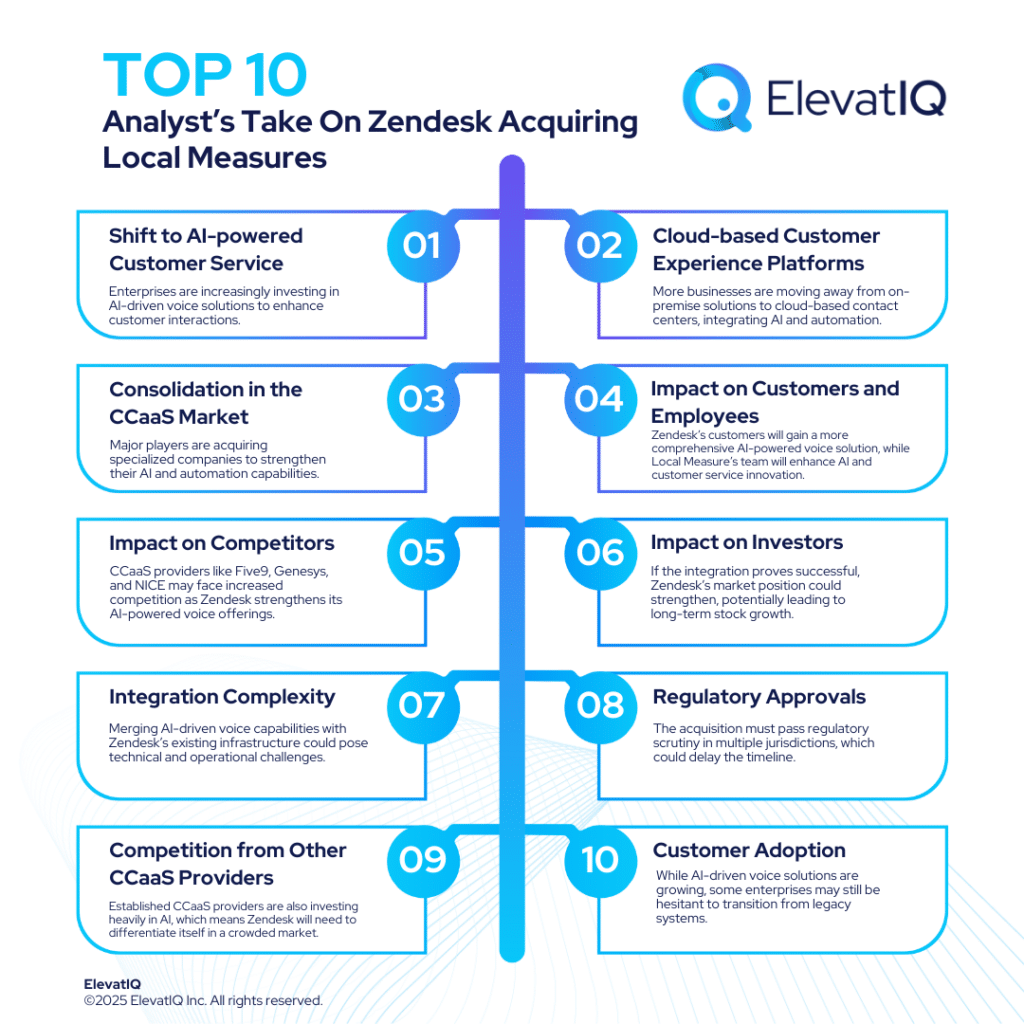
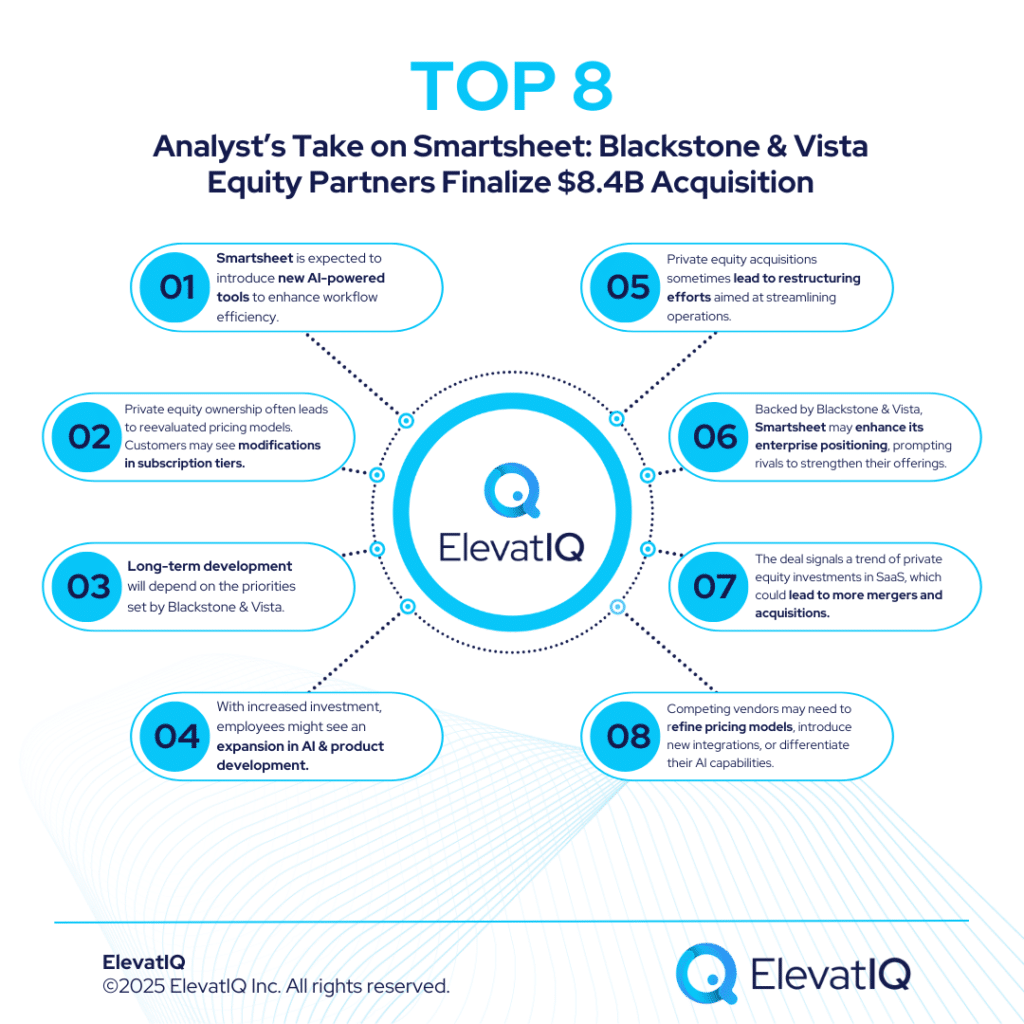
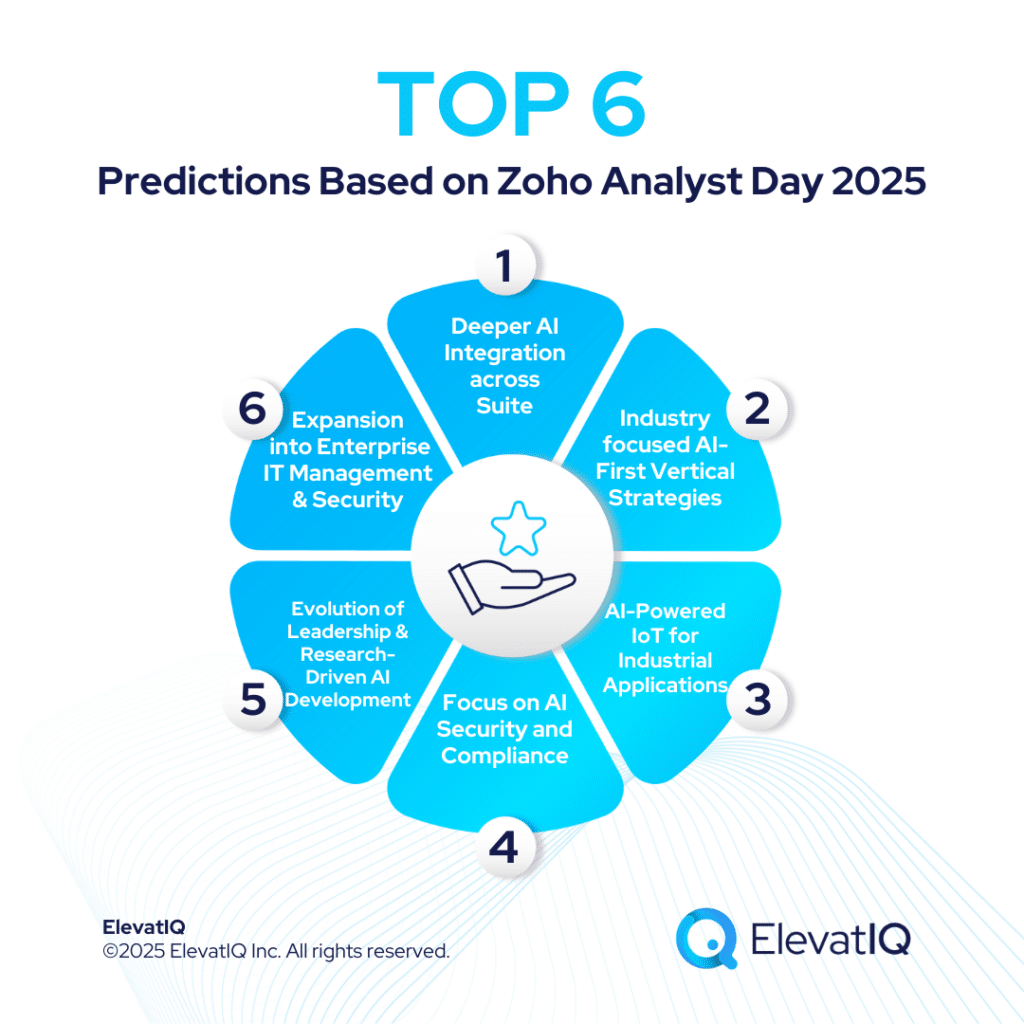
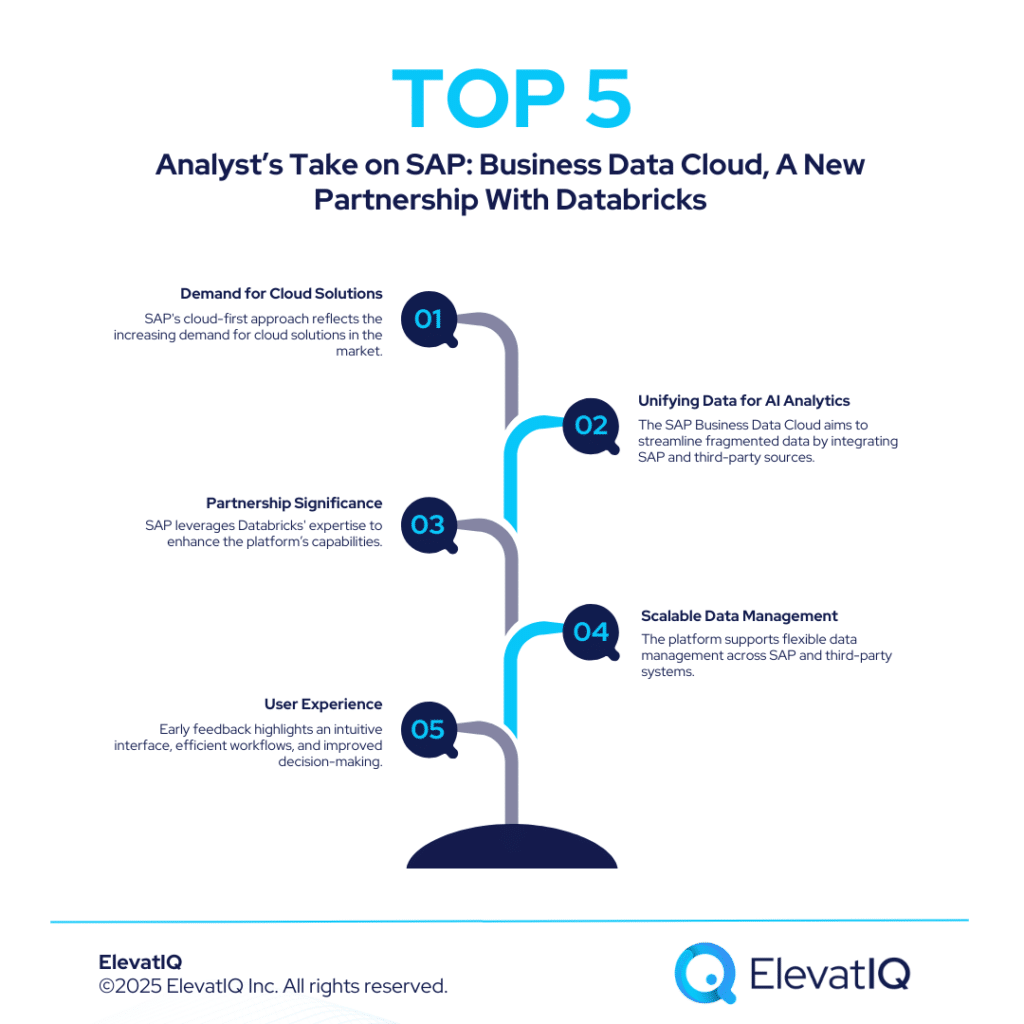
Databricks: New Updates To Simplify AI-App Development
Databricks has announced a series of new features particularly aimed at streamlining the development and governance of generative AI applications and agents. These updates are designed to enhance enterprise AI adoption by providing tools for model governance, batch inference, AI-driven analytics, and also evaluation frameworks. Therefore, by simplifying the AI deployment process, Databricks aims to reduce costs, increase accessibility, and improve compliance for enterprises utilizing large language models (LLMs).
This blog provides a detailed breakdown of Databricks‘ new updates, their implications, and also a broader analysis of the trends shaping enterprise AI adoption
Breakdown of Databricks New Updates
Centralized Governance with Mosaic AI Gateway
One of the key elements of Databricks’ new updates is the Mosaic AI Gateway, which particularly provides enterprises with a unified platform for governing LLMs.
Features and Benefits:
- Ensures security, compliance, and access control for both open and closed-source AI models.
- Streamlines licensing costs by preventing model duplication.
- Allows companies to monitor model behavior, addressing concerns such as bias, drift, and regulatory compliance.
- Provides an interface for legal, compliance, and security teams to approve AI models efficiently.
With this feature currently in public preview, enterprises can expect improved AI model governance and reduced risks associated with unregulated deployments.
Provision-Less Batch Inference
Another major enhancement in Databricks’ new updates is provision-less batch inference, which simplifies the process of running inference at scale.
Key Advantages:
- Enables batch inference execution via SQL queries, eliminating the need for complex infrastructure setup.
- Reduces costs by charging enterprises only for resources consumed.
- Makes AI more accessible to data analysts without requiring MLOps expertise.
Use Cases:
- Customer Support Analysis: Detecting trends in support tickets using AI.
- E-commerce Optimization: Enriching product catalogs with AI-generated descriptions.
- Compliance Audits: Running periodic risk assessments for financial institutions.
- Customer Retention: Scoring customer databases for churn prediction.
Currently in public preview, this update is expected to benefit businesses seeking cost-effective AI scalability.

Enhanced Agent Evaluation Review App
AI agents play a crucial role in automating workflows, but ensuring their accuracy remains a challenge. To address this, Databricks’ new updates include an improved agent evaluation review app.
Key Enhancements:
- Allows domain experts to review AI outputs and submit traces for labeling.
- Supports the creation of custom evaluation criteria, eliminating reliance on spreadsheets and custom-built tools.
- Enhances AI performance through structured feedback collection and iterative refinement.
With this feature, enterprises can enhance AI agent accuracy while maintaining transparency in evaluation.
AI/BI Genie Conversation API Suite
Databricks’ new updates also introduce the AI/BI Genie Conversation API Suite, a no-code tool designed for natural language-based data analysis.
Features:
- Allows users to query datasets using natural language.
- Automatically generates data visualizations for easy interpretation.
- Enables developers to embed chatbot-based data analysis into platforms like Microsoft Teams, SharePoint, and Slack.
- Supports context-aware follow-up queries, maintaining continuity in conversations.
Benefits:
- Democratizes access to data insights, removing technical barriers such as SQL expertise.
- Helps business users make data-driven decisions without requiring advanced analytics skills.
This update, also in public preview, could drive broader AI adoption in enterprise analytics.

Analyst’s Take on Databricks New Updates
Industry Trends
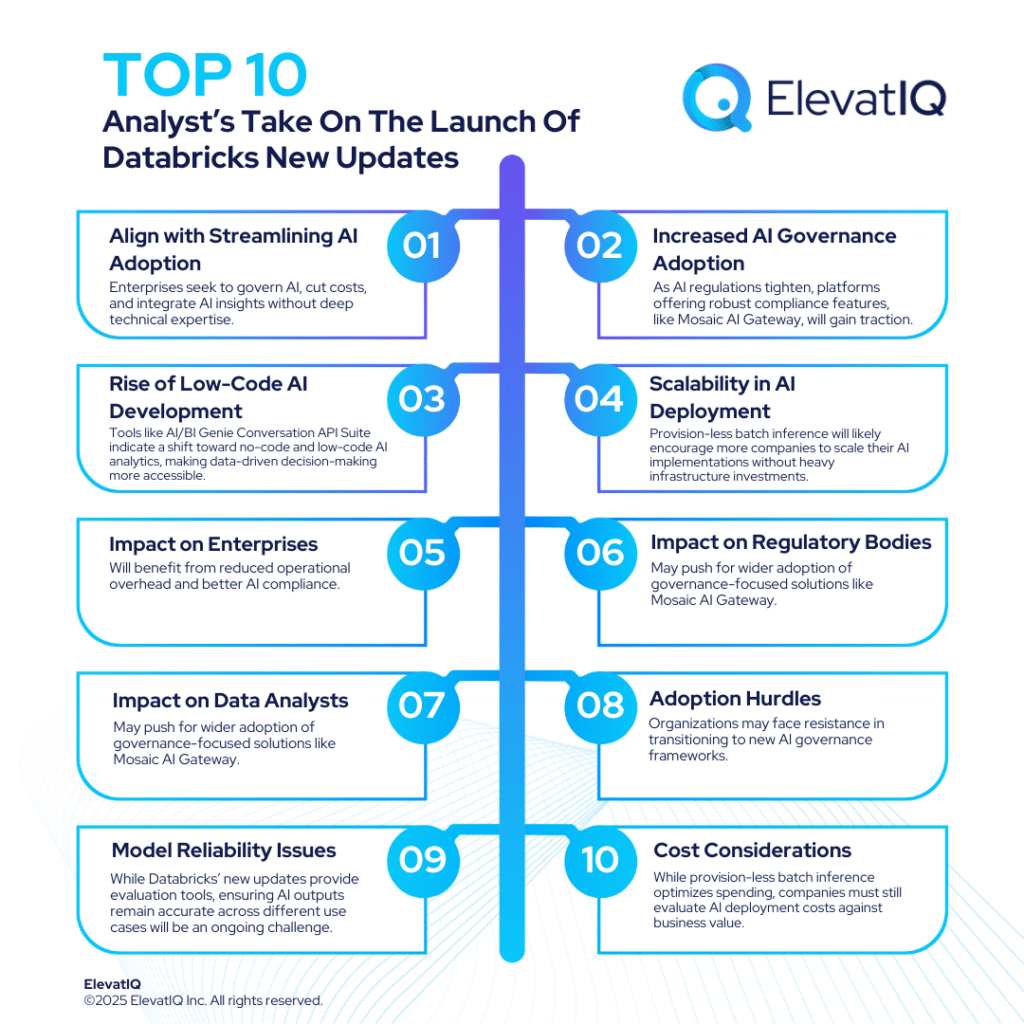
Databricks’ new updates align with a broader industry trend of streamlining AI adoption. Enterprises are increasingly looking for ways to govern AI models, reduce operational costs, and integrate AI-driven insights without requiring deep technical expertise.
Future Predictions
- Increased AI Governance Adoption: As AI regulations tighten, platforms offering robust compliance features, like Mosaic AI Gateway, will gain traction.
- Rise of Low-Code AI Development: Tools like AI/BI Genie Conversation API Suite indicate a shift toward no-code and low-code AI analytics, making data-driven decision-making more accessible.
- Scalability in AI Deployment: Provision-less batch inference will likely encourage more companies to scale their AI implementations without heavy infrastructure investments.
Impact on Stakeholders
- Enterprises: Will benefit from reduced operational overhead and better AI compliance.
- Data Analysts: Can leverage batch inference and AI chat tools without requiring extensive coding skills.
- Developers: Gain the ability to integrate AI functionalities seamlessly into existing applications.
- Regulatory Bodies: May push for wider adoption of governance-focused solutions like Mosaic AI Gateway.
Possible Challenges
- Adoption Hurdles: Organizations may face resistance in transitioning to new AI governance frameworks.
- Model Reliability Issues: While Databricks’ new updates provide evaluation tools, ensuring AI outputs remain accurate across different use cases will be an ongoing challenge.
- Cost Considerations: While provision-less batch inference optimizes spending, companies must still evaluate AI deployment costs against business value.

FAQs
Databricks: New Updates To Simplify AI-App Development Read More »