Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 ERP Independent Review 2024
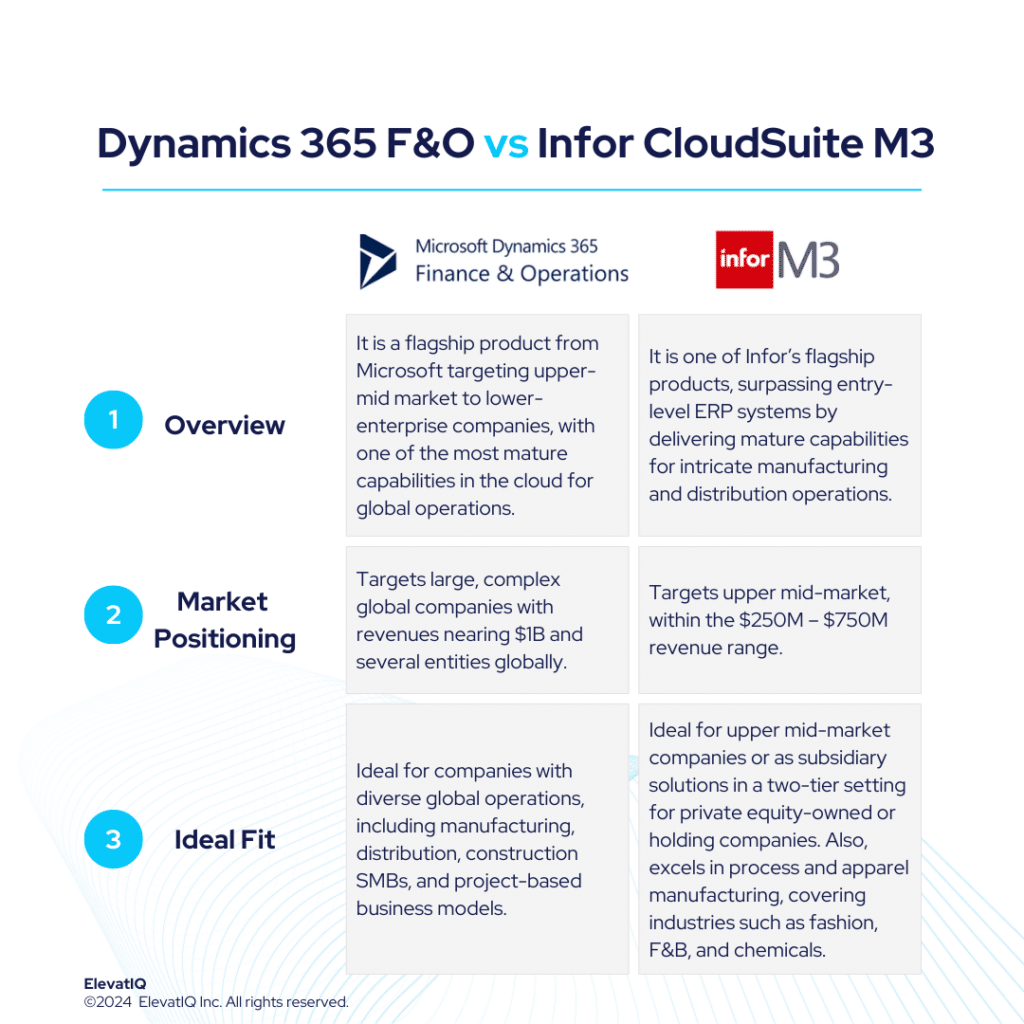
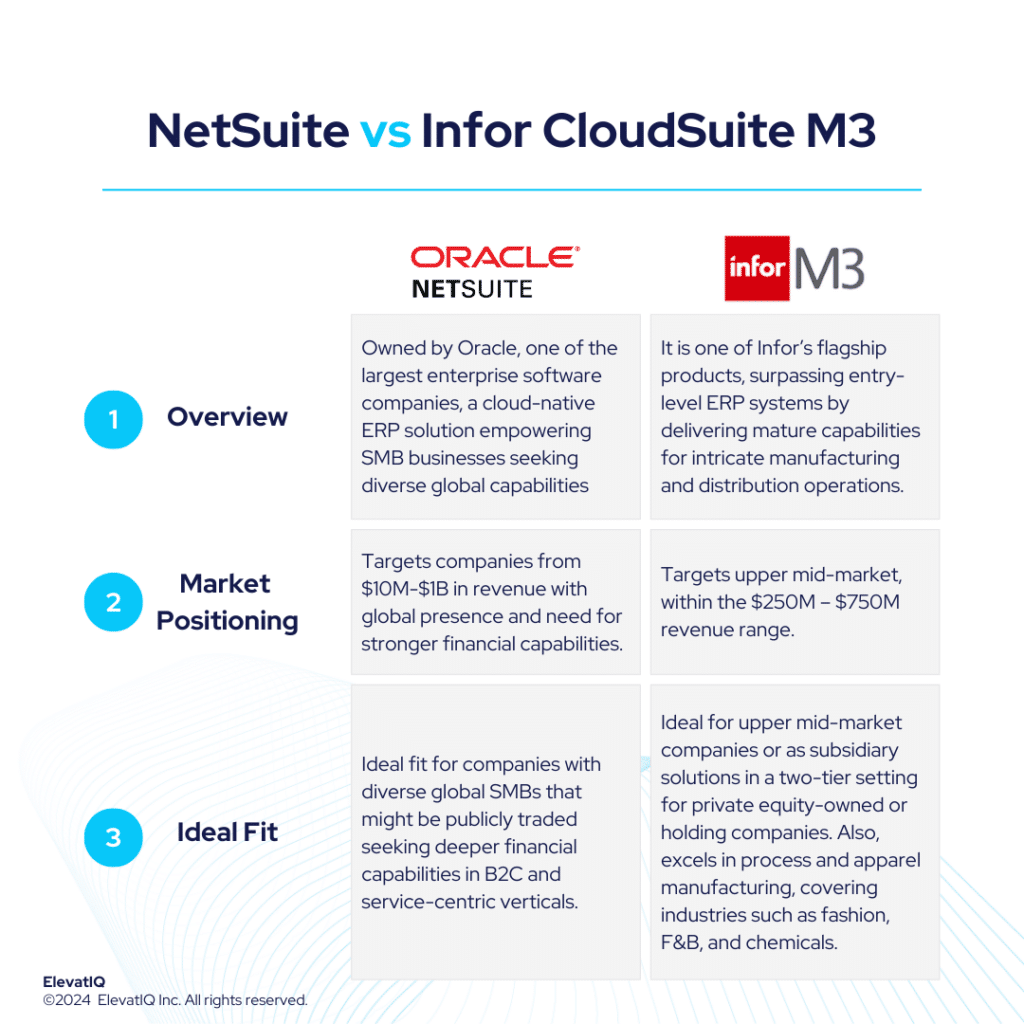
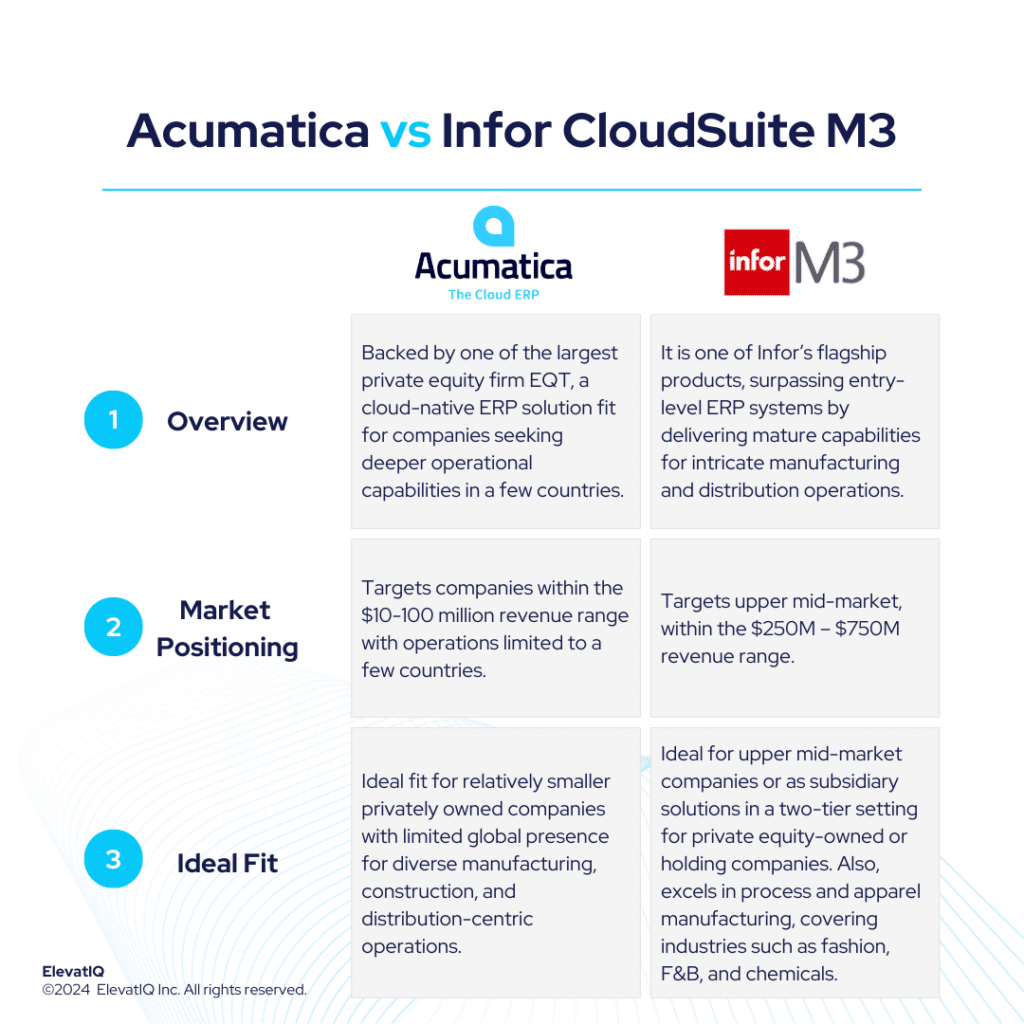
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central serves as a logical choice for companies outgrowing smaller ERP, MRP, and accounting systems like QuickBooks, Microsoft GP, Odoo, Katana, or Fulcrum. On the other hand, Infor CloudSuite M3 targets companies surpassing entry-level ERP systems like Acumatica, Infor CSI, or NetSuite. It also delivers mature capabilities for intricate manufacturing and distribution operations.
The sweet spot for Dynamics 365 BC would be $30M-$250 in revenue and a higher revenue band for companies that might use Dynamics 365 BC just for accounting and financial reporting while using mature operational systems at the subsidiary level. Whereas, Infor CloudSuite M3 is successful in the upper mid-market, targeting the $250M – $750M revenue range. The biggest advantage of Dynamics 365 BC is its consulting ecosystem and community support, which is much bigger than most ERP ecosystems. On the other hand, Infor CloudSuite M3 provides a superior suite experience akin to SAP and Oracle, featuring enterprise-grade best-of-breed functionalities, including PLM, WMS, WFM, BI, and a Supply Chain collaboration platform.
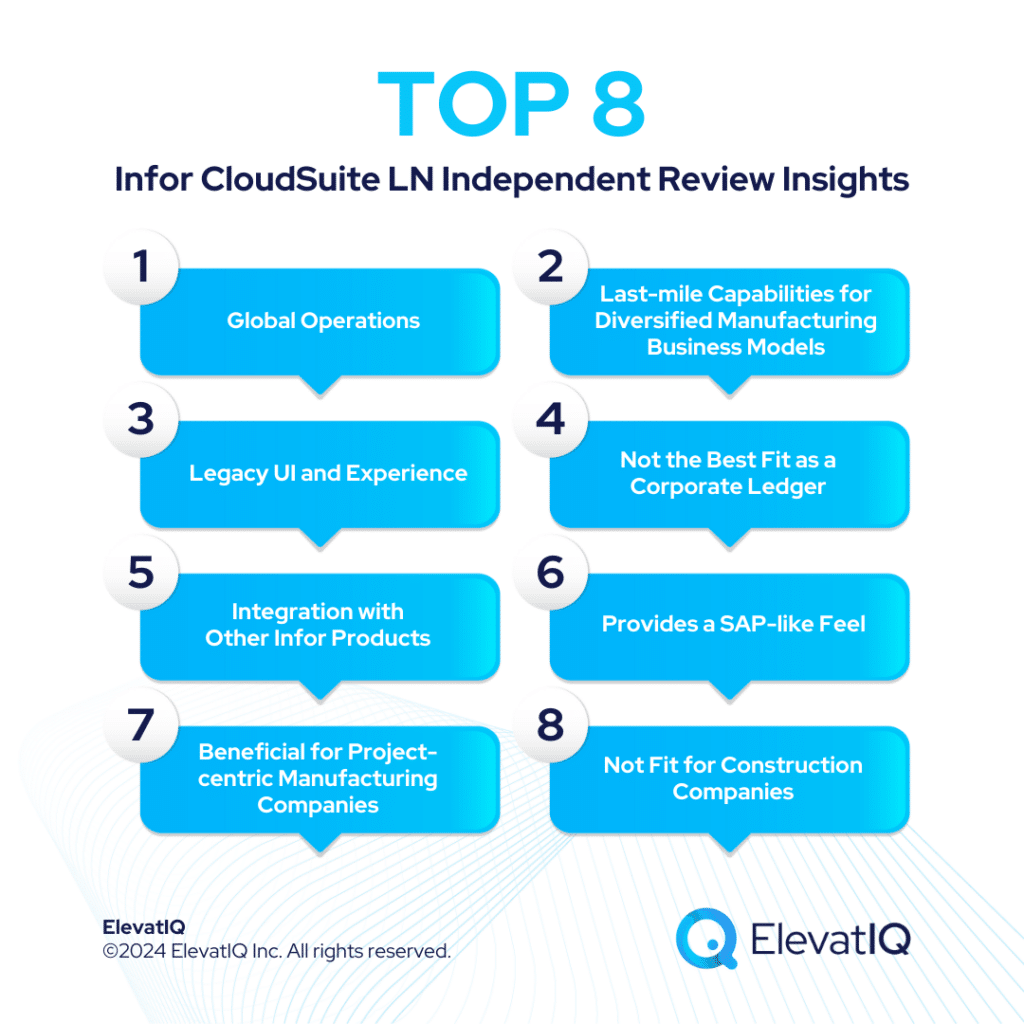
Dynamics 365 BC is also ideal for companies with diversified, global operations aspiring to keep all of their entities in one database for easier reconciliation and tracking. Whereas, Infor CloudSuite M3 boasts about its extensive features tailored for process and apparel manufacturing, covering industries such as fashion, F&B, and chemicals. It is also adept at facilitating advanced global operations, particularly for companies spanning multiple countries seeking to optimize cost synergies globally. Choosing between Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 requires a detailed examination, and thus, this comparison offers valuable insights for ERP selection projects. Therefore, let’s explore further.

| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 | |
| Started in | 2018 (Previously NAV) | 2006 (Acquired by Infor) |
| Ownership by | Microsoft | Koch Industries |
| No. of customers | 60,000+ | 1000+ |
What Is MS Dynamics 365 Business Central?
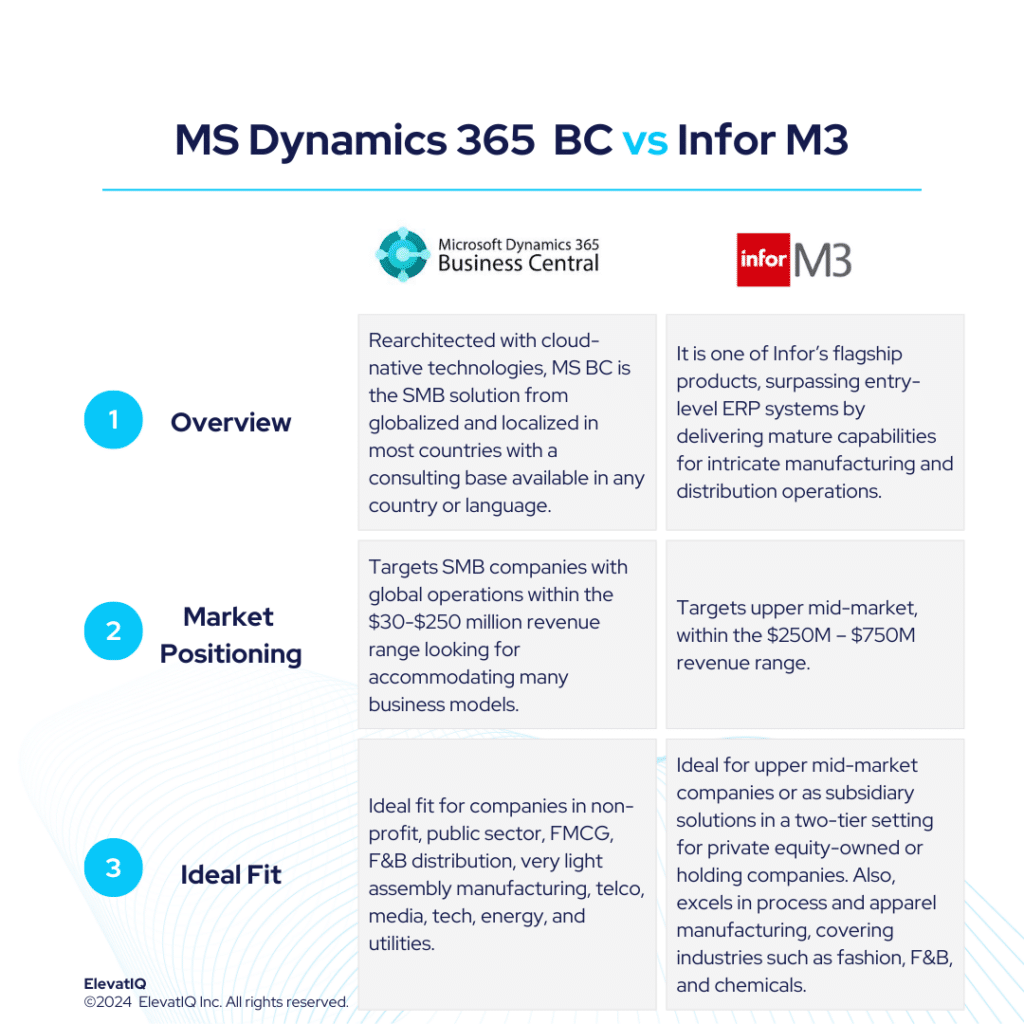
Rearchitected with cloud-native technologies, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is the SMB solution from Microsoft, globalized and localized in most countries with a consulting base available virtually in any country or language. Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central serves as a logical choice for companies outgrowing smaller ERP, MRP, and accounting systems like QuickBooks, Microsoft GP, Odoo, Katana, or Fulcrum. It is positioned against competitors such as Netsuite, Sage Intacct, and Acumatica. It also offers a vibrant ecosystem with numerous add-ons catering to industry-specific needs.
The sweet spot for Dynamics 365 BC would be $30M-$250 in revenue and a higher revenue band for companies that might use Dynamics 365 BC just for accounting and financial reporting while using mature operational systems at the subsidiary level. The biggest advantage of Dynamics 365 BC is its consulting ecosystem and community support, which is much bigger than most ERP ecosystems, and that’s why it’s probably one of the most popular solutions across geographies.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is also ideal for companies with diversified, global operations aspiring to keep all of their entities in one database for easier reconciliation and tracking. While the add-ons might allow companies to use Microsoft Dynamics Business Central for complex industrial operations, the natural design and core would be compatible with companies in industries such as non-profit, public sector, FMCG, F&B distribution, very light assembly manufacturing, telco, media, tech, energy, and utilities.
What Is Infor CloudSuite M3?
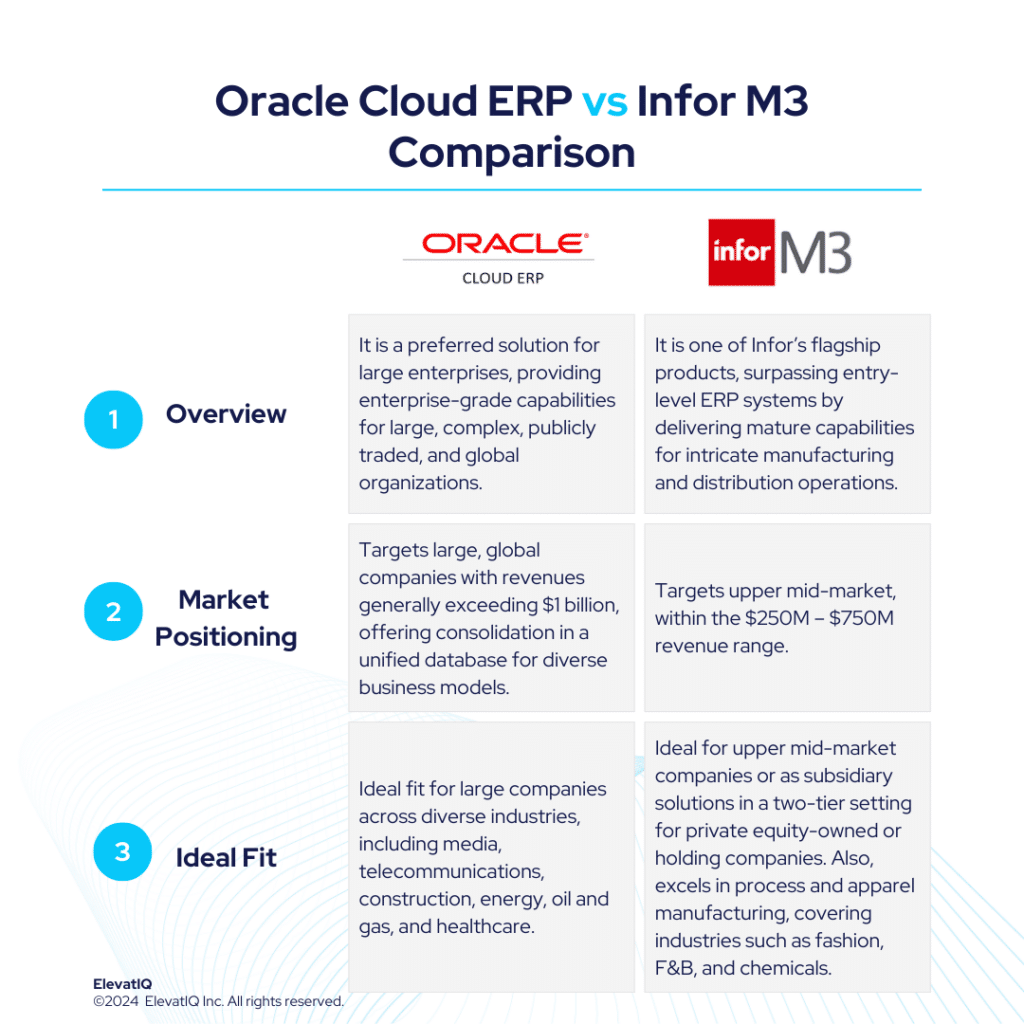
Infor CloudSuite M3, is one of Infor’s flagship solutions, catering to particularly distinct micro-verticals across various industries. Sharing similar suites with Infor LN and also built on the Infor OS platform, it is successful in the upper mid-market, targeting the $250M – $750M revenue range. Positioned for companies surpassing entry-level ERP systems like Acumatica, Infor CSI, or NetSuite, this solution delivers mature capabilities for intricate manufacturing and also distribution operations. Infor CloudSuite M3 provides a superior suite experience akin to SAP and Oracle thus, featuring enterprise-grade best-of-breed functionalities, including PLM, WMS, WFM, BI, and a Supply Chain collaboration platform.
Infor CloudSuite M3 boasts extensive features tailored for process manufacturing and apparel manufacturing, covering industries such as fashion, F&B, and chemicals. It is also adept at facilitating advanced global operations, particularly for companies spanning multiple countries seeking to optimize cost synergies globally. The native capabilities of Infor M3 address global trade and compliance concerns, which are particularly crucial for international business operations.
While Infor CloudSuite M3 serves as an excellent operational solution for a 2-tier architecture for enterprise companies, its limited focus on certain industries might not be the best fit for enterprise companies diversifying their operations or aggressive with their M&A strategy. The intricate data model and Bill of Materials (BOM) demand significant internal expertise and also external advisory assistance to extract operational efficiencies. Notably, the technology landscape for Infor CloudSuite M3 remains somewhat patchy and less modern compared to its competitors. Furthermore, the ecosystem and consulting support for this solution is relatively limited. Despite these challenges, Infor CloudSuite M3 stands out as a robust manufacturing solution for upper mid-market companies with budget constraints.
Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 Comparison
Navigating the choice between Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 is a significant decision for businesses particularly looking for operational efficiency and strategic alignment. Thus, this section delves into the comprehensive comparison of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 across various critical dimensions.
| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 | |
| Global Operational Capabilities | Supported and actively installed in most countries globally. | Robust financial hierarchies and global trade compliance functionality integrated. |
| Diverse Capabilities | Supports multiple industries and business models. | Supports diversified manufacturing business models. |
| Best-of-breed Capabilities | Pre-integrated with Microsoft CRM and field service but relies on third-party add-ons for additional capabilities. | Best-of-breed integrations provided out-of-the-box. |
| Last-mile Capabilities | May require add-ons for specific micro-verticals. | Last-mile capabilities along with breadth of capabilities for diversified manufacturing business models. |
| Operational Functionalities | Emphasizes core ERP capabilities, relying on partner add-ons for industry-specific capabilities. | Infor CloudSuite M3 is a legacy solution with limited cloud-natve capabilities such as universal search, mobile experience, etc. |
| Integration Capabilities | Common data model, power platform and automate along with MS Azure platform for additional development and integration. | Tools such as HCM, PLM, data lake, ERP, WMS, TMS, and advanced supply chain planning, are all pre-integrated. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities | Lighter manufacturing capabilities. | Delivers mature capabilities for apparel, F&B, and chemical manufacturing. |
| Pricing Model | Per named user, per month. True consumption-based licenses can be adjusted without long-term contracts | Subscription-based |
| Key Modules | 1. Financial Management 2. CRM 3. Distribution Management 4. Supply Chain Management 5. Project Accounting Management 6. Inventory Management 7. Reporting, Dashboard and BI | 1. Financial Management 2. Manufacturing Operations 3. Enterprise Asset Management 4. Supply Chain Management 5. Customer Sales and Service 6. Application Foundation |
Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 Feature Comparison
Both platforms offer a plethora of features and functionalities designed to streamline business operations and enhance efficiency. In this feature comparison, we delve into particularly the distinct capabilities of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 across various critical dimensions, providing insights to aid businesses in making informed decisions regarding their ERP selection. Thus, this section discusses features under each of the following modules, particularly financial management, supply chain management, and manufacturing management.
Financial Management Comparison
In this section, we are discussing a detailed comparison of the financial management capabilities particularly offered by Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3. By examining their respective strengths and functionalities, particularly in managing financial processes. Businesses can therefore gain valuable insights to determine the best-suited ERP solution for their financial management needs.
| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 | ||
| Financial Management | General Ledger | Initiates general ledger postings, chart of accounts, general journals, VAT facilities, recurring journals, and source codes. | Enables organizations to manage financial transactions, maintain accurate balances, and generate complete financial statements. |
| Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable | Automates accounts receivables and payables and facilitates seamless reconciliation of accounts for swift and precise financial reporting. | Supports analysis across all accounting dimensions, including non-reconciled data for the AP model. | |
| Cash Flow Management | Provides comprehensive forecasting, analysis, and Azure ML-based prediction of cash inflows and outflows. | Provides complete control over accounts receivable and cash flow processes, unifying all AR information to monitor cash collection and enhance productivity and efficiency. | |
| Currency Management | Manages multiple currencies across the system, including payables and receivables, general ledger reports, resource and inventory items, and bank accounts. | Enables currency conversion for better monetary analysis, allowing amounts to be expressed in transaction, division, and company currencies, with a default exchange rate type for conversions. | |
| Tax Management | Offers automated, configurable, and scalable tax determination, calculation, and settlement capabilities, accommodating complex tax scenarios across various business requirements. | Ensures accurate VAT calculation and recording for each country, automating tax calculations based on recipient location and country-specific rules, and maintaining financial compliance. |
Supply Chain Management Comparison
In this comparison, we explore and analyze the supply chain management capabilities of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3, shedding light particularly on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 | ||
| Supply Chain Management | Warehouse Management | Can be implemented in different complexity levels, depending on a company’s processes and order volume. The main difference is that activities are performed order-by-order in basic warehousing when they are consolidated for multiple orders in advanced warehousing. | Optimizes operations with inventory management, labor management, 3PL billing, and 3D visualization, enhancing efficiency and interactivity. |
| Service Management | Service management is not built as part of the core platform but a pre-integrated specialized app is available for field service operations. | Offers work order processing, maintenance, material management, and operation reporting, aiding global manufacturers, distributors, and after-sales service providers in managing complex value chains efficiently. | |
| Inventory Management | Ensures inventory availability by automatically computing stock levels, lead times, and reorder thresholds. Also, maintains optimal inventory levels by adjusting orders dynamically based on real-time inventory updates. | Provides advanced statistical forecasting and stock recommendations for efficient inventory management, as well as supplier and customer rebate management to maintain high margins. | |
| Purchase Order Management | Manages purchase orders, including blanket orders and related processes. | Includes automation, vendor payment tracking, payment scheduling, check printing, open purchase order alerts, document management, direct ACH bill payment, and vendor records | |
| Requisition Management | Organizes complex distribution processes involving multiple products and suppliers. | Automates procurement processes from requisition to payment, including supplier selection, purchase order management, and invoice matching. |
Manufacturing Management Comparison
In this comparison, we explore and analyze the manufacturing management capabilities of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3, shedding light, particularly on their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 | ||
| Manufacturing Management | Production Planning | Enables the creation of production orders, definition of routings, allocation of resources, and optimization of production sequences, ensuring seamless operations. | Supports planning in both multi-facility and single-facility production environments, managing critical materials at the facility level. |
| BOM and Routing | Allows for the detailed mapping of production processes, including the components, subassemblies, and resources used, as well as the sequence of operations. | Defines the product structure and assembly sequence, listing components and specifying the operations, work centers, and machines required for manufacturing. | |
| Advanced Planning and Scheduling | Takes into account all demand and supply data, nets the results, and creates suggestions for balancing the supply to meet the demand, ensuring optimized resource utilization and efficient production control. | Generates real-time projections by comparing demands against a long-term plan, optimizing production resources, reducing costs, improving performance, and synchronizing supply chain operations. |
Pros of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3
When evaluating ERP solutions, understanding the distinct advantages of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 is crucial. In this section, we are particularly exploring the strengths of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 across various dimensions. Thus, shedding light on their respective capabilities and functionalities.
| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 |
| Natively supports global regions and localizations where Acumatica, Epicor, or Infor might have limited support. | Ideal for upper mid-market companies or as subsidiary solutions in a two-tier setting for private equity-owned or holding companies. |
| Unlike several products, it has support for several European, Asian, and African countries where most products might struggle. | It can support the most complex manufacturing business models, WBS-centric manufacturing, or support for attributes with MRP planning. |
| The data model is friendlier for FMCG and distribution companies, light maufacutring, or service companies. | Most tools that make-to manufacturer would require, such as HCM, PLM, data lake, ERP, WMS, TMS, and advanced supply chain planning, are all pre-integrated with Infor CloudSuite M3. |
| The product has been completely rearchitected using the cloud-native architecture. Cloud ERP capabilities are stronger than those of competing products. | While most smaller solutions might require ad-hoc arrangements for global financial operations, Infor CloudSuite M3 has them natively built. |
Cons of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3
Just like recognizing strengths is important, it’s also crucial to weigh the specific drawbacks of Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3. Therefore, in this section, we will delve into the limitations and challenges associated with Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 across various operational and financial dimensions.
| MS Dynamics 365 BC | Infor CloudSuite M3 |
| Only fit for FMCG-centric distributors, service companies, and light manufacturing industries. Complex manufacturing and distribution might require add-ons. | The limited focus on certain business models poses the risk of requiring other ERP systems to support complex and diverse business operations. |
| While the ecosystem may have options for distribution industries, it might not have integrations with the best-of-breed eCommerce systems in the industrial distribution space. | Private equity and holding companies requiring global solutions with a tier-2 solution at the subsidiary level might not be the best use of Infor CloudSuite M3’s strengths. |
| The financial traceability may not be as intuitive for global, publicly traded non-profit companies. | Infor CloudSuite M3 is a legacy solution with limited cloud-native capabilities such as universal search, mobile experience, etc |
| The data layers are highly detailed, requiring substantial consulting help to be successful. | The consulting base and marketplaces are virtually non-existent for Infor CloudSuite M3. |
| Microsoft doesn’t offer any support or control to its smaller products, leading to ERP implementation issues. | Verticals such as apparel manufacturing demand deeper integration of PLM, vendor portals, and merchandising solutions to effectively manage their unique processes. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing between Dynamics 365 BC vs Infor M3 requires a thorough analysis of the unique needs and operational demands of your business. Dynamics 365 BC stands out for its extensive global reach and flexibility, making it an excellent choice for SMBs with diverse business models and complex, multi-entity structures. Its robust consulting ecosystem and community support provide a significant advantage, especially for industries such as non-profit, public sector, FMCG, and light manufacturing. However, it may require additional integrations and add-ons for more intricate industrial processes, and its financial traceability might pose challenges for globally diversified, publicly traded entities.
On the other hand, Infor CloudSuite M3 excels in delivering mature, best-of-breed capabilities for upper mid-market companies, particularly those in process and apparel manufacturing sectors like fashion, F&B, and chemicals. Its comprehensive suite experience, including advanced supply chain and manufacturing management, makes it a strong contender for companies seeking deep industry-specific functionalities. Despite its robust feature set, Infor CloudSuite M3’s legacy technology and limited consulting ecosystem may pose hurdles, especially for businesses needing modern, cloud-native solutions or those with aggressive M&A strategies.
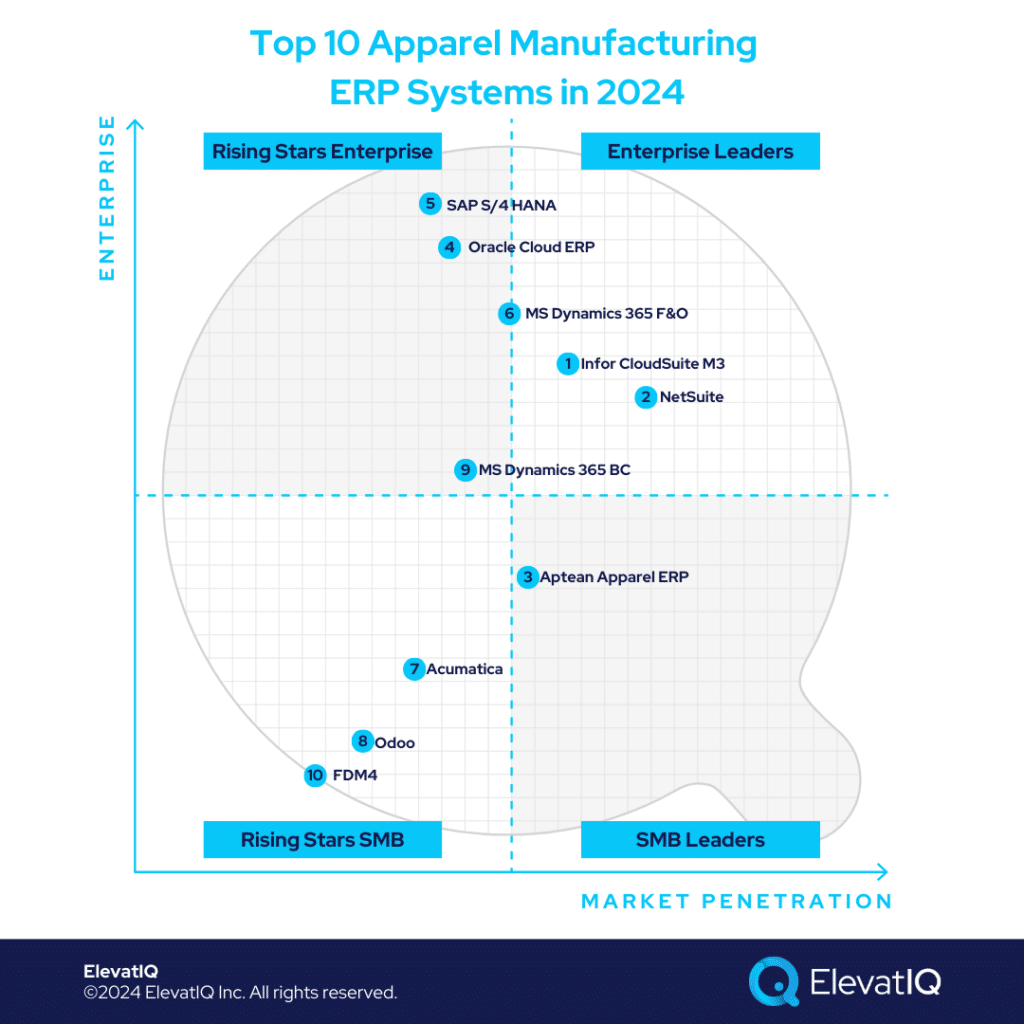
To get a 360-degree view of feature comparisons, it’s essential to explore not only Dynamics 365 BC vs. Infor M3 but also insights from other analyses such as Dynamics 365 BC vs. NetSuite, SAP S/4 HANA, Oracle Cloud ERP, MS Dynamics 365 F&O, Acumatica, and Infor CloudSuite LN. Also, seeking assistance from an independent ERP consultant can significantly aid the decision-making.