Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic ERP Independent Review
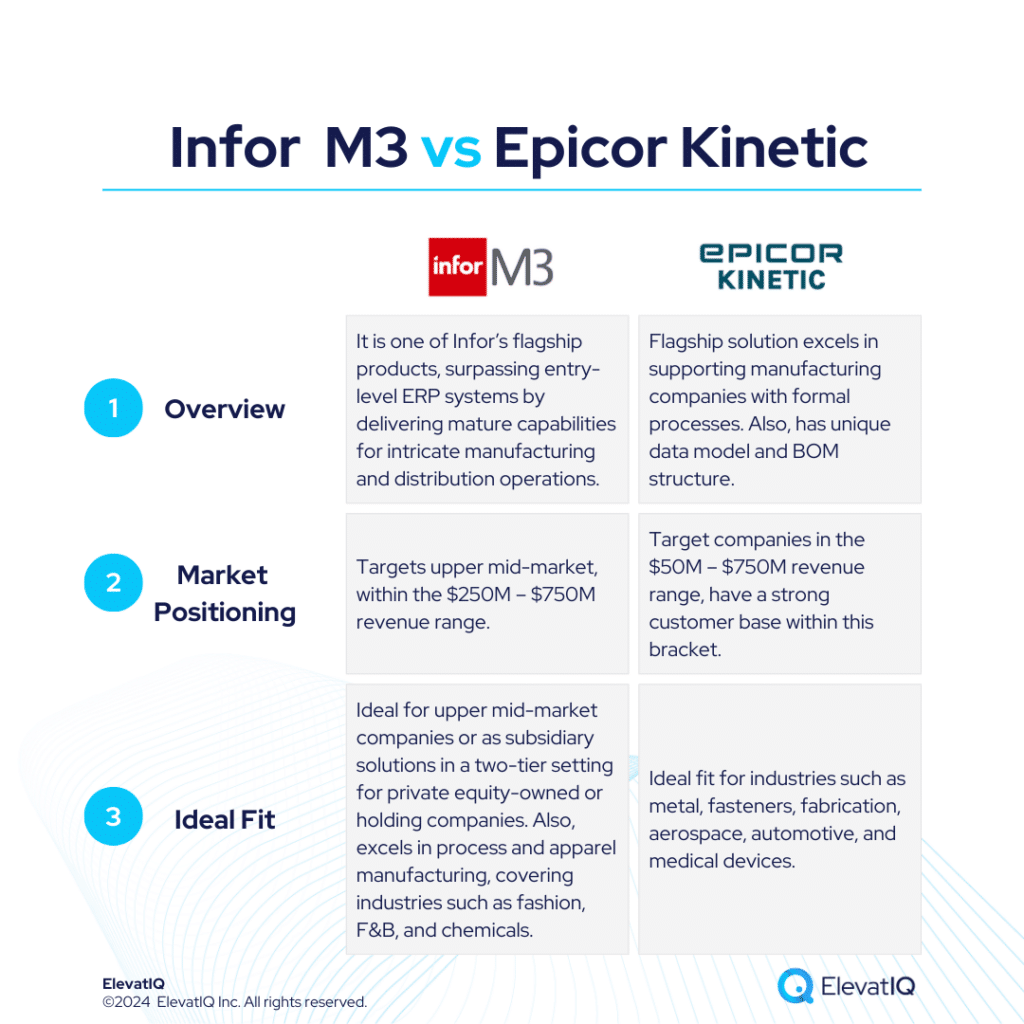
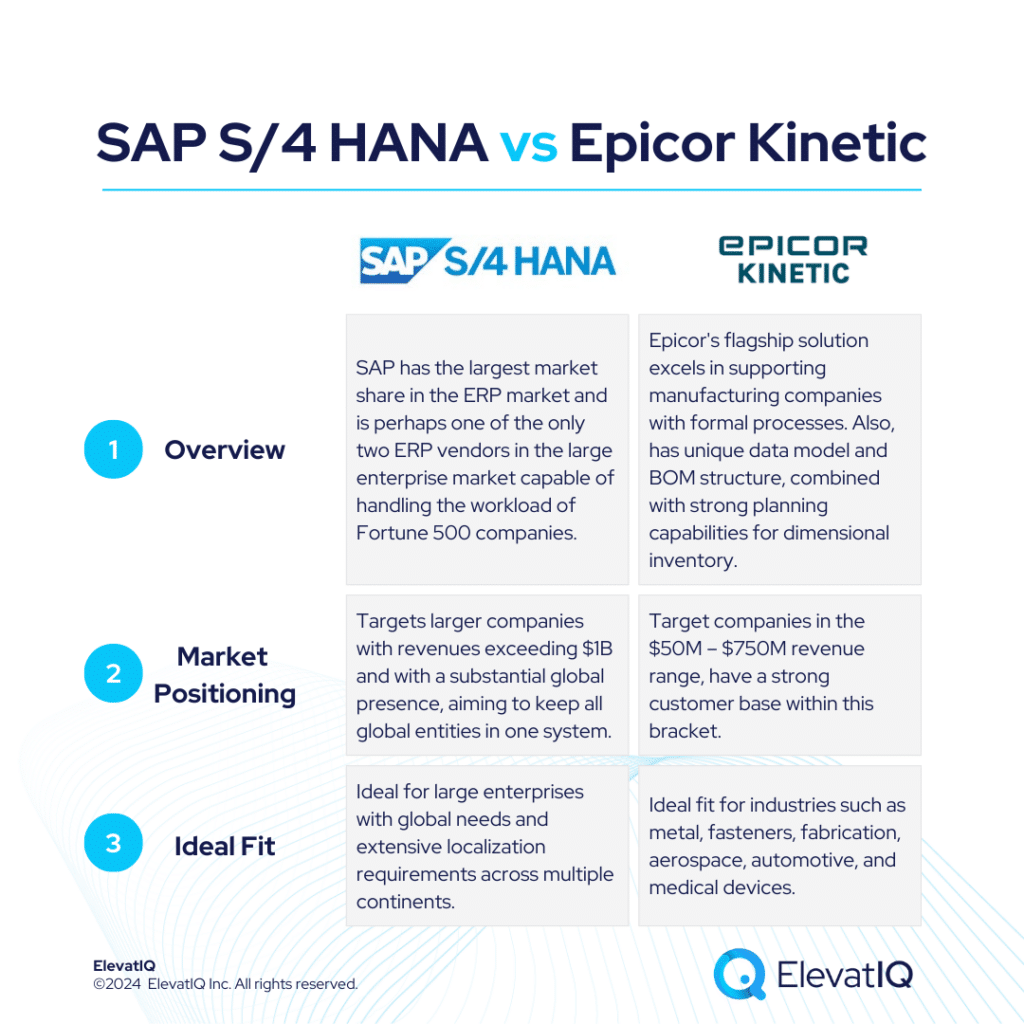
Infor M3 targets companies surpassing entry-level ERP systems like Acumatica, Infor CSI, or NetSuite. On the other hand, Epicor Kinetic boasts a sophisticated data model, surpassing entry-level ERP systems like Acumatica or NetSuite. Infor M3 also delivers mature capabilities for intricate manufacturing and distribution operations. It is successful in the upper mid-market, targeting the $250M – $750M revenue range. Whereas, Epicor Kinetic is positioned for companies in the $50M – $750M revenue range and it has a strong customer base within this bracket.
Infor M3 provides a superior suite experience akin to SAP and Oracle, featuring enterprise-grade best-of-breed functionalities, including PLM, WMS, WFM, BI, and a Supply Chain collaboration platform. On the other hand, Epicor Kinetic excels in catering to manufacturing companies with formal processes. Its distinctive data model and BOM structure, coupled with robust planning capabilities for dimensional inventory, make it ideal for industries like metal, fasteners, fabrication, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Infor M3 boasts extensive features tailored for process and apparel manufacturing, covering industries such as fashion, F&B, and chemicals. It is also adept at facilitating advanced global operations, particularly for companies spanning multiple countries seeking to optimize cost synergies globally. Whereas Epicor Kinetic is tailored for companies advancing beyond basic transactional processing, it targets those in need of mature manufacturing capabilities such as MRP, allocation, and scheduling. Therefore, choosing between Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic requires a detailed examination, and this comparison offers valuable insights for ERP selection projects. Let’s delve deeper into the specifics.

| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic | |
| Started in | 2006 (Acquired by Infor) | Rebranding in 2021 (legacy version existed for more than 20 years) |
| Ownership by | Koch Industries | CD&R, over $57B in assets, and CVC with over $220B in assets |
| No. of customers | 1,000+ | 23,000+ |
What Is Infor CloudSuite M3?
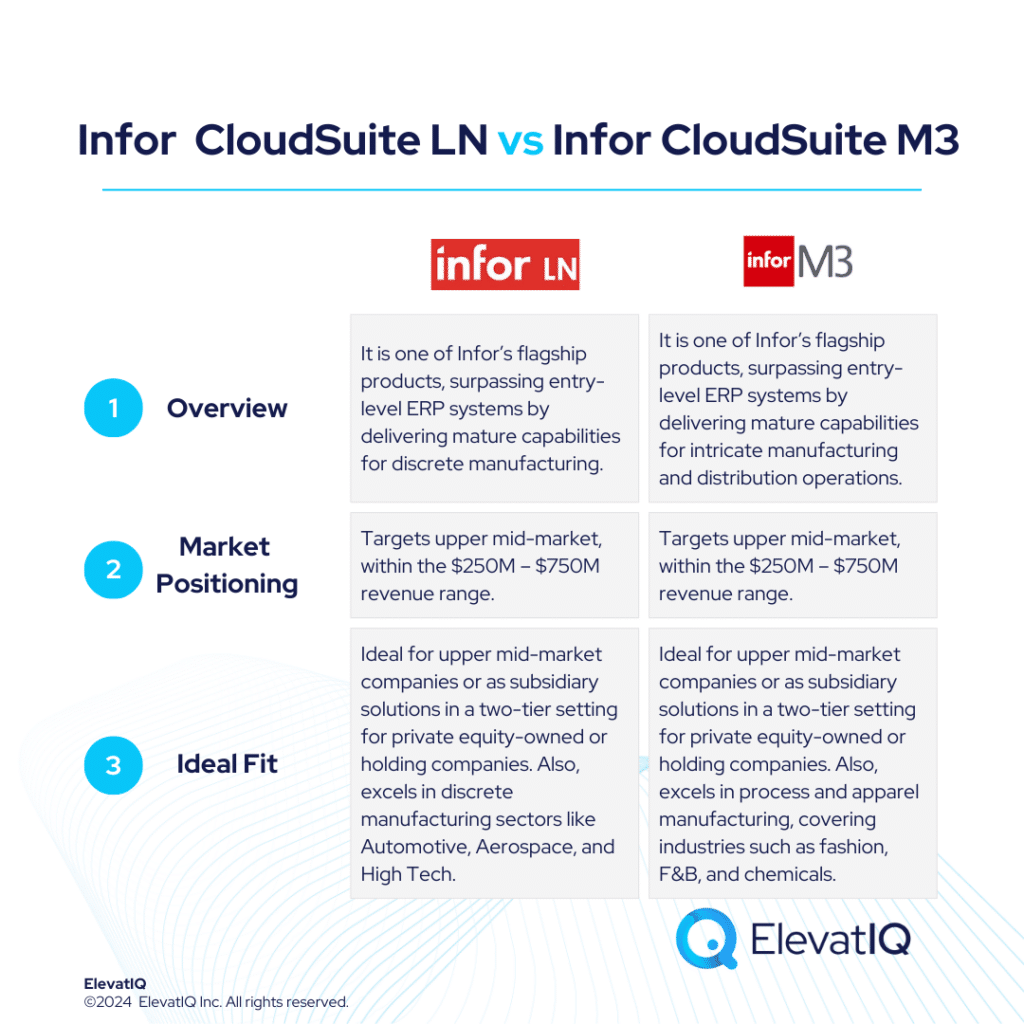
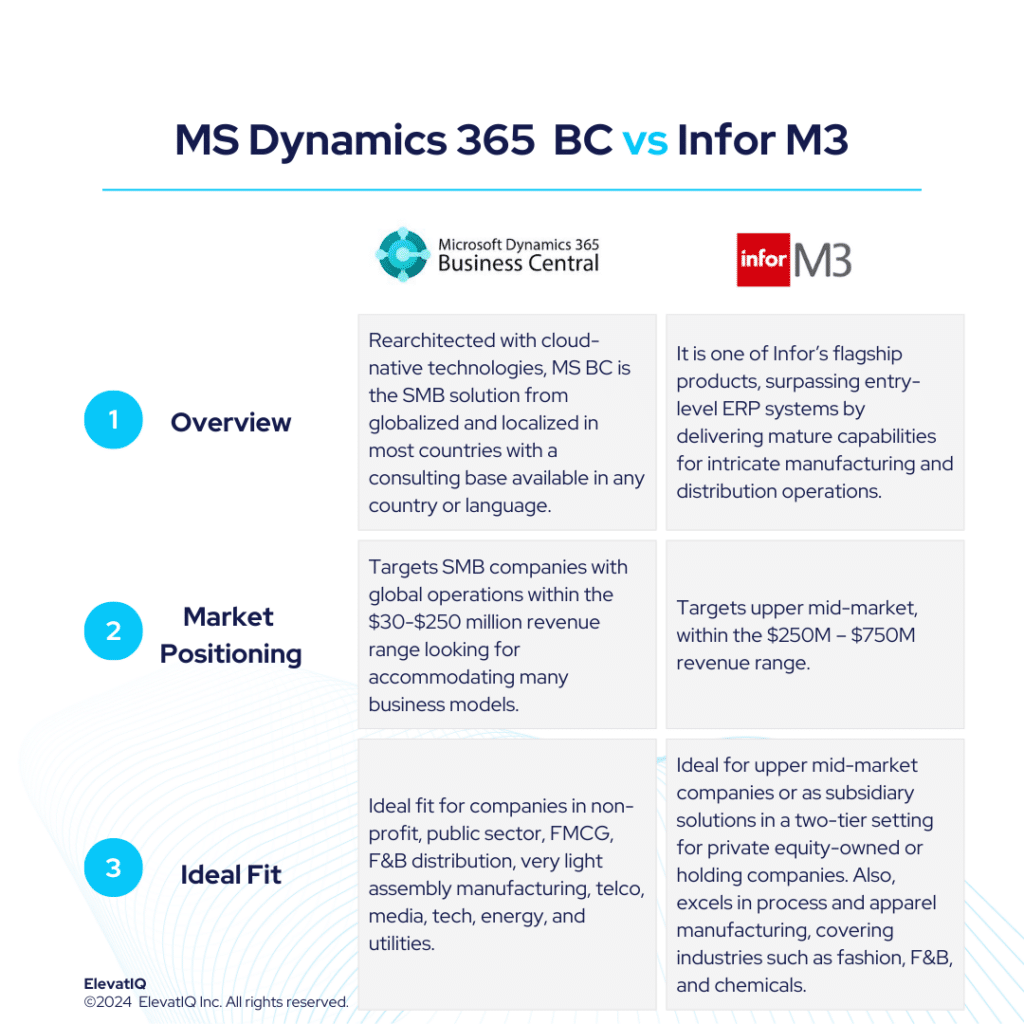
Infor CloudSuite M3, is one of Infor’s flagship solutions, catering to distinct micro-verticals across various industries. Sharing similar suites with Infor LN and built on the Infor OS platform, it is successful in the upper mid-market, targeting the $250M – $750M revenue range. Positioned for companies surpassing entry-level ERP systems like Acumatica, Infor CSI, or NetSuite, this solution delivers mature capabilities for intricate manufacturing and distribution operations. Infor CloudSuite M3 provides a superior suite experience akin to SAP and Oracle, featuring enterprise-grade best-of-breed functionalities, including PLM, WMS, WFM, BI, and a Supply Chain collaboration platform.
Infor CloudSuite M3 boasts extensive features tailored for process and apparel manufacturing, covering industries such as fashion, F&B, and chemicals. It is also adept at facilitating advanced global operations, particularly for companies spanning multiple countries seeking to optimize cost synergies globally. The native capabilities of Infor CloudSuite M3 address global trade and compliance concerns, which are particularly crucial for international business operations.
While Infor CloudSuite M3 serves as an excellent operational solution for a 2-tier architecture for enterprise companies, its limited focus on certain industries might not be the best fit for enterprise companies diversifying their operations or aggressive with their M&A strategy. The intricate data model and Bill of Materials (BOM) demand significant internal expertise and also external advisory assistance to extract operational efficiencies. Notably, the technology landscape for Infor CloudSuite M3 remains somewhat patchy and less modern compared to its competitors. Furthermore, the ecosystem and consulting support for this solution is relatively limited. Despite these challenges, Infor CloudSuite M3 stands out as a robust manufacturing solution for upper mid-market companies with budget constraints.
What Is Epicor Kinetic?
Epicor Kinetic, their flagship solution, particularly excels in catering to manufacturing companies with formal processes. Its distinctive data model and BOM structure, coupled with robust planning capabilities for dimensional inventory, make it ideal for industries like metal, fasteners, fabrication, aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Epicor Kinetic’s versatile data model addresses complex planning needs for companies particularly with diverse business models, encompassing manufacturing, distribution, and construction. Moreover, its advanced features support WBS-centric processes, enabling efficient management of large manufacturing programs with centralized cost tracking.
Epicor Kinetic boasts a sophisticated data model, surpassing entry-level ERP systems particularly like Acumatica or NetSuite. Tailored for companies advancing beyond basic transactional processing, it targets those in need of mature manufacturing capabilities such as MRP, allocation, and scheduling. Implementation success with Epicor Kinetic also requires substantial expertise in process and data coding, making it unsuitable for founder-led companies lacking seasoned operational and financial executives with ERP experience. Given its rigid revision model, companies with suboptimal SKU and BOM models may face challenges during implementation, emphasizing the need for robust internal capabilities and advisory support.
Epicor Kinetic has also undergone noteworthy technological advancements, adopting a look and feel reminiscent of Microsoft Dynamics ERP systems. Despite its legacy status, it supports mature cloud capabilities like enterprise search. Positioned for companies particularly in the $50M – $750M revenue range, it has a strong customer base within this bracket. Current limitations also include its field service capabilities, which are being addressed through an acquired add-on, and its finance and accounting module, not as tightly integrated as other modern cloud-native solutions.
Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic Comparison
Navigating the choice between Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic is a significant decision for businesses particularly looking for operational efficiency and strategic alignment. Thus, this section delves into the comprehensive comparison of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic across various critical dimensions.
| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic | |
| Global Operational Capabilities | Robust financial hierarchies and global trade compliance functionality integrated. | The limited number of global and financial layers would require inefficient workarounds. |
| Diverse Capabilities | Supports diversified manufacturing business models. | The versatile data model addresses complex planning needs for companies with diverse business models. |
| Best-of-breed Capabilities | Best-of-breed integrations provided out-of-the-box. | Limited, relying on third party add-ons for field service and quality module. |
| Last-mile Capabilities | Last-mile capabilities along with breadth of capabilities for diversified manufacturing business models. | Pre-packaged capabilities for metal, automotive, and aerospace verticals. |
| Operational Functionalities | Legacy solution with limited cloud-natve capabilities. | Equipped with strong mixed-mode manufacturing capabilities, and strong WBS-centric processes. |
| Integration Capabilities | Tools such as HCM, PLM, data lake, ERP, WMS, TMS, and advanced supply chain planning, are pre-integrated. | With out-of-the-box MES functionality, particularly appeals to smaller companies seeking pre-integrated Industry 4.0 capabilities. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities | Delivers mature capabilities for apparel, F&B, and chemical manufacturing. | Manufacturing organizations with formal processes and revision numbers will relate more. |
| Pricing Model | Subscription-based | Per user, monthly. |
| Key Modules | 1. Financial Management 2. Manufacturing Operations 3. Enterprise Asset Management 4. Supply Chain Management 5. Customer Sales and Service 6. Application Foundation | 1. Financial Management 2. Supply Chain Management 3. Production Management 4. Risk and Compliance 5. Customer Relationship Management 6. Project Management 7. Cloud Business Platform 8. Business Intelligence and Analytics 9. Planning and Scheduling 10. Services and Assets 11. Omnichannel Sales 12. Product Management 13. Global Business Management |

Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic Feature Comparison
Both platforms offer a plethora of features and functionalities designed to streamline business operations and enhance efficiency. In this feature comparison, we delve into particularly the distinct capabilities of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic across various critical dimensions, providing insights to aid businesses in making informed decisions regarding their ERP selection. Thus, this section discusses features under each of the following modules, particularly financial management, supply chain management, and manufacturing management.
Financial Management Comparison
In this section, we are discussing a detailed comparison of the financial management capabilities particularly offered by Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic. By examining their respective strengths and functionalities, particularly in managing financial processes. Businesses can therefore gain valuable insights to determine the best-suited ERP solution for their financial management needs.
| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic | ||
| Financial Management | General Ledger | Enables organizations to manage financial transactions, maintain accurate balances, and generate complete financial statements. | It is a customizable, secure core component of its Financial Management suite. Offers accounting controls, seamless integration with other financial modules, global capabilities, and also advanced reporting tools. |
| Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable | Supports analysis across all accounting dimensions, including non-reconciled data for the AP model. | Includes AR (managing invoicing, credit, cash, and customer payments) and AP (automating invoice processing, supporting multiple payment methods, and tracking expenses). | |
| Cash Flow Management | Provides complete control over accounts receivable and cash flow processes, unifying all AR information to monitor cash collection and enhance productivity and efficiency. | Features automated cash handling, bank reconciliation, multi-currency and multi-bank management, integration with other financial modules, and also real-time reporting and analysis. | |
| Currency Management | Enables currency conversion for better monetary analysis, allowing amounts to be expressed in transaction, division, and company currencies, with a default exchange rate type for conversions. | Simplifies multi-currency transactions, automates exchange rate management, integrates with other financial modules, ensures global compliance, and provides real-time reporting and analysis. | |
| Tax Management | Ensures accurate VAT calculation and recording for each country, automating tax calculations based on recipient location and country-specific rules, and maintaining financial compliance. | Automates sales and use tax calculations, integrates with financial modules, supports multiple jurisdictions, provides real-time updates, and simplifies reporting and filing. |

Supply Chain Management Comparison
In this comparison, we explore and analyze the supply chain management capabilities of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic, shedding light particularly on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic | ||
| Supply Chain Management | Warehouse Management | Optimizes operations with inventory management, labor management, 3PL billing, and 3D visualization, enhancing efficiency and interactivity. | Optimizes operations with real-time inventory tracking, advanced material management, seamless integration with other systems, and configurable workflows. |
| Service Management | Offers work order processing, maintenance, material management, and operation reporting, aiding global manufacturers, distributors, and after-sales service providers in managing complex value chains efficiently. | Streamlines operations with maintenance management, service contract handling, case management, RMA tracking, and real-time insights for efficient equipment upkeep and customer support. | |
| Inventory Management | Provides advanced statistical forecasting and stock recommendations for efficient inventory management, as well as supplier and customer rebate management to maintain high margins. | Optimizes processes with detailed tracking, smart planning, advanced units of measure, automated purchase contracts, and seamless integration with supply chain and production modules. | |
| Purchase Order Management | Includes automation, vendor payment tracking, payment scheduling, check printing, open purchase order alerts, document management, direct ACH bill payment, and vendor records. | Streamlines procurement with tools for supplier negotiations, order tracking, automated processes, and supplier relationship management. | |
| Requisition Management | Automates procurement processes from requisition to payment, including supplier selection, purchase order management, and invoice matching. | Automates procurement with real-time budget checks, vendor support, standing and blanket orders, multi-level approvals, and effective expenditure management. |
Manufacturing Management Comparison
In this comparison, we explore and analyze the manufacturing management capabilities of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic, shedding light, particularly on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic | ||
| Manufacturing Management | Production Planning | Assists manufacturers in addressing production demand with the agility to adjust to fluctuating schedules, unforeseen equipment malfunctions, delayed deliveries from suppliers, and other unexpected occurrences affecting operations on the factory floor. | Enhances manufacturing efficiency with Master Production Scheduling, Material Requirements Planning, Advanced Planning and Scheduling, Job Management, Lean Manufacturing, Quality Management, and Advanced MES for real-time monitoring. |
| BOM and Routing | Let’s you efficiently plan and manage inventories, costs and manufacturing processes. | Streamlines production with multi-level BOM management, dynamic BOM creation, CAD and PLM integration, strong change control, centralized routing management, detailed routing steps, real-time adjustments, and precise cost and time estimation. | |
| Advanced Planning and Scheduling | Lets you create a more streamlined and accurate production scheduled, better enforce delivery dates and optimize for capacity. | Enhances production efficiency with automated scheduling, flexible capacity planning, real-time adjustments, what-if scenarios, integrated material constraints, and multi-site management. |
Pros of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic
When evaluating ERP solutions, understanding the distinct advantages of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic is crucial. In this section, we are particularly exploring the strengths of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic across various dimensions. Thus, shedding light on their respective capabilities and functionalities.
| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic |
| Ideal for upper mid-market companies or as subsidiary solutions in a two-tier setting for private equity-owned or holding companies. | Epicor has a very similar look and feel to Microsoft ERP products, providing you with the same experience but with much deeper last-mile capabilities. |
| It can support multi-entity and supply-chain collaboration with international vendors, but the global footprint might not be as comprehensive as that of larger peers such as SAP S/4 HANA. | 90% of the capabilities required by verticals such as metal, automotive, and aerospace are pre-packaged with the core platform. |
| Most tools that process and apparel manufacturers would require, such as HCM, PLM, data lake, ERP, WMS, TMS, and advanced supply chain planning, are all pre-integrated with Infor CloudSuite M3. | Great fit for manufacturing organizations that follow formal manufacturing processes with revision numbers. |
| While most smaller solutions might require ad-hoc arrangements for global financial operations, Infor CloudSuite M3 has them natively built. | Although a legacy product, it includes mature cloud capabilities such as enterprise search and transactional maps for end-to-end transactional traceability. |
Cons of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic
Just like recognizing strengths is important, it’s also crucial to weigh the specific drawbacks of Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic. Therefore, in this section, we will delve into the limitations and challenges associated with Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic across various operational and financial dimensions.
| Infor CloudSuite M3 | Epicor Kinetic |
| The limited focus on certain business models poses the risk of requiring other ERP systems to support complex and diverse business operations. | The data layers are highly detailed, requiring substantial consulting help to be successful with the product. |
| Private equity and holding companies requiring global solutions with a tier-2 solution at the subsidiary level might not be the best use of Infor CloudSuite M3’s strengths. | The limited focus on certain business models poses the risk of requiring other ERP systems to support complex and diverse business operations. |
| Infor CloudSuite M3 is a legacy solution with limited cloud-native capabilities such as universal search, mobile experience, etc. | The field service capabilities are not as embedded and proven as some of the other products. |
| The consulting base and marketplaces are virtually non-existent for Infor CloudSuite M3. | Epicor takes a suite approach to its products while selling directly to its customers. This limits the overall consulting and marketplace penetration. |
| Verticals such as apparel manufacturing demand deeper integration of PLM, vendor portals, and merchandising solutions to effectively manage their unique processes. | Requires ad-hoc arrangements for larger mid-market companies with more than three financial hierarchies. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic present robust ERP solutions, each with distinct strengths that cater to different business needs and market segments. Infor M3 is ideally suited for upper mid-market companies, especially those in industries like fashion, food and beverage, and chemicals, that require sophisticated manufacturing capabilities and global operational support. Its extensive suite of integrated tools and best-of-breed functionalities make it a compelling choice for companies particularly seeking a comprehensive, enterprise-grade ERP solution. However, its legacy system architecture and limited focus on certain business models may necessitate supplementary ERP systems for companies with diverse and complex operations.
On the other hand, Epicor Kinetic excels in supporting manufacturing companies with formal processes, particularly in sectors such as metal, aerospace, and automotive. Its modernized interface and advanced planning capabilities make it a strong contender for mid-market companies that demand precise control over manufacturing operations and also supply chain management. While Epicor Kinetic offers deep vertical capabilities, its reliance on external consulting for detailed data layers and some limitations in global financial operations may pose challenges for larger, more complex organizations.
Both systems have their strengths and limitations, so businesses should carefully evaluate their specific needs and growth aspirations to determine the most suitable ERP solution. Also, seeking assistance from an independent ERP consultant can significantly aid the decision-making process. To get a 360-degree view of feature comparisons, it’s essential to explore not only Infor M3 vs. Epicor Kinetic but also insights from other analyses such as Infor M3 vs. NetSuite, SAP S/4 HANA, Oracle Cloud ERP, MS Dynamics 365 F&O, MS Dynamics 365 BC, Acumatica, and Infor CloudSuite LN.

FAQs
Infor M3 vs Epicor Kinetic ERP Independent Review Read More »