Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O ERP Independent Review
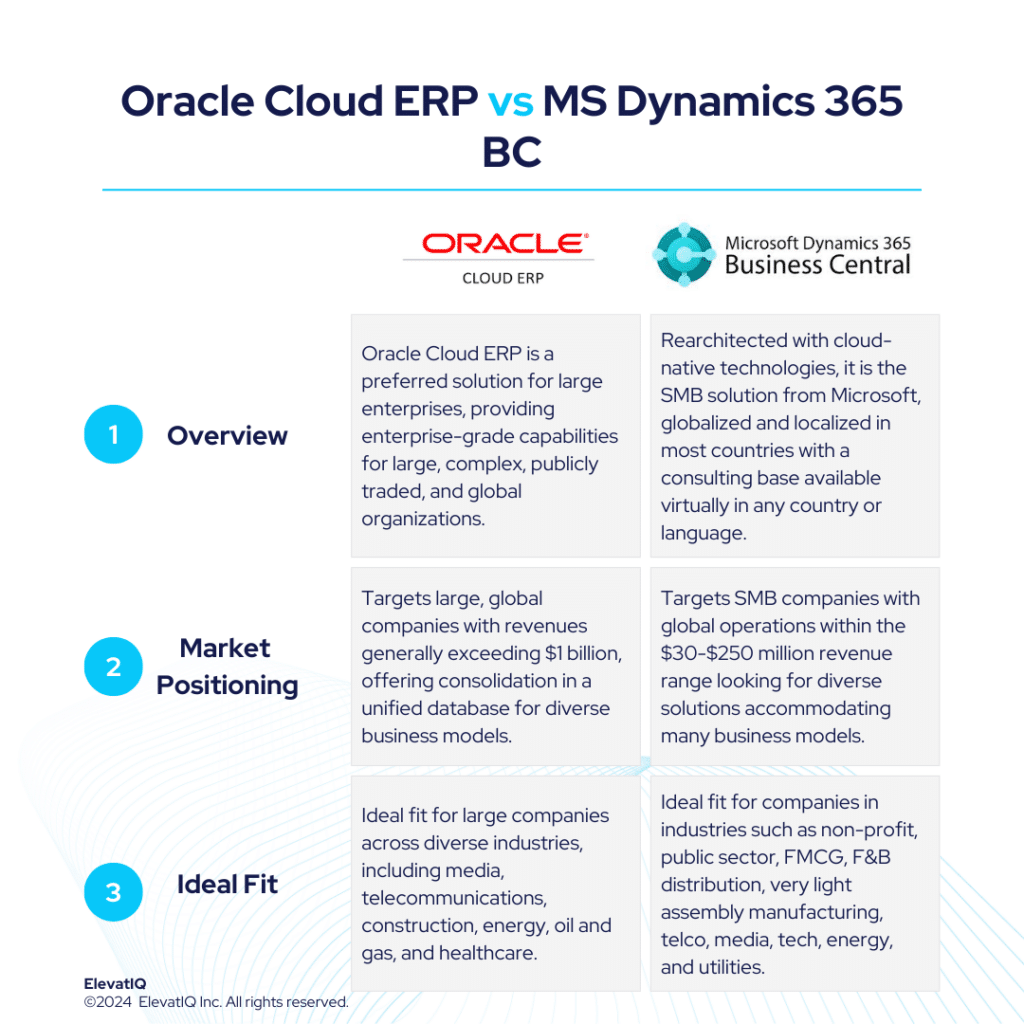
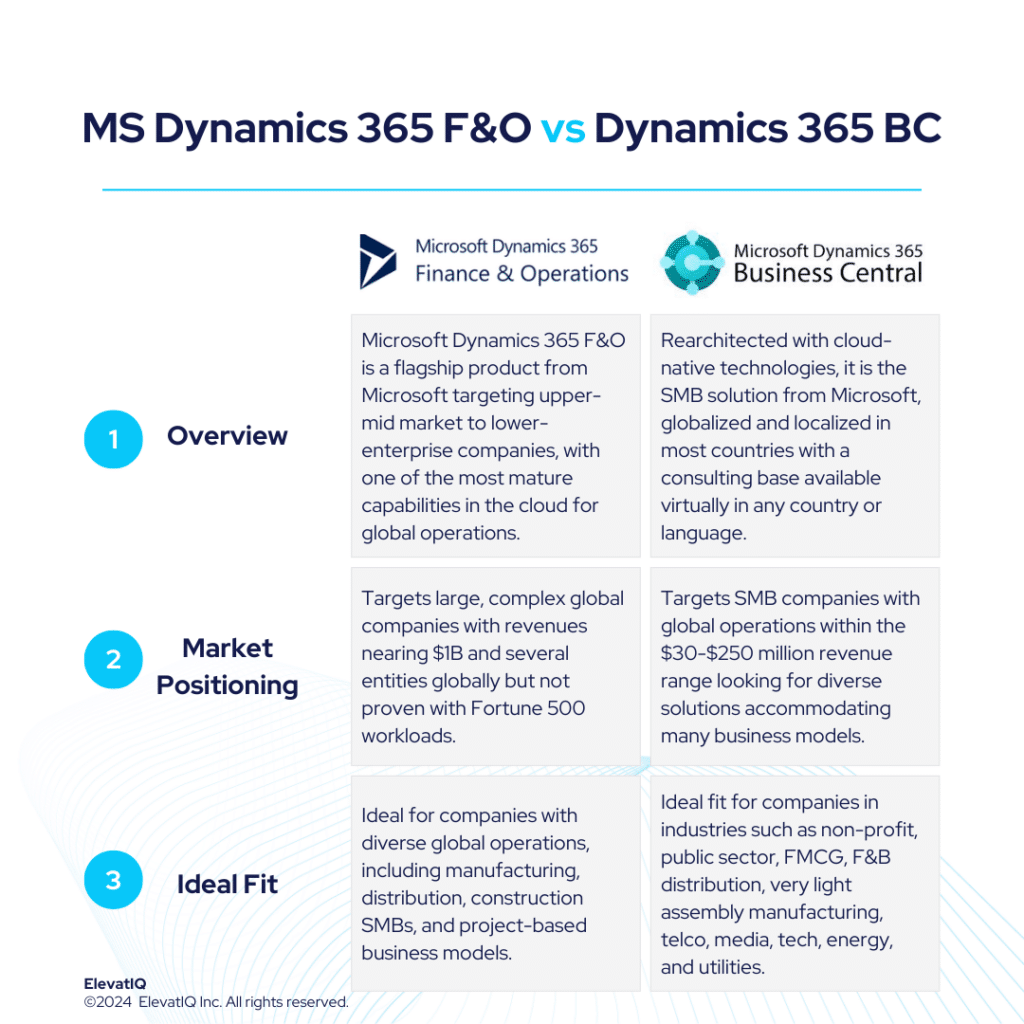
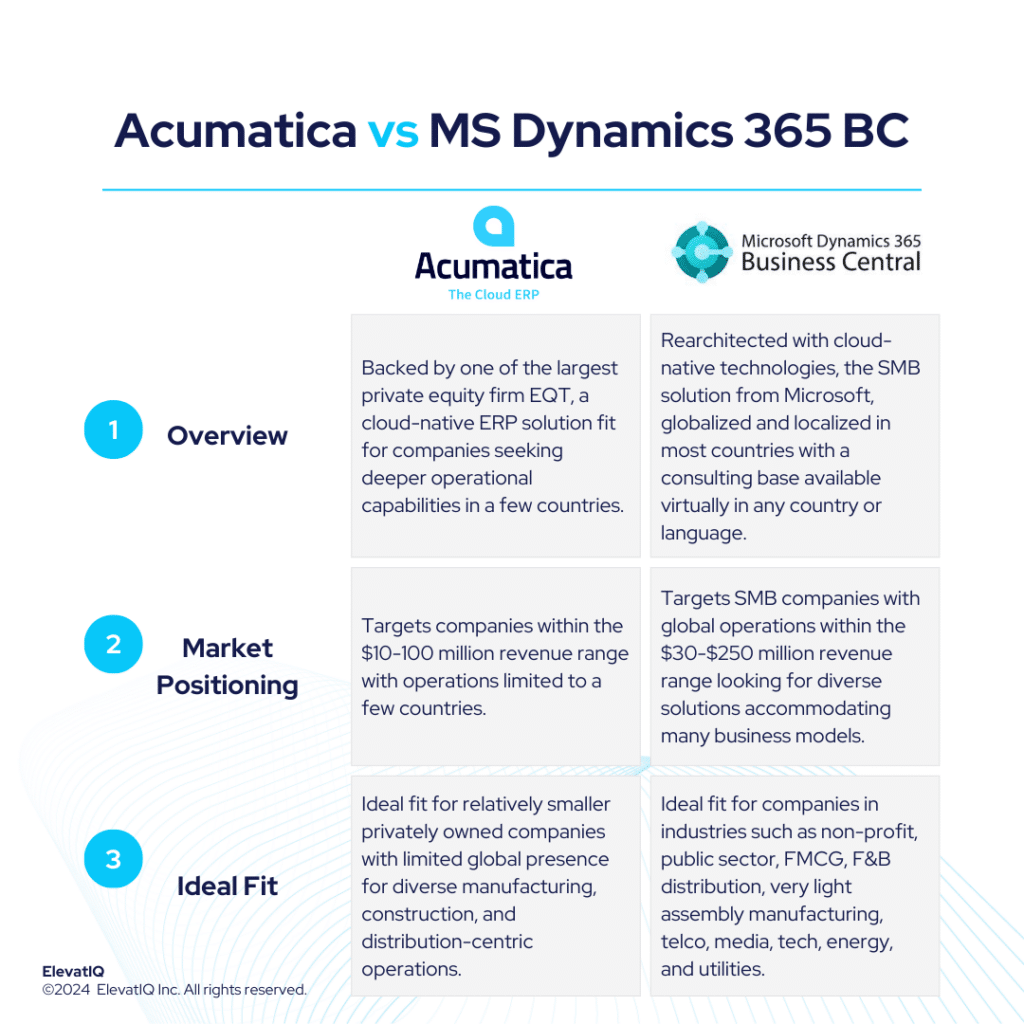
What is Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O? Microsoft Dynamics F&O is the flagship product from Microsoft. It is one of the strongest particularly in cloud-native enterprise-grade operational capabilities. Compared to other enterprise-grade products such as SAP S/4 HANA or Oracle Cloud ERP, which might not be as rich in their out-of-the-box operational capabilities, Microsoft Dynamics F&O packages capabilities for upper mid-market and lower enterprise global and diverse organizations.
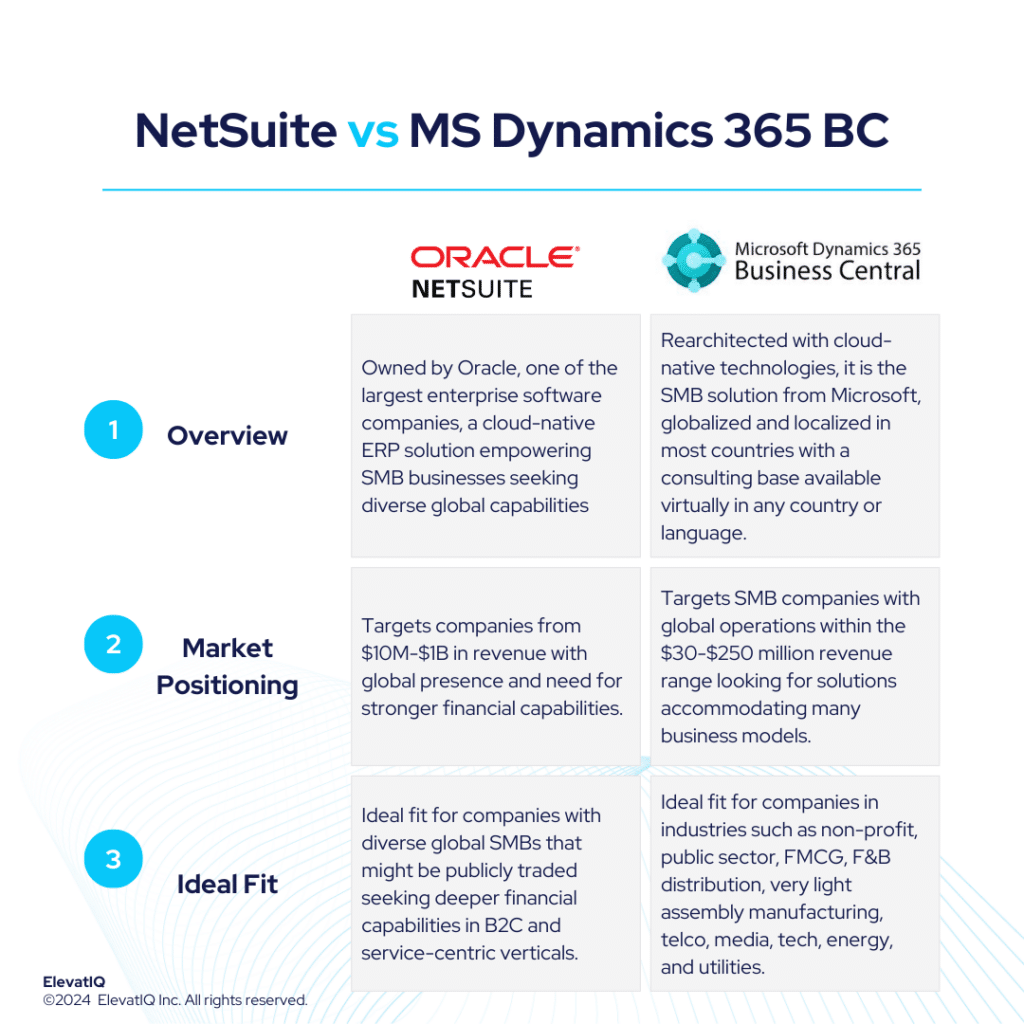
In contrast to smaller products such as Mircosoft Dynamics Business Central or NetSuite, which generally rely on add-ons for mature operational capabilities, Microsoft Dynamics would provide them out of the box. While the operational capabilities are richer, it might not have the same pre-baked and pre-integrated suite as with comparable prescribed systems such as Infor LN or QAD. However, the ecosystem stands out with the presence of large enterprise software companies such as ISVs, backed by substantial funding, filling the gap despite these capabilities not being out-of-the-box and provided directly by Microsoft.
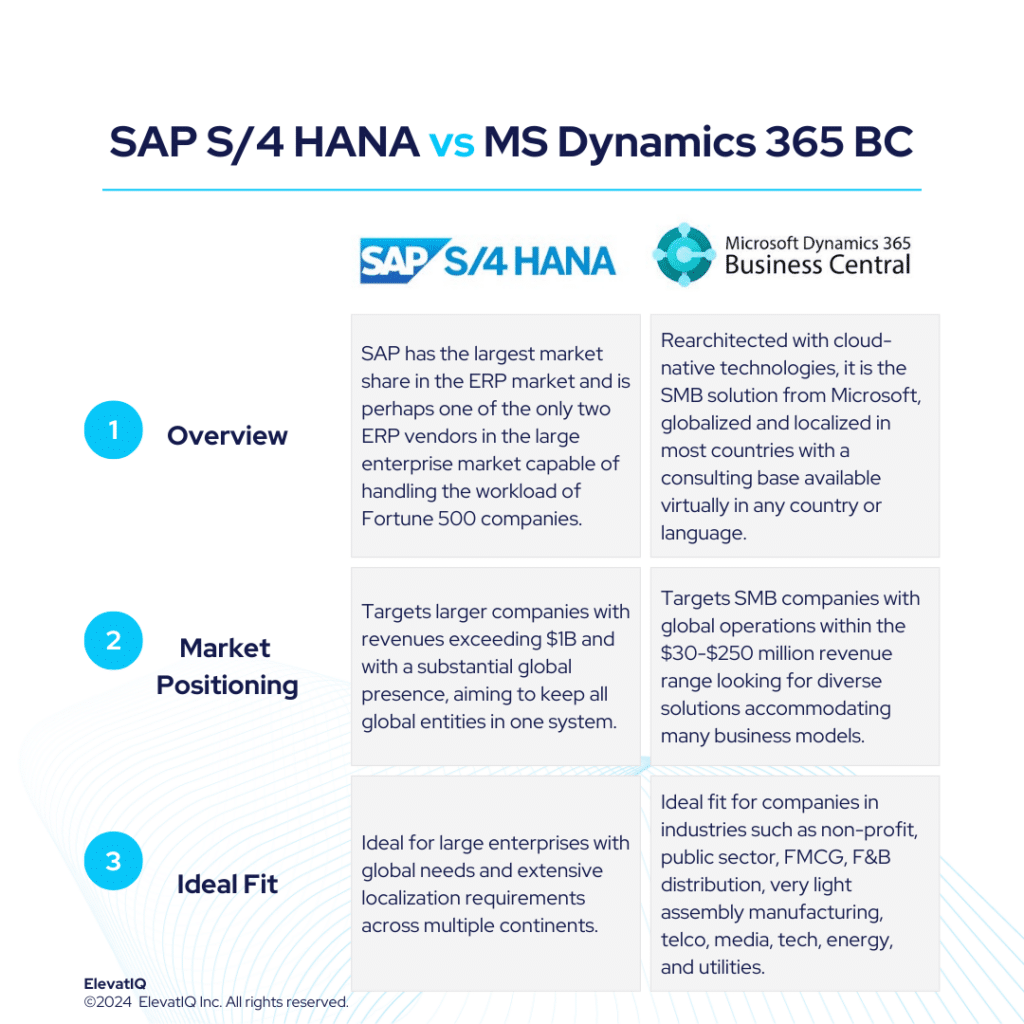
Despite richer operational capabilities, MS Dynamics 365 F&O is not as proven with the Fortune 500 workloads, but it’s a solid option for upper mid-market or lower mid-market, especially for companies aiming to keep all of their processes in one system globally. The way the Microsoft channel is structured also has an impact on the distribution and support model of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O. Microsoft also does not provide direct support to its partners. While this would not be an issue with the larger partners whose support organizations are likely to be as big as Microsoft, smaller organizations might struggle. Despite pros and cons, Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O is one of the solid options for companies with diverse business models and sizes.

Key Review Insights of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O
1. Designed for Large, Diverse and Global Organizations
Businesses that have multiple global entities with complex business models such as discrete and process manufacturing, distribution, and project-based business models would find Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O attractive.
2. Cloud-Native Architecture
Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O has been completely rearchitected particularly using the cloud-native architecture. Cloud capabilities are stronger than competing products for distributors such as SAP S/4 HANA and Oracle ERP Cloud.
3. Powerful Ecosystem
The consultants are present in most countries and solutions available to augment the core capabilities of most industries. Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O is considered to have a powerful ecosystem. This is especially beneficial for private equity and holding companies trying to streamline all of their entities on one solution. They can find add-ons if the core solution doesn’t meet their needs for last-mile industry capabilities.

4. Overwhelming for Smaller Organizations
Companies under $250M in revenue or outgrowing smaller ERP or accounting systems such as QuickBooks might struggle in using Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O. This is due to their limited data modeling and translation expertise.
5. Not Fit for Large Workloads
Dynamics 365 F&O might not be the most suitable for the transactional workload and the MRP run of the Fortune 500 due to the heavy lifting required. Compared to SAP S/4 HANA, it might not be able to match the performance expectations of large complex organizations. Because these companies may need to process millions of journal entries per hour.
6. Limited Governance Process
Since Microsoft sells licenses in the OEM setting with a limited governance process in place, buying these products from unqualified resellers fires back and may lead to ERP implementation failure.
7. Mixed-mode Manufacturing Capabilities
Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O can accommodate several business models as part of the same solution, such as PSA, process, and discrete manufacturing. Its strength includes the core ERP capabilities such as native support for mixed-mode manufacturing, including deep process manufacturing such as formulation management, catch weight management, approvals, and commitments.
8. Integrated Best-of-breed Products
While Microsoft has best-of-breed ERP integration such as CRM or field service, it might be especially friendly for companies trying to decouple business processes to gain operational efficiencies or expedite the sales or field service cycles. Like industries such as food and beverage machinery or appliances. Although, they might not be as directly relevant for make-to-order companies but will be useful for make-to-order companies with diverse business models.
Key Features of Microsoft dynamics 365 F&O
Financial Management
Some of the financial management features of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O are as follows:
| Financial Management | Features | |
| General Ledger | Creates and maintains accurate records for financial transactions and generates regular financial reports. | |
| Accounts Receivable and Payable | Automates workflows for managing vendor invoices, payments, and customer invoicing, streamlining the entire invoicing process and improving cash flow management. | |
| Cash Flow Management | Provides comprehensive cash flow forecasting capabilities, allowing to project future cash positions, identify potential shortfalls, and make informed decisions. | |
| Chart of Accounts | Enables the creation of a hierarchical structure for categorizing financial information. | |
| Budgeting and Forecasting | Creates and manages budgets across different departments and business units. Also, leverages historical data and predictive analytics, to make accurate projections and align their financial strategies with business goals. |

Supply Chain Management
Some of the supply chain management features of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O are as follows:
| Supply Chain Management | Features | |
| Warehouse Management | Provides advanced warehouse and transportation management features, including inventory tracking, order fulfillment, shipment planning, and real-time visibility into logistics operations. | |
| Service Management | Establishes service agreements and service subscriptions, handles service orders and customer inquiries, and manages and analyzes the delivery of services to customers. | |
| Inventory Management | Offers real-time visibility into inventory levels, demand, and supply, enabling organizations to optimize their inventory planning, reduce stockouts, and improve customer satisfaction. | |
| Procurement and Sourcing | Streamlines the procurement process by providing end-to-end visibility and control over purchasing activities. Also automates and optimizes the procurement workflows, reducing costs and improving supplier relationships. | |
| Transportation Management | Offers real-time visibility into logistics operations. | |
| Demand Planning and Forecasting | Generates accurate demand forecasts, helping organizations optimize production planning, inventory levels, and procurement decisions. |

Manufacturing Management
Some of the manufacturing management ERP features of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O are as follows:
| Manufacturing Management | Features | |
| Production Planning | Provides comprehensive production planning and control capabilities, allowing organizations to optimize their manufacturing processes. The system supports various production scenarios, including make-to-order, make-to-stock, and engineer-to-order, while providing real-time visibility into production schedules, resource allocation, and material requirements. | |
| Shop Floor Management | Offers real-time monitoring of shop floor activities, capturing data on machine utilization, labor productivity, and production progress. | |
| Product Lifecycle Management | Enables organizations to manage the entire product lifecycle, from design and engineering to manufacturing and after-sales service. The system integrates product data, engineering change orders, and quality management processes, ensuring seamless collaboration and visibility across different departments. | |
| Quality Control and Compliance | Provides robust quality control and compliance features, allowing organizations to define quality standards, perform inspections, track non-conformances, and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements. |
Business Intelligence And Reporting
Some of the business intelligence and reporting features of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O are as follows:
| Business Intelligence and Reporting | Features | |
| Real-time Analytics and Dashboard | Enables organizations to gain real-time insights into their operations with interactive dashboards and reports. Also, provides visual representations of key performance indicators, financial metrics, and operational data, empowering stakeholders to make data-driven decisions. | |
| Reporting | Creates custom reports and visualizations tailored to specific needs. This flexibility enables in-depth analysis, data exploration, and the generation of actionable insights to drive continuous improvement and strategic decision-making. |
Pros and Cons of Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O
| Pros | Cons |
| Ideal for large, global companies with complex business models operating in multiple countries. | Companies under $250M in revenue or outgrowing smaller ERP might find it overwhelming due to the data modeling and translation expertise required. |
| Embedded WMS and TMS processes help companies requiring end-to-end traceability including external supply chain. | While Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O has a vibrant marketplace to augment its core capabilities, crucial capabilities such as PLM, etc, might not be owned and pre-integrated by Microsoft. |
| Supports global operations and business models and pre-baked integration for the best-of-breed CRM and field service solutions. | The last-mile capabilities required in specific micro-verticals such as dairy, plastic, building supplies, or metal might require add-ons or expensive development on top of the core platform. |
| It has richer operational functionality for the cloud than SAP S/4 HANA and Oracle ERP Cloud. | While MS Dynamics may have been used as a financial ledger for the workload of Fortune 1000, it is not as proven for the global MRP workload in one solution. |
| The largest marketplace with solutions to augment most A&D business models not supported by the core product. | Microsoft channel is very complex, without any direct support for its resellers and partners, making navigating the Microsoft channel extremely hard. |
| The technical architecture includes integration with other Microsoft products, such as Logic Apps and Azure Data Factory, allowing them to isolate their infrastructure for validation requirements. | Complex global organizations may struggle with financial traceability and SOX compliance capabilities. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (F&O) emerges as a formidable contender, particularly for upper mid-market businesses seeking comprehensive financial management solutions. Its cloud-native architecture, coupled with its ability to handle diverse business models within a single platform, sets it apart from its competitors. However, navigating the ecosystem, characterized by a mix of ISVs and VARs, may require guidance from independent ERP consulting firms. This is to ensure successful implementations and mitigate risks associated with unqualified resellers.
While Dynamics 365 F&O offers robust features and integration capabilities, it may not be the optimal choice for smaller organizations or those with exceptionally large transactional workloads. Despite these limitations, its strengths lie in its powerful ecosystem, extensive consulting base, and the availability of add-ons to augment core functionalities. In essence, Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O presents a compelling solution for large organizations with complex operational requirements, offering advanced financial management, supply chain optimization, and business intelligence capabilities. This Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O independent review intends to provide you with unbiased insights for further discussion with your independent ERP consultants.

FAQs
Microsoft Dynamics 365 F&O ERP Independent Review Read More »