SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo ERP Independent Review
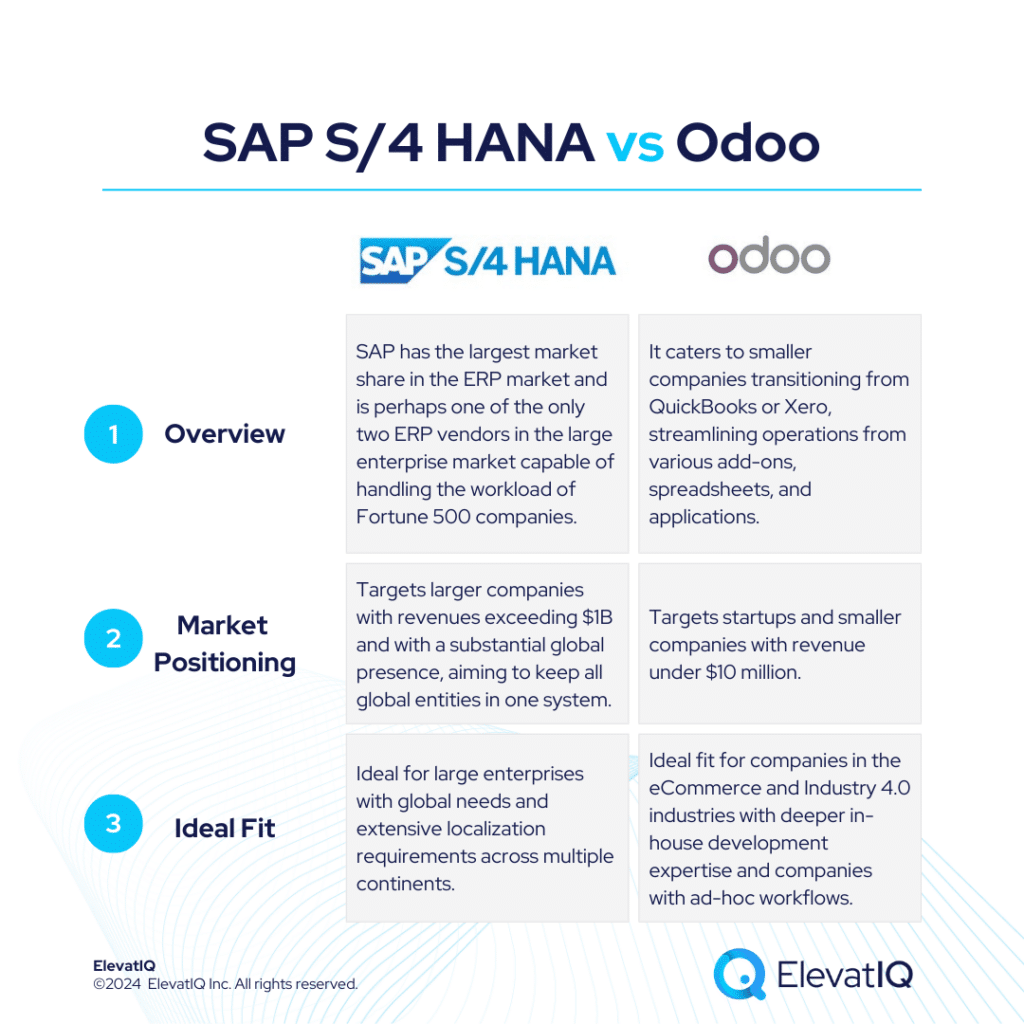
SAP maintains its dominance in the ERP market, largely due to its stronghold in the enterprise segment where deals are significantly larger compared to the mid-market. The architecture complementing the S/4 HANA Suite is particularly favored by enterprise-grade companies, offering leading products like SuccessFactors, Hybris, EWM, Ariba, and Concur. On the other hand, Odoo caters to smaller companies transitioning from QuickBooks or Xero, streamlining operations from various add-ons, spreadsheets, and applications.
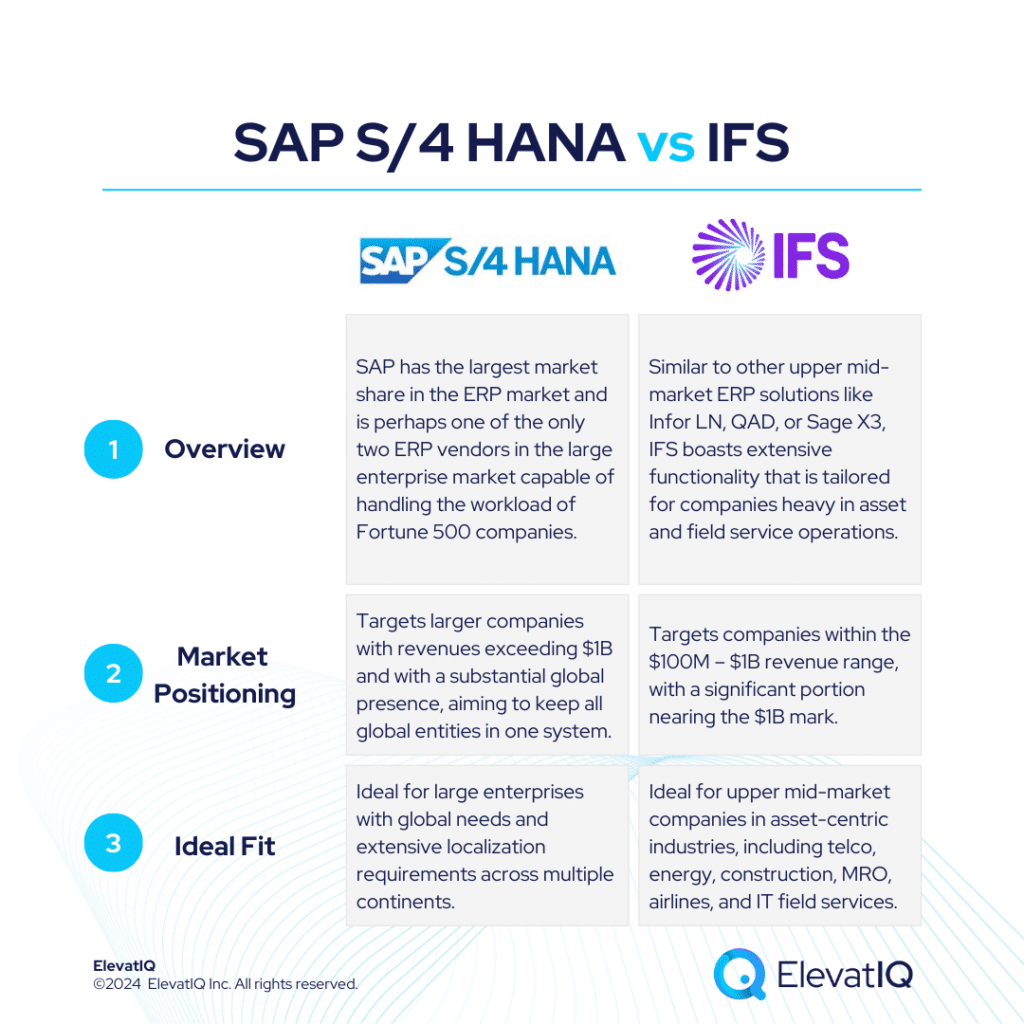
For enterprise companies, SAP S/4 HANA often becomes a default choice due to high transaction volumes, stringent governance, and traceability needs. It particularly shines in product-centric enterprises requiring robust capabilities like MRP and allocation for global workloads. It also targets larger companies with revenues exceeding $1B and with a substantial global presence. Whereas, Odoo primarily caters to startups and smaller companies with revenue under $10 million.
SAP S/4 HANA excels in managing entities across multiple countries within a unified database, Acumatica’s strength lies in its multi-branch capabilities and tailored support for various business models such as manufacturing, distribution, construction, and field service. Whereas, Odoo’s unique advantage lies in hosting operations across multiple countries in a single database. an excellent choice for budget-conscious companies, especially those with in-house development teams. Although, it may face challenges without guidance from experienced ERP consultants. While Odoo’s modular design allows flexible app purchasing and provides scalability, it lacks tight integration at the data model level. Therefore, choosing between SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo requires a detailed examination, and this comparison offers valuable insights for ERP selection projects. Let’s delve deeper into the specifics.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo | |
| Started in | Pioneers of ERP | 2014 |
| Ownership by | SAP | Odoo S.A. |
| No. of customers | 28,000+ | 100,000+ relatively smaller companies |

What Is SAP S/4 HANA?
SAP S/4 HANA remains the top choice particularly for large enterprises with global needs and extensive localization requirements across multiple continents. Although in this league, its primary rival is Oracle. While alternatives like Unit4, IFS, or Deltek might handle the workload for larger enterprises, they often lack the robust global compliance and transactional capabilities that SAP S/4 HANA offers. Additionally, SAP S/4 HANA excels in providing superior transactional workflow capabilities that are purpose-built to streamline traceability for large and complex organizations.
Moreover, SAP S/4 HANA is an ideal choice for companies seeking a best-of-breed architecture tailored to the needs of specific functions. This architecture allows for operational cores on different ledgers, which is crucial particularly for larger distribution and 3PL companies managing complex WMS networks. Companies with intricate HCM operations and stringent compliance requirements may find it particularly necessary to integrate a best-of-breed system.
Additionally, for enterprises requiring sophisticated eCommerce platforms with components like CDP or CPQ, SAP S/4 HANA provides the essential capabilities. The flexibility and enterprise-grade best-of-breed architecture make SAP S/4 HANA a standout solution for particularly such diverse operational needs. Although, the cloud version may require additional third-party add-ons, similar to NetSuite. Nevertheless, organizations opting for the on-prem version can access superior capabilities, potentially outperforming other ERP systems.
What Is Odoo?
Odoo caters to smaller companies transitioning from QuickBooks or Xero, streamlining operations from various add-ons, spreadsheets, and applications. It provides basic transactional processing across several enterprise software categories, such as ERP, CRM, and HCM. And a lot more in a consolidated database, eliminating the need for costly integrations.
An excellent choice for budget-conscious companies, especially those with in-house development teams, Odoo may face challenges without guidance from experienced ERP consultants. While Odoo’s modular design allows flexible app purchasing and provides scalability, it lacks tight integration at the data model level. This limitation can be a concern for companies aiming for stringent financial control particularly at the data layer. This is especially true for less seasoned companies that might already struggle to regulate their internal process and data codings.
A rapidly growing platform with substantial funding and a large user base, it particularly caters to startups and smaller companies with revenue under $10 million. Its unique advantage lies in hosting operations across multiple countries in a single database. Distinguishing from solutions like QuickBooks or Xero, it might also use separate financial instances for each country. The other similar ERP systems designed for multi-entity operations might not contain particularly CRM-specific processes.
SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo Comparison
Navigating the choice between SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo is a significant decision for businesses particularly looking for operational efficiency and strategic alignment. Thus, this section delves into the comprehensive comparison of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo across various critical dimensions.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo | |
| Global Operational Capabilities | Deeper multi-entity capabilities. | Fit for smaller companies that might have entities in many different countries. |
| Diverse Capabilities | Supports diverse business models globally, may require add-ons for deeper operational capabilities. | The data and process model supports diverse industries, including product and service-centric startups. |
| Best-of-breed Capabilities | Enterprise-grade capabilities with pre-integrated applications supported by SAP, augmented by third-party add-ons. | Extremely limited best-of-breed capabilities compared to its larger peers. |
| Last-mile Capabilities | Limited pre-baked last-mile capabilities for specific micro-industries. | The last-mile capabilities for specific micro-verticals are limited. |
| Operational Functionalities | Enterprise-grade operational capabilities, limited to industry-specific functionalities. | Matrix functionality built as part of the inventory core. Also, maintains a cohesive design across screens and modules being a cloud-product. |
| Integration Capabilities | Lacks out-of-the-box integration with industry-specific PLMs, configurators, and CPQ systems. | It lacks tight integration at the data model level. This limitation can be a concern for companies aiming for stringent financial control at the data layer. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities | Supports complex manufacturing operations and product models, limited to industry-specific manufacturing functionalities. | Matrix functionality built as part of the inventory core. However, many advanced transactions may have limited support natively. |
| Pricing Model | FUE (Full Use Equivalent) | Per-user, per-app, per-month model |
| Key Modules | 1. Financial Management 2. Sales 3. Procurement 4. Manufacturing Management 5. Supply Chain Management 6. Professional Services Automation 7. CRM | 1. Sales 2. CRM 3. Inventory Management 4. Accounting and Finance 5. Purchase Management 6. Project Management 7. Manufacturing Management 8. Human Resources Management 9. Website and eCommerce |

SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo Feature Comparison
Both platforms offer a plethora of features and functionalities designed to streamline business operations and enhance efficiency. In this feature comparison, we delve into particularly the distinct capabilities of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo across various critical dimensions, providing insights to aid businesses in making informed decisions regarding their ERP selection. Thus, this section discusses features under each of the following modules, particularly financial management, supply chain management, and manufacturing management.
Financial Management Comparison
In this section, we are discussing a detailed comparison of the financial management capabilities particularly offered by SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo. By examining their respective strengths and functionalities, particularly in managing financial processes. Businesses can therefore gain valuable insights to determine the best-suited ERP solution for their financial management needs.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo | ||
| Financial Management | General Ledger | Can support the needs of even the most complex financial organizations with more than ten ledger rollups at the country level and conversions. | A financial record-keeping system that tracks all financial transactions and integrates seamlessly with other modules. |
| Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable | Supports global collaboration of customers and vendors, also including shared service model. | The AR tracks money owed to the business by customers, while AP manages money the business owes to suppliers. | |
| Cash Flow Management | Complex treasury capabilities with the support for global operations, including maintaining treasury KPIs, workflows, and processes for dedicated treasury departments. | Helps monitor and forecast company’s cash inflows and outflows to ensure liquidity and financial stability. | |
| Currency Management | Can support complex currency workflows such as hedging and planning for current impact on different financial statements and accounts globally. | Supports multi-currency transactions, automatic exchange rate updates, exchange difference entries, foreign currency reports, and managing bank accounts in multiple currencies. | |
| Tax Management | Has built-in support for taxes of over 100 countries. | Automates tax calculations, updates, and reporting, ensuring compliance and efficiency across multiple currencies and modules. |

Supply Chain Management Comparison
In this comparison, we explore and analyze the supply chain management capabilities of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo, shedding light particularly on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo | ||
| Supply Chain Management | Warehouse Management | Supports embedded or standalone architectural patterns and complex business models like 3PL or warehouse value-added services. | Optimizes inventory control, streamlines operations, and enhances visibility with real-time tracking and automated processes. |
| Service Management | Supports complex quotes and service scheduling workflows particularly for globally operated companies. | Streamlines service delivery, enhances customer satisfaction, and optimizes resource allocation with integrated project management and invoicing. | |
| Inventory Management | Accommodates many different business models and inventory types of complex, global organizations. | Offers real-time tracking, multi-location management, and automated reordering to optimize stock levels and streamline operation. | |
| Purchase Order Management | Manages complex workflows with automated approval rules and multiple hierarchies. | Automates procurement processes, optimizes supplier interactions, and ensures accurate order tracking and invoicing. | |
| Sales Order Management | Manages complex order types tailored to different business models. | Streamlines the entire sales process, from creating and sending quotations to converting them into sales orders and managing invoicing, all within a single platform. | |
| Requisition Management | Manages complex requisition processes of globally complex enterprises. | Streamlines the process of creating, reviewing, and approving purchase requisitions, ensuring compliance with budgets and procurement policies |
Manufacturing Management Comparison
In this comparison, we explore and analyze the manufacturing management capabilities of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo, shedding light, particularly on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo | ||
| Manufacturing Management | Production Planning | One of the most complex planning capabilities with enterprise-grade strategies to optimize production cycles for global companies. | Optimizes manufacturing processes by efficiently scheduling, allocating resources, and managing work orders to meet production goals. |
| BOM and Routing | Enterprise-grade BOM scalability for a variety of business models and products. | Defines the components and operations required for manufacturing a product, optimizing production efficiency. | |
| Advanced Planning and Scheduling | Enterprise-grade advanced APS capabilities for complex globally distributed planning workloads that need to be collaborated across geographies. | Optimizes production by centralizing data, providing real-time visibility, and automating scheduling to enhance efficiency. |
Pros of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo
When evaluating ERP solutions, understanding the distinct advantages of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo is crucial. In this section, we are particularly exploring the strengths of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo across various dimensions. Thus, shedding light on their respective capabilities and functionalities.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo |
| It is an ideal solution as the corporate financial ledger for global companies with multiple layers of financial hierarchies operating in multiple countries. | It is widely adopted, especially among Industry 4.0 companies and other machinery businesses. |
| The item master, product model, and warehouse architecture can accommodate the needs of most manufacturing business models. | It can support many different business models, many different localizations, countries, etc, as part of the same product. |
| Because of the power of HANA, SAP S/4 HANA can process very complex MRP runs with product models containing millions of serial numbers and SKUs, making it much faster than most ERP systems. | The availability of cheaper technical talent globally helps product-centric startups extend or augment core capabilities. |
| Ideal fit for complex operations with its transactional maps capabilities built with the products, making debugging complex financial enterprises easier. | The lean data model and workflows make it easier for product-centric startups transitioning from QuickBooks-like solutions. |
Cons of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo
Just like recognizing strengths is important, it’s also crucial to weigh the specific drawbacks of SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo. Therefore, in this section, we will delve into the limitations and challenges associated with SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo across various operational and financial dimensions.
| SAP S/4 HANA | Odoo |
| The controls provided as part of the product may feel unnecessary and also overwhelming for smaller companies. | The open-source nature leads to a tendency to over-customize, resulting in an inferior product experience. |
| Overbloated financial control processes, such as compliance, allocation, and approval flows, are only necessary for large organizations. | Consisting primarily of developers, the ecosystem particularly doesn’t have a seasoned program, change management, and business consultants. |
| The data model is overwhelming for smaller organizations outgrowing QuickBooks or smaller ERP systems. | The last-mile capabilities for specific micro-verticals are limited, requiring significant customization for their work with specific industries. |
| Despite advanced financial traceability and technical capabilities, the functional capabilities are not as rich as with its on-prem version. | Mature capabilities such as MRP, allocation, and batch are not as detailed as with other richer ERP systems. |
| While SAP S/4 HANA has one of the best best-of-breed solutions, they might not be as pre-integrated as other solutions. | Adoption in the apparel manufacturing space, which is more complex, may not be as widespread. |
| In industries where it might not be the most frequently installed as an operational solution, the other solutions are likely to have deeper last-mile capabilities. | To tailor, customize, and configure these capabilities—already included in the suite, Odoo requires a very mature internal IT team. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, both SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo offer robust ERP solutions tailored to distinct types of businesses, each with unique strengths and limitations. SAP S/4 HANA stands out as a premier choice for large enterprises with complex, global operations, thanks to its enterprise-grade capabilities and ability to handle intricate financial processes and compliance requirements. It is particularly suited for companies with large transaction volumes, multiple entities, and the need for seamless integration across various business functions. However, its complexity and advanced features may overwhelm smaller companies or startups, making it a better fit for organizations with extensive financial hierarchies and stringent governance needs.
On the other hand, Odoo is a more flexible and budget-friendly solution designed for smaller companies or startups, especially those transitioning from simpler software like QuickBooks or Xero. Its modular approach and scalability make it ideal for businesses with in-house development teams looking for customizable solutions without breaking the bank. While Odoo excels in providing basic transactional and operational functionalities, it may face challenges in managing more complex financial controls or global compliance requirements.
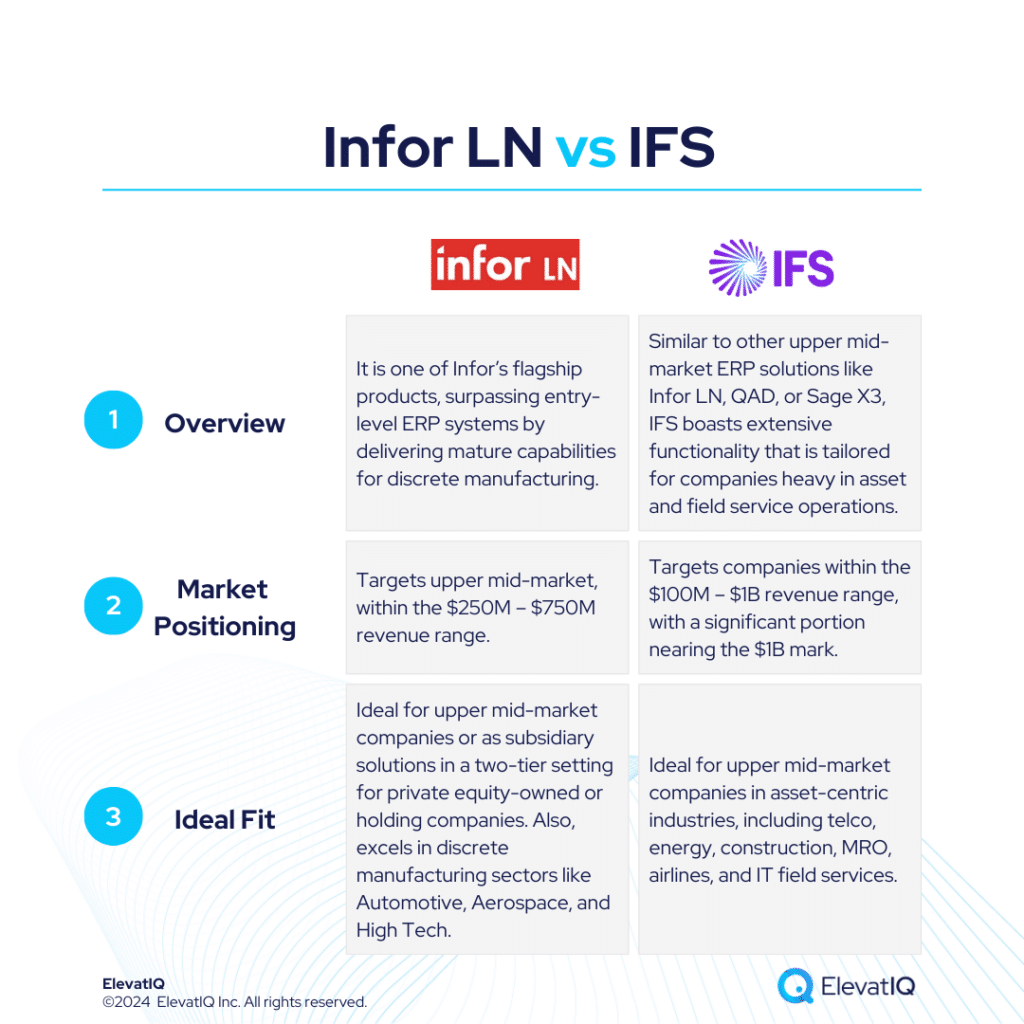
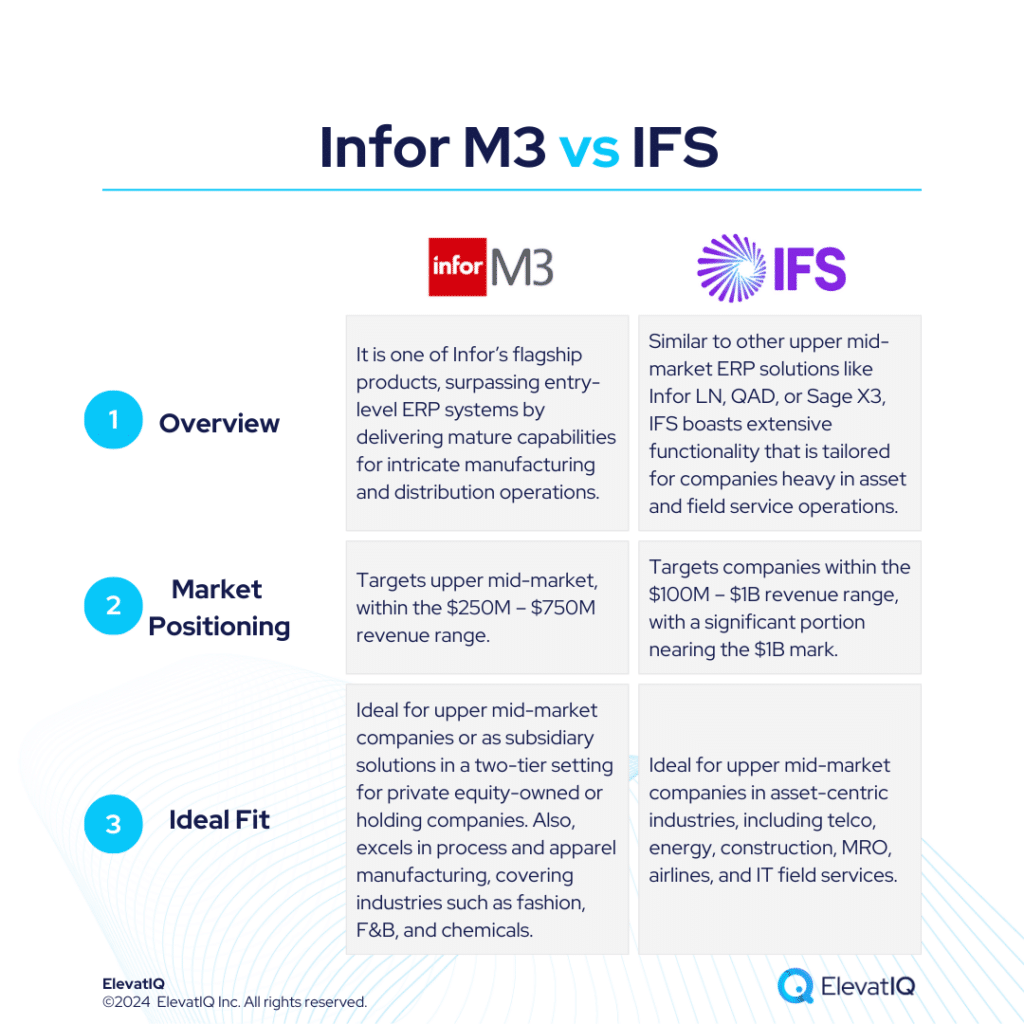
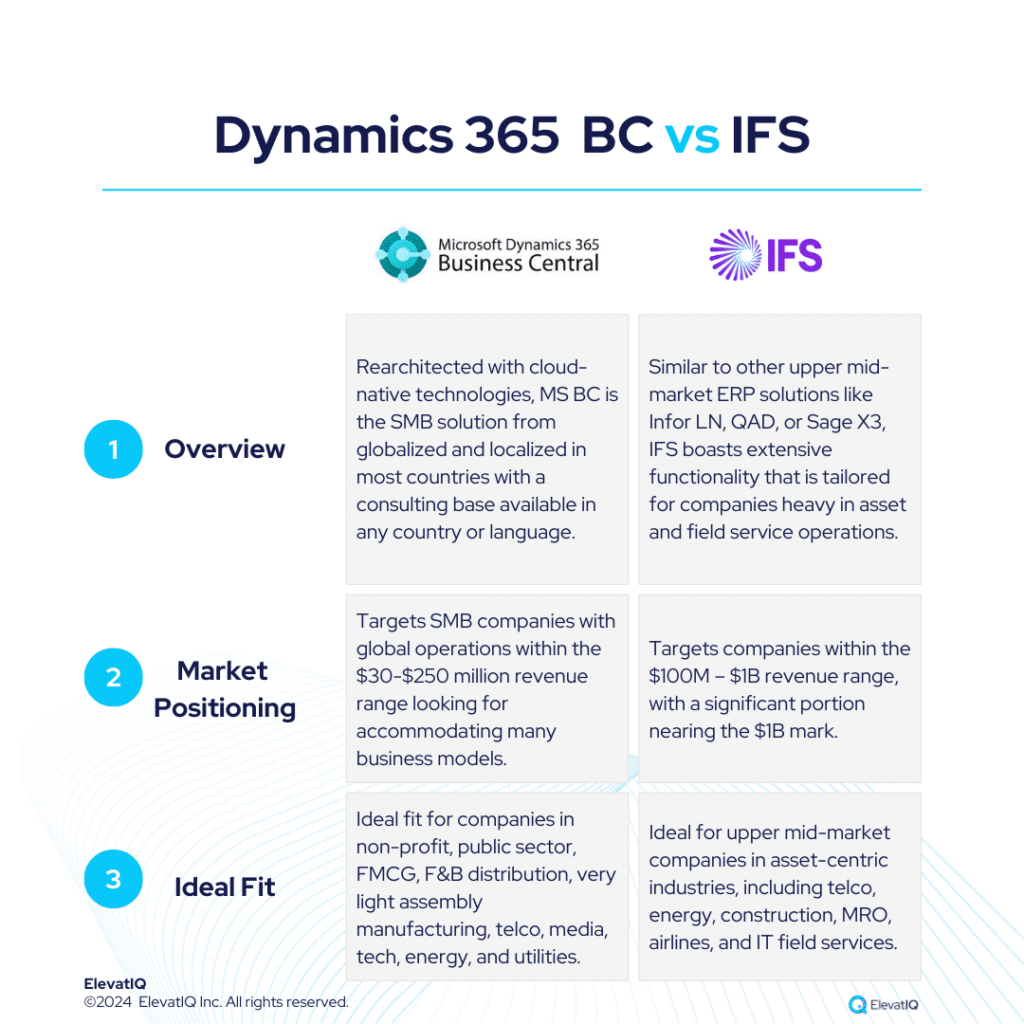
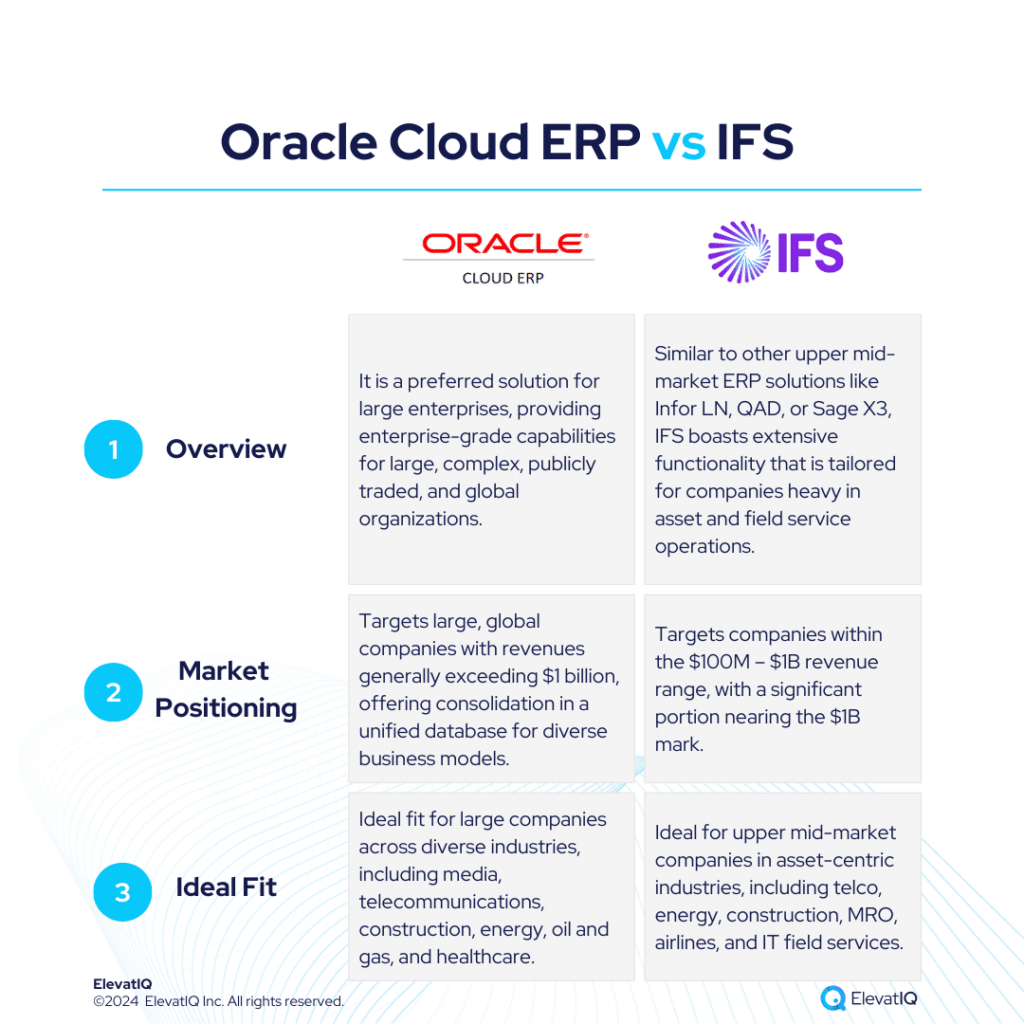
Both systems have their strengths and limitations, so businesses should carefully evaluate their specific need. Also, seeking assistance from an independent ERP consultant can significantly aid the decision-making process. To get a 360-degree view of feature comparisons, it’s essential to explore not only SAP S/4 HANA vs. Odoo but also insights from other analyses such as SAP S/4 HANA vs. NetSuite, Acumatica, Oracle Cloud ERP, Dynamics F&O, Dynamics 365 BC, Infor LN, Infor M3, Epicor Kinetic, and IFS.

FAQs
SAP S/4 HANA vs Odoo ERP Independent Review Read More »