. This includes evaluating whether new features like AI Studio address genuine business needs or represent capabilities the organization is not prepared to utilize effectively. Not every feature provides equal value to every organization, and independent advisors help prioritize based on actual requirements rather than vendor marketing messages.
- Change management and user adoption strategies, minimizing disruption during transitions. Independent consultants bring experience from multiple implementations, helping organizations anticipate challenges like user interface transitions and deploy proven mitigation strategies. This cross-industry perspective often reveals solutions that internal teams, focused on their specific context, might overlook.
- Integration with adjacent systems such as CRM, supply chain, or data analytics platforms, creating a unified digital ecosystem. The value of ERP features multiplies when data flows seamlessly between systems, and independent advisors help architect these connections without vendor bias. They evaluate integration options based on technical merit and organizational fit rather than vendor partnerships or preferred solutions.
- Governance framework development for capabilities like AI Studio, helping organizations establish appropriate policies and oversight mechanisms that balance empowerment with control.
Strategic Considerations for Implementation
Organizations evaluating the Acumatica R2 2025 features should consider several strategic factors beyond the immediate technical capabilities:
- Timing matters. Does the organization have the bandwidth to implement updates effectively, or would delaying adoption until a less busy period produce better results? Sometimes waiting for the right organizational moment yields better outcomes than rushing to adopt the latest version during peak business cycles. Organizations should also consider whether they want to adopt immediately or wait for early adopters to identify any unforeseen issues.
- Phasing deserves attention. Should all features be implemented simultaneously, or would a phased approach that introduces capabilities incrementally work better? For example, organizations might deploy the new user interface first, allow users to adjust, and then introduce AI Studio capabilities once teams are comfortable with the foundational changes. Gradual rollout allows teams to adapt to changes without overwhelming users, though it requires careful planning to ensure phases build logically on one another.
- Measurement is essential. What metrics will the organization use to evaluate whether the Acumatica R2 2025 features deliver expected value? Establishing clear success criteria before implementation enables objective assessment of outcomes and helps justify the investment to stakeholders. Relevant metrics might include user adoption rates, time saved through automation, reduction in document search time, or improvement in planning cycle frequency.
- Capability readiness requires honest assessment. Not every organization is ready to fully leverage advanced capabilities like AI Studio. Organizations should evaluate whether they have the data quality, process maturity, and user sophistication needed to benefit from democratized automation. Sometimes achieving foundational capabilities delivers more value than rushing to adopt advanced features prematurely.
Conclusion
The Acumatica R2 2025 features reflect a clear shift toward usability, automation, and industry-specific optimization. For businesses already on Acumatica, the release provides opportunities to improve efficiency and empower employees. For prospective buyers, it highlights the platform’s commitment to evolving with user needs and delivering capabilities that address real operational challenges. At the same time, adopting new ERP functionality requires careful planning. Organizations must balance the appeal of new features with the realities of integration, training, and long-term digital strategy. Independent advisors such as ElevatIQ play an essential role in helping enterprises make these decisions with clarity and objectivity.
As ERP systems continue to evolve, releases like Acumatica R2 2025 serve as a reminder that technology should adapt to people—and not the other way around. The emphasis on user interface personalization, plain-English automation through AI Studio, and industry-specific enhancements demonstrates a commitment to making powerful technology accessible and practical for everyday users.
The most sophisticated features deliver value only when implemented thoughtfully, with attention to how they fit within the broader context of organizational goals, culture, and operational realities. Organizations that approach the Acumatica R2 2025 features strategically—assessing them against specific business needs rather than adopting them simply because they are new—position themselves to extract maximum value while minimizing disruption. In an era where technology changes rapidly, this measured approach to ERP evolution represents the difference between chasing trends and building sustainable competitive advantages.

FAQs
Acumatica R2 2025 Features: An Independent Review Read More »